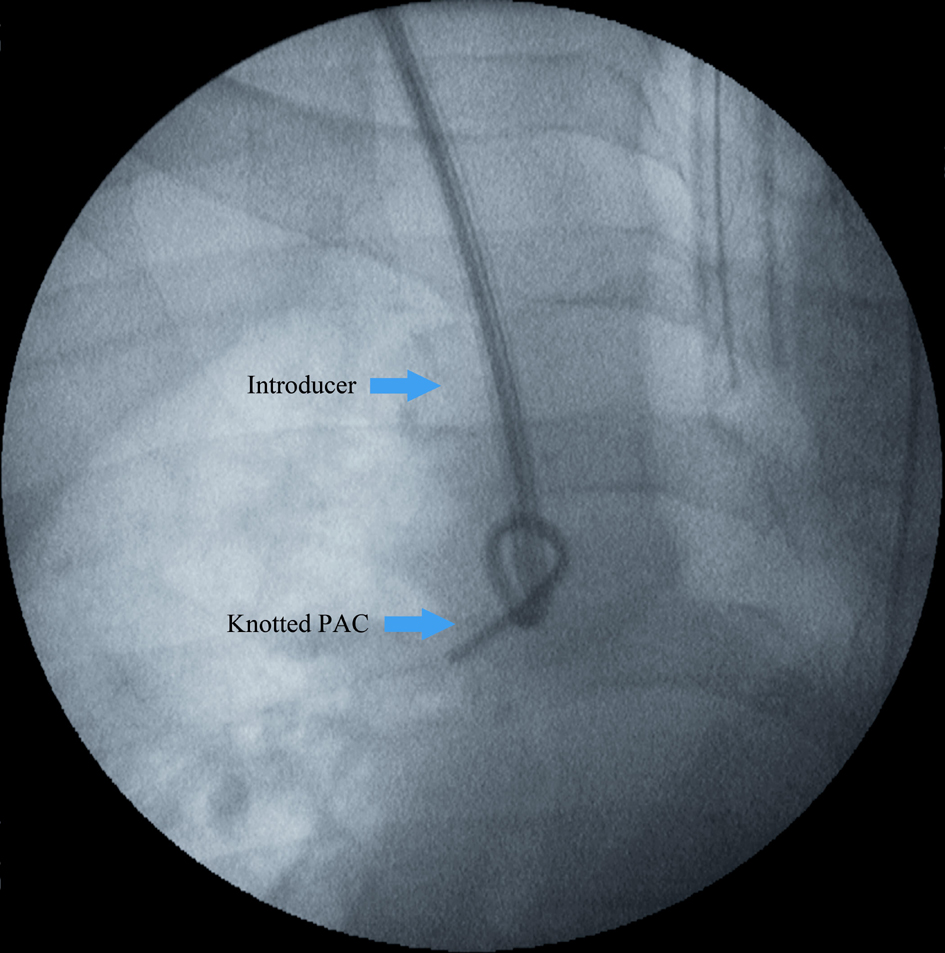
Figure 1. Fluoroscopy demonstrating knotted pulmonary artery catheter (PAC). The introducer sheath abuts the loose knot prior to applying traction to the PAC to reduce the knot size against the introducer.
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 4, Number 3, March 2013, pages 163-165
Nonsurgical Removal of Knotted Pulmonary Artery Catheter
Figures

Table
| Procedure | Hemoglobin | INR | PTT | Platelet | Fibrinogen | TEG, R | TEG, K | TEG, α-Angle | TEG, maximum amplitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (RR 13.5 - 17.5 g/dL) | (RR 0.8 - 1.2) | (RR 21 - 33 sec) | (RR 150 - 450 × 109/L) | (RR 175 - 430 mg/dL) | (RR 2.9 - 6.4 min) | (RR 1.0 - 1.8 min) | (RR 64 - 78 deg) | (RR 57.1 - 72.6 mm) | ||
| Combined liver kidney transplantation (CLKT), international normalized ratio (INR), orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), reference range (RR), thromboelastogram (TEG). | ||||||||||
| Patient 1 | OLT | 12.3 | 1.4 | 36 | 60 × 109 | 226 | 6.5 | 2.8 | 52.9 | 53.8 |
| Patient 2 | CLKT | 7.2 | 1.9 | 58 | 76 × 109 | 124 | 13.3 | 3.1 | 50.4 | 44.5 |