Figures
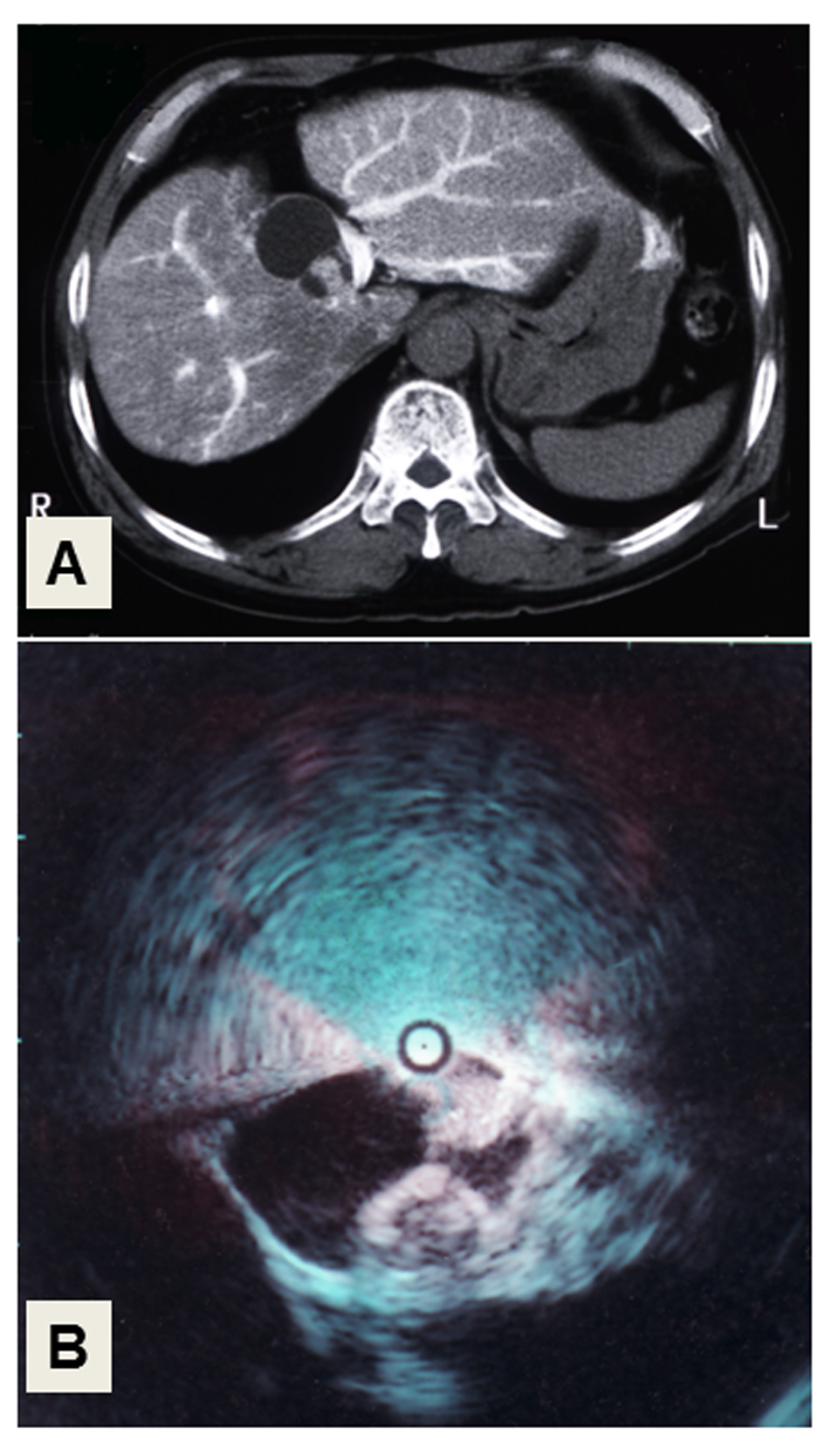
Figure 1. Liver imaging. (A) CT-angiography. The cystic tumor with solid masses in its cavity, showing faint arterial staining in the medial segment of the liver. (B) Intraductal ultrasonography (IDUS) of the choledochus. Two solid, irregular masses arise from the wall of the cystic tumor.
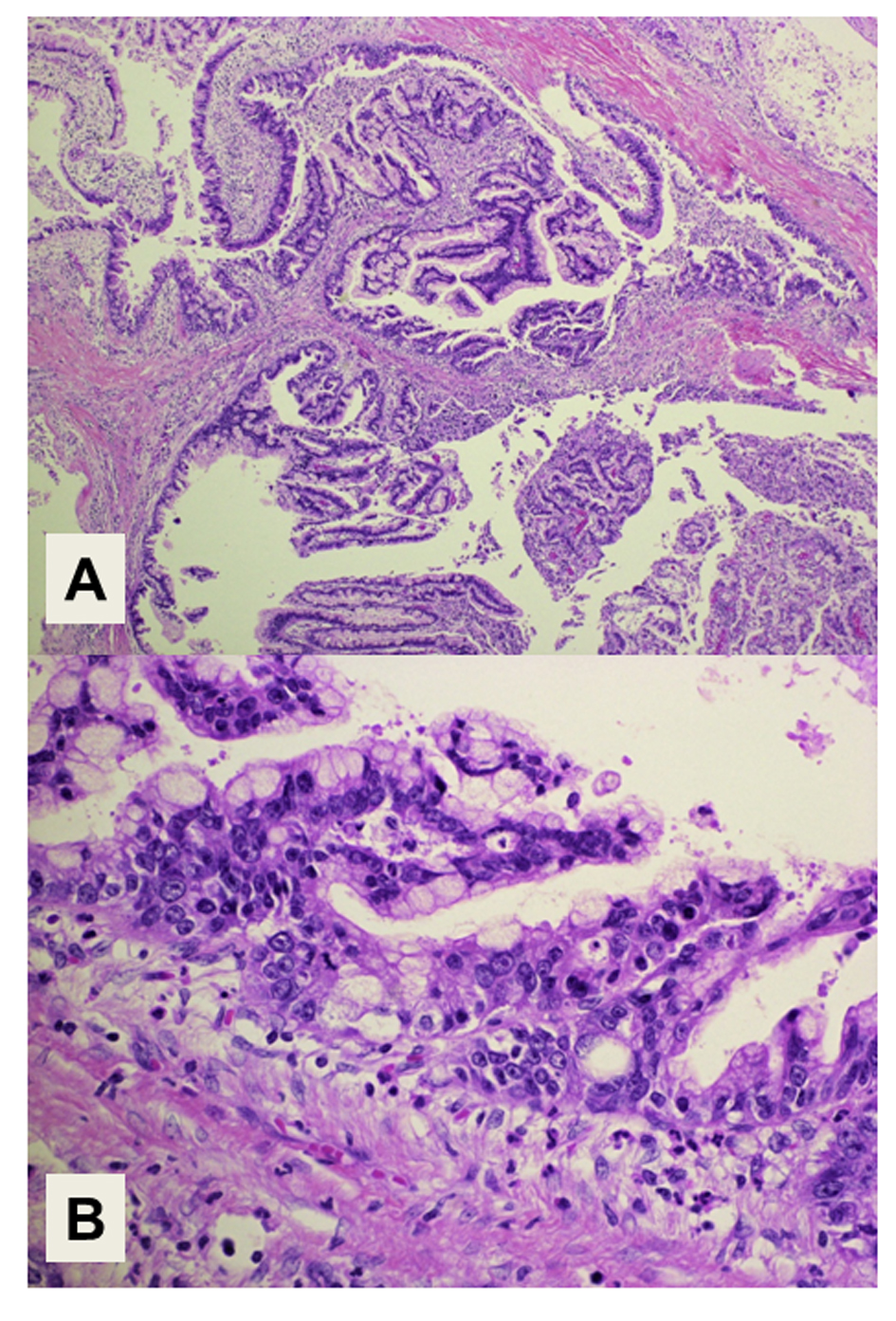
Figure 2. Histology of the tumor. (A) Intraductal papillary structures of the epithelial tumor cells with a fibrous stroma. Magnification: × 40. (B) Adenocarcinoma components extend along the epithelium of the intrahepatic bile ducts, showing a carcinoma in situ. Magnification: × 400. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining.
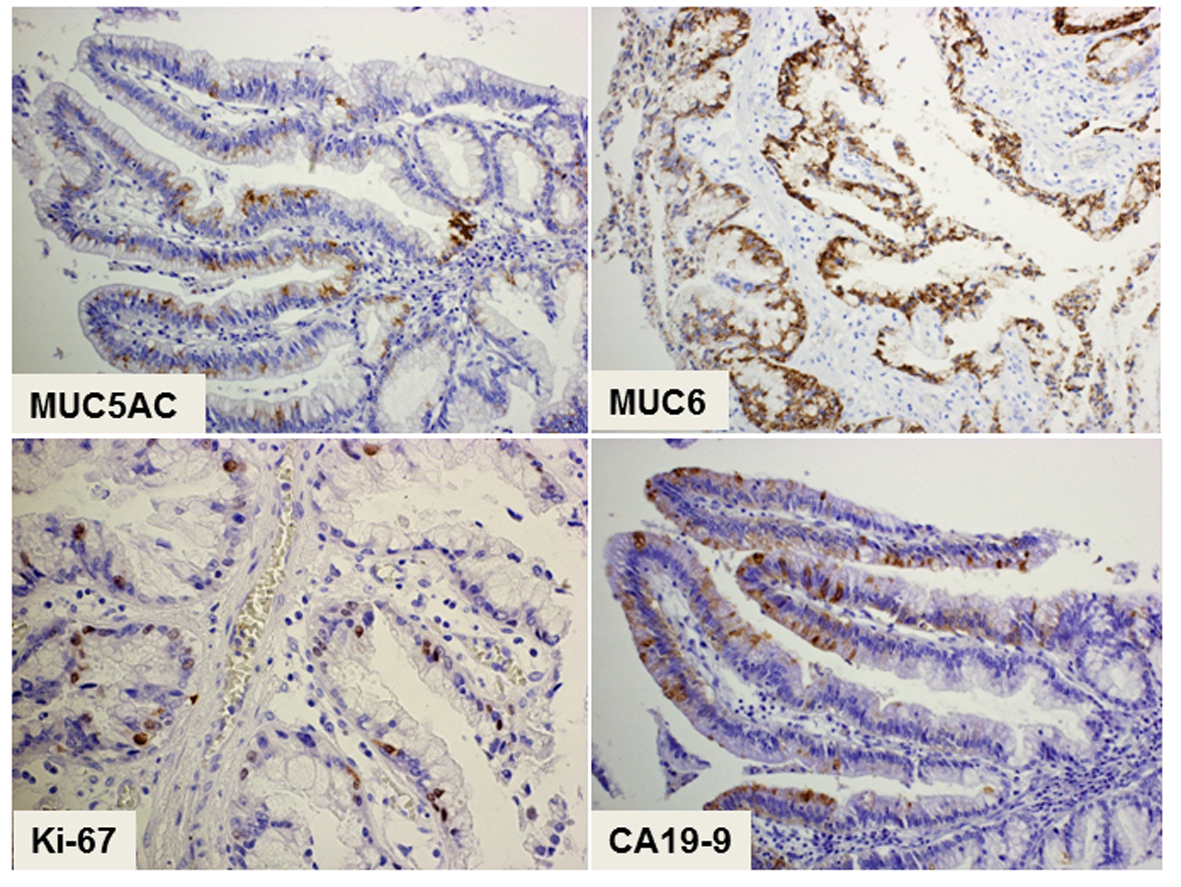
Figure 3. Immunohistochemical staining of the tumor showing a pancreatobiliary-type intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct. The cytoplasmic expression of both MUC5A and MUC6 as mucin-related proteins is positive in the epithelial tumor cells. The cells show nuclear expression of Ki-67 and cytoplasmic expression of CA19-9, suggesting their malignant potential. Magnification: × 200.
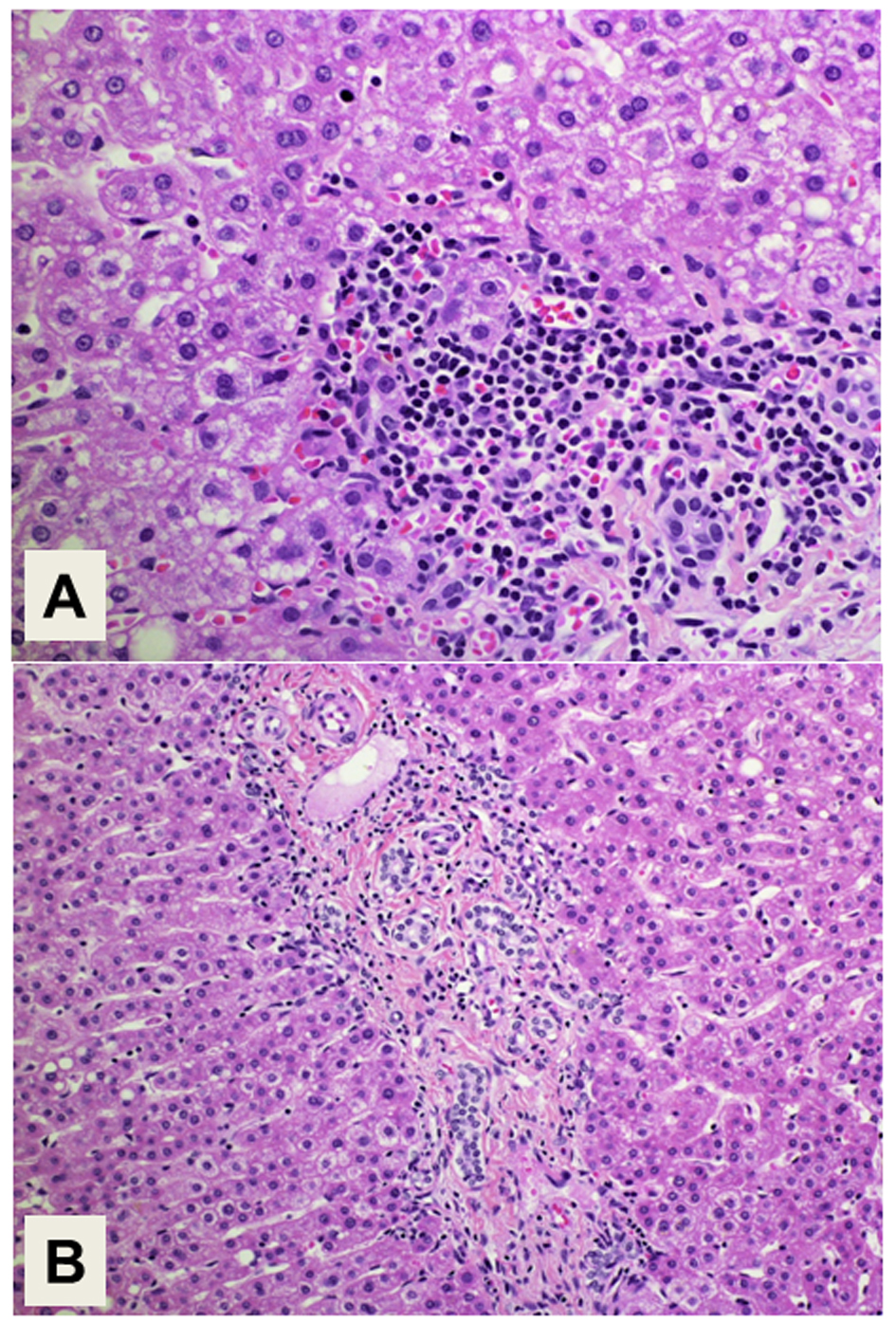
Figure 4. Histology of the background liver. (A) Interface hepatitis with plasma cell infiltration is compatible with the histology of autoimmune hepatitis. Magnification: × 400. (B) Proliferation of intrahepatic bile ducts is also demonstrated. Magnification: × 200. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining.
Table
Table 1. Laboratory Data on Admission
| Biochemistry | Hematology | Coagulation |
|---|
| AST, aspartate transferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; GGT: γ-glutamyl transpeptidase; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; IgM-HAAb: IgM-hepatitis A antibody; HBsAg/Ab: hepatitis B surface antigen/antibody; HBcAb: hepatitis B core antibody; HCV Ab: hepatitis C virus antibody; INR: International normarized ratio; AMA: anti-mitochondrial antibody; DUPAN-2: pancreatic cancer associated antigen. |
| Total protein | 7.3 g/dL | White blood cell | 5,910/µL | INR | 1.13 |
| Albumin | 3.3 g/dL | Red blood cell | 452 × 104/µL | Immunology |
| Total bilirubin | 8.8 mg/dL | Hemoglobin | 14.3 g/dL | Immunoglobulin G | 2,200 mg/dL |
| Direct bilirubin | 7.8 mg/dL | Hematocrit | 42.3% | Immunoglobulin A | 521 mg/dL |
| Indirect bilirubin | 1.0 mg/dL | Platelet | 22.0 × 104/µL | Immunoglobulin M | 199 mg/dL |
| AST | 271 U/L | Viral marker | | anti-nuclear antibody | (+)160 × |
| ALT | 580 U/L | IgM-HAAb | (-) | AMA | (-) |
| LDH | 439 U/L | HBsAg | (-) | Tumor marker |
| ALP | 173 U/L | HBsAb | (-) | α-fetoprotein | 24 ng/mL |
| GGT | 175 U/L | HBcAb | (-) | carcinoembryonic antigen | 0.98 ng/mL |
| BUN | 17 mg/dL | HCV Ab | (-) | carbohydrate antigen 19-9 | 14.4 U/mL |
| Creatinine | 0.8 mg/dL | | | DUPAN-2 | 470 U/mL |



