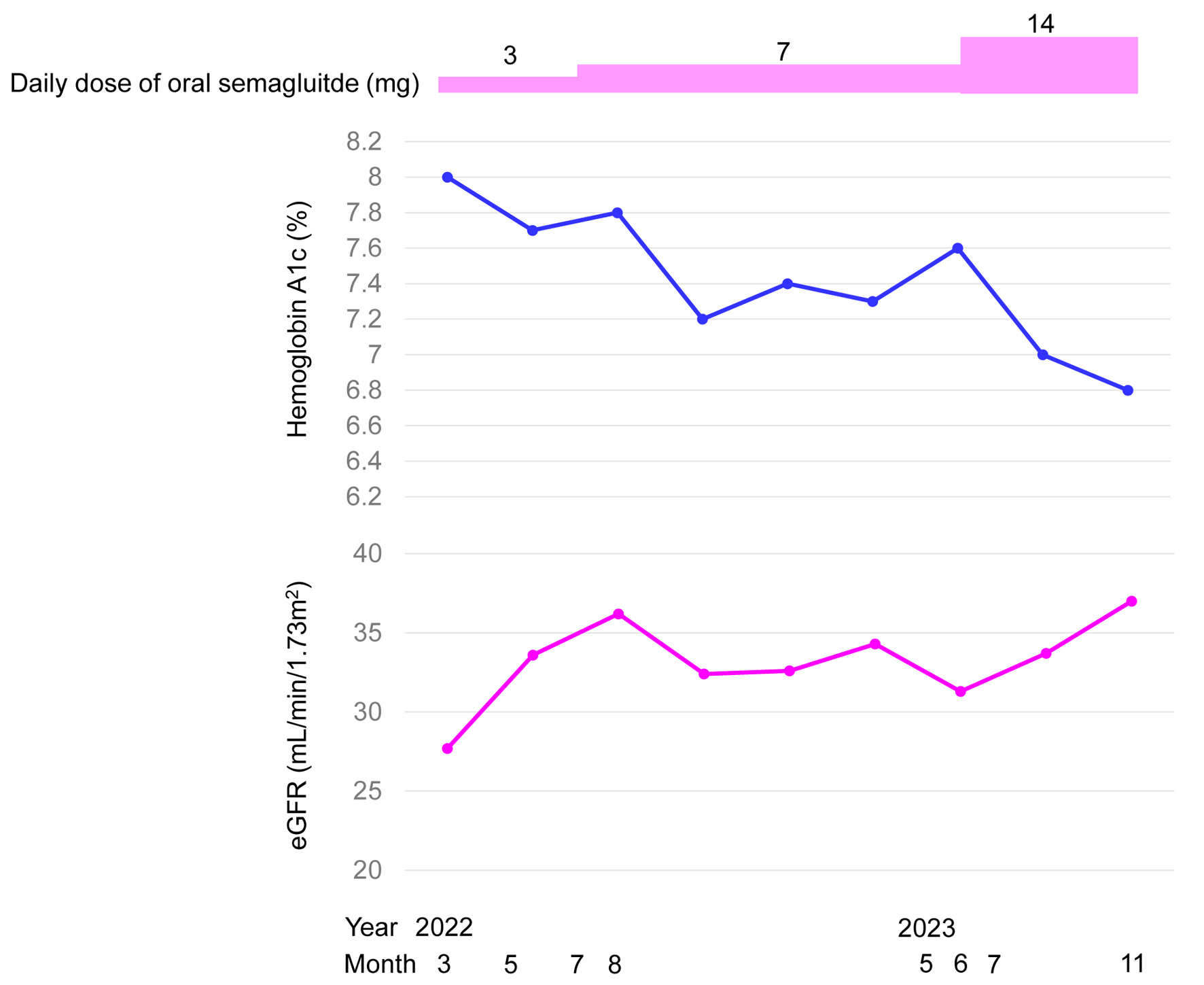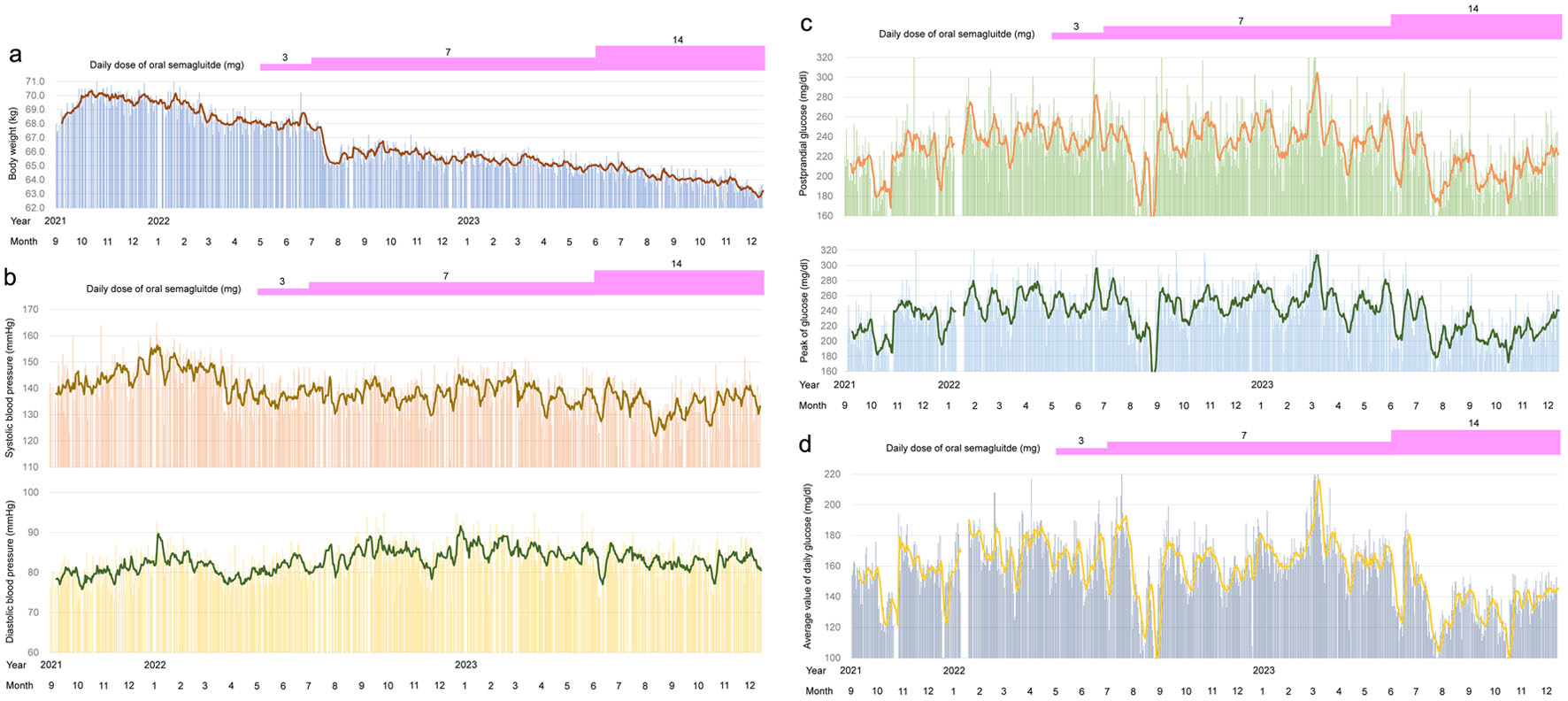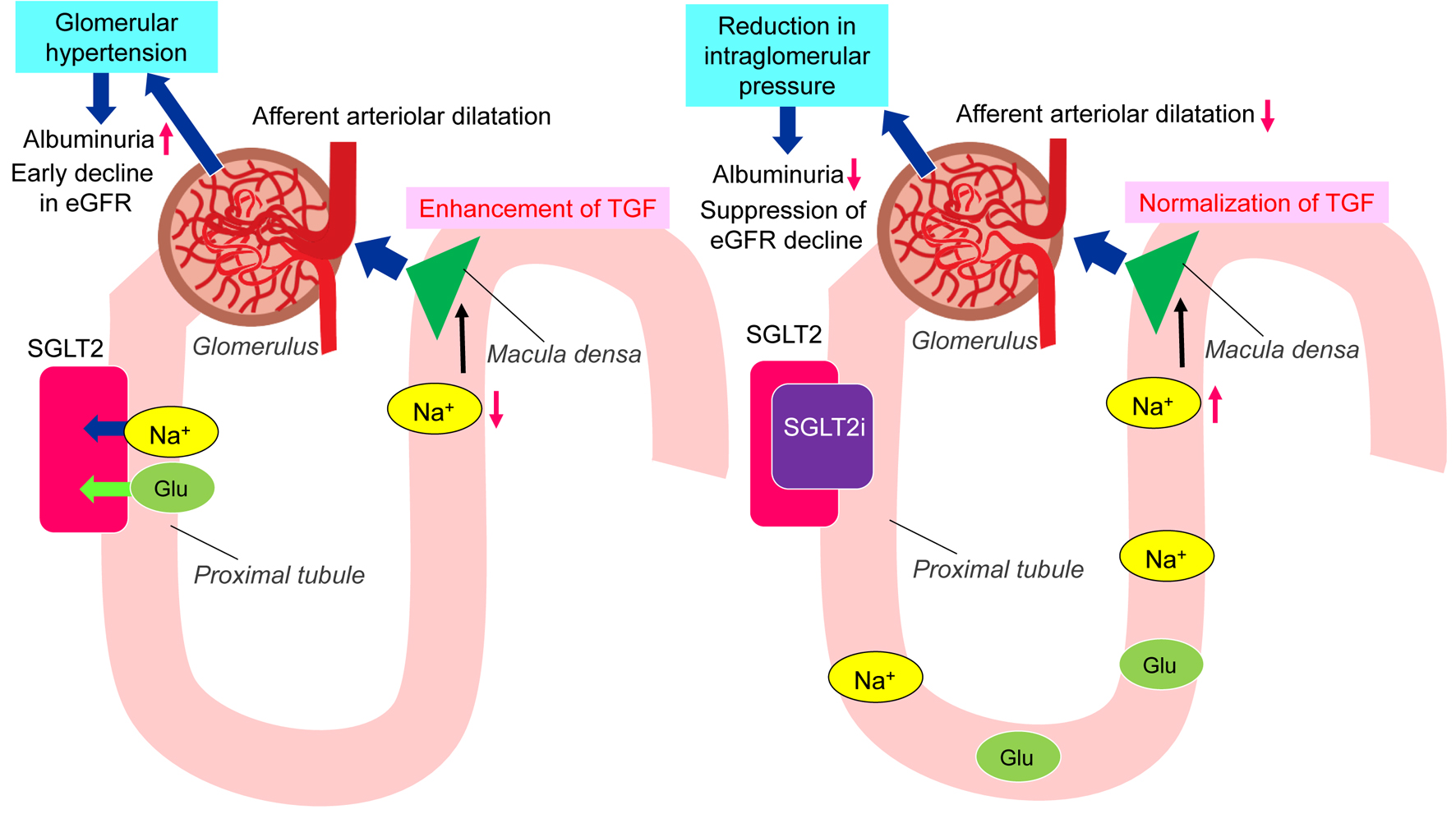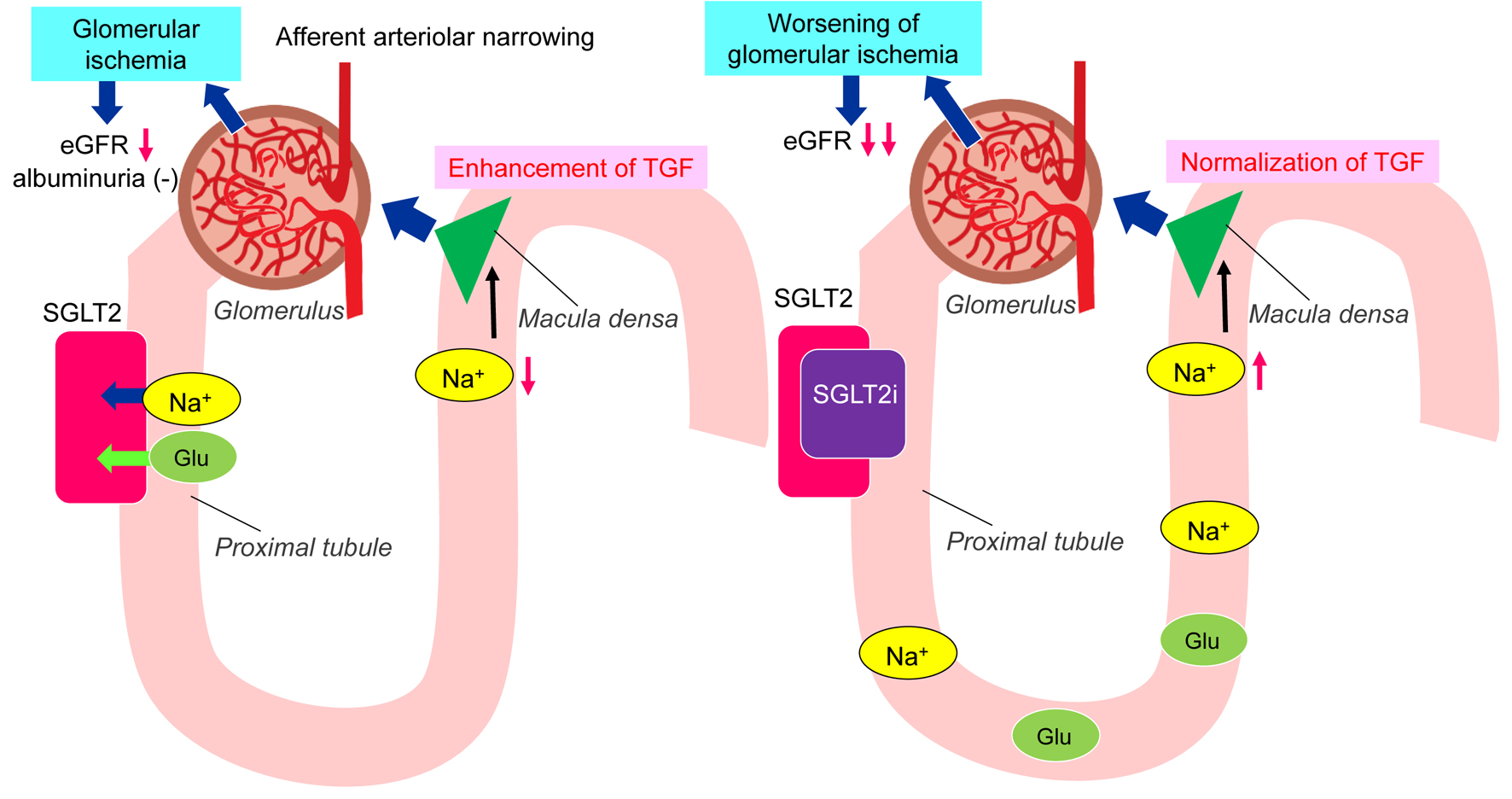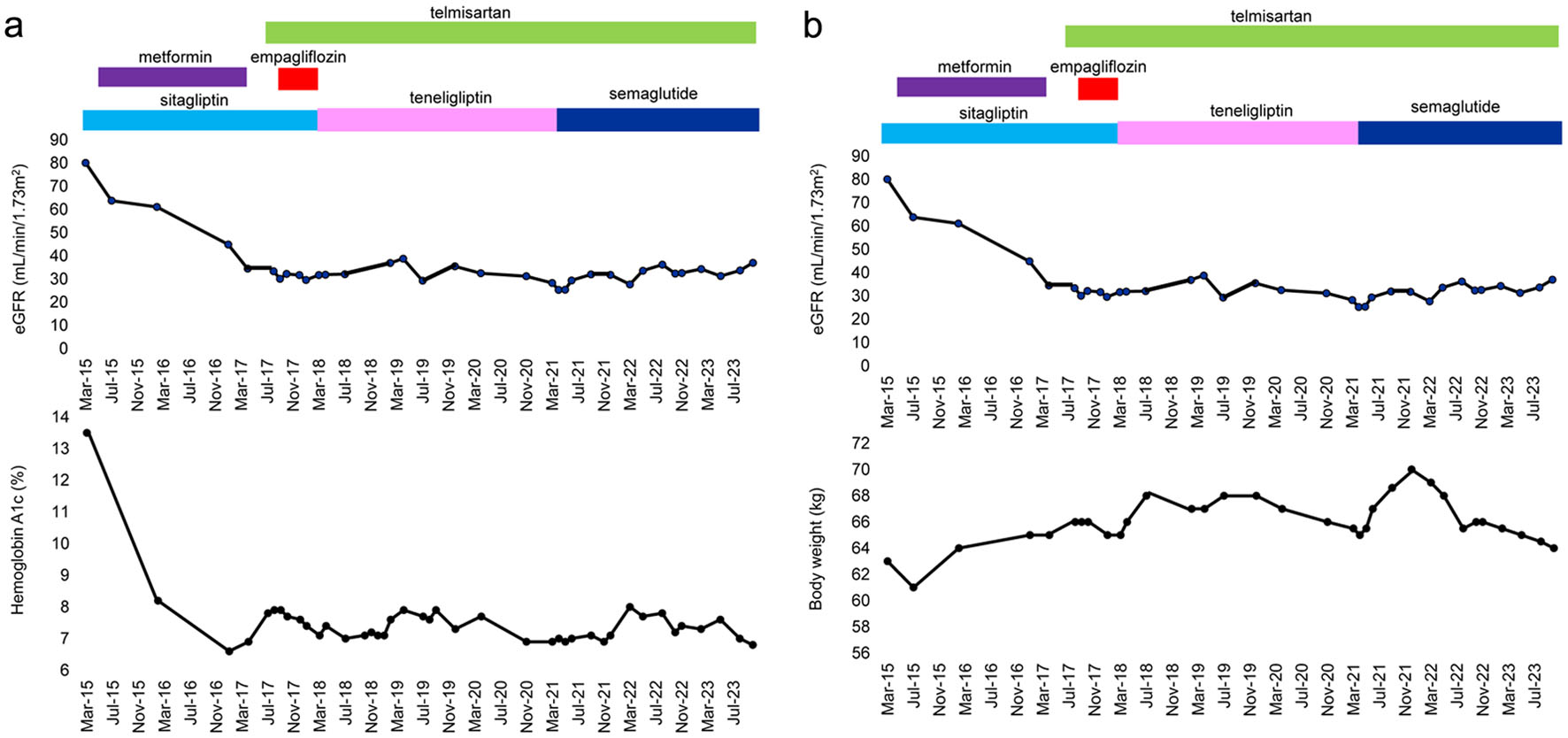
Figure 1. Changes in the treatments for type 2 diabetes, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and hemoglobin A1c (a) and body weight (b).
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 15, Number 2-3, April 2024, pages 37-42
Renal Function Improvement With Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist in a Patient With Type 2 Diabetes
Figures