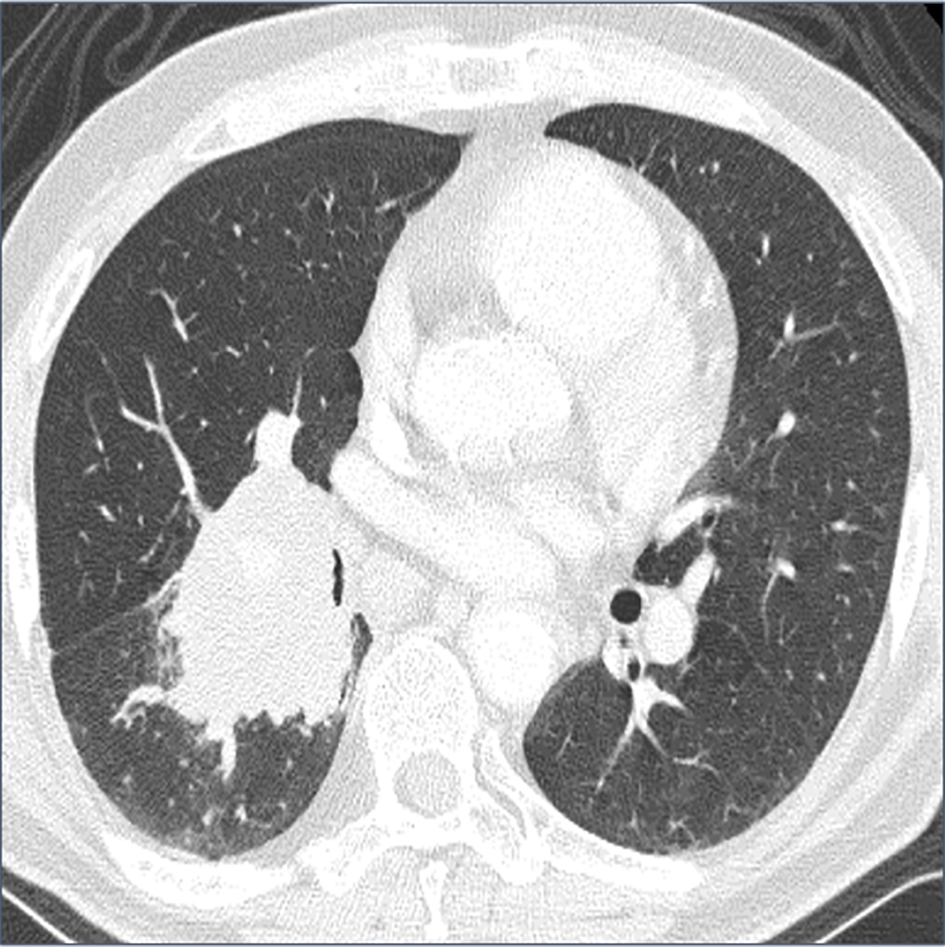
Figure 1. Computed tomography (CT) shows a 60-mm mass shadow in the right lung hilar region.
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 7, Number 9, September 2016, pages 411-415
Asymptomatic Duodenal Metastasis From Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration
Figures

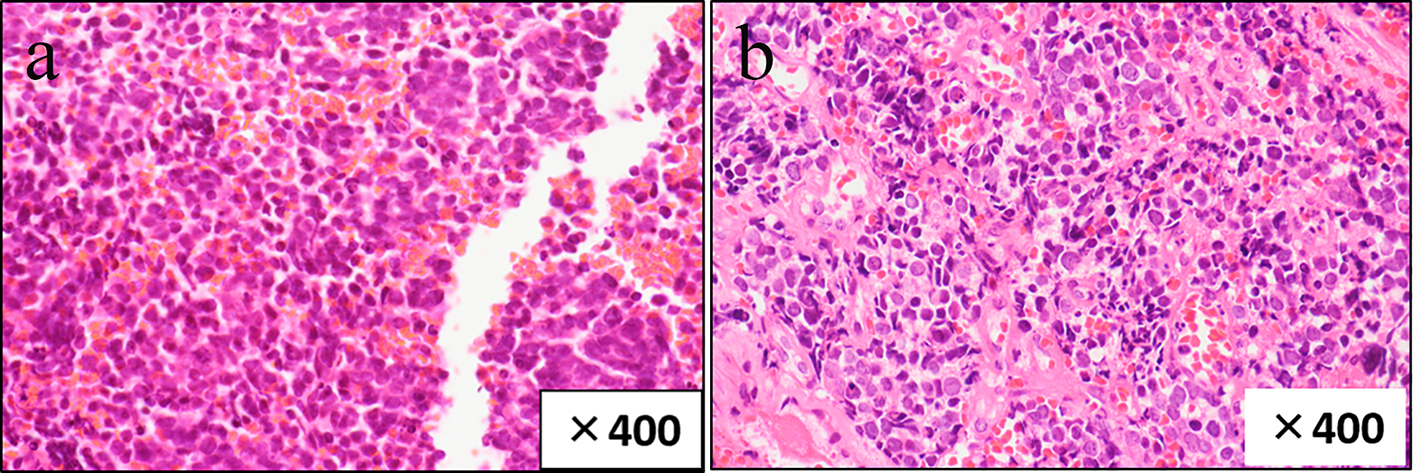
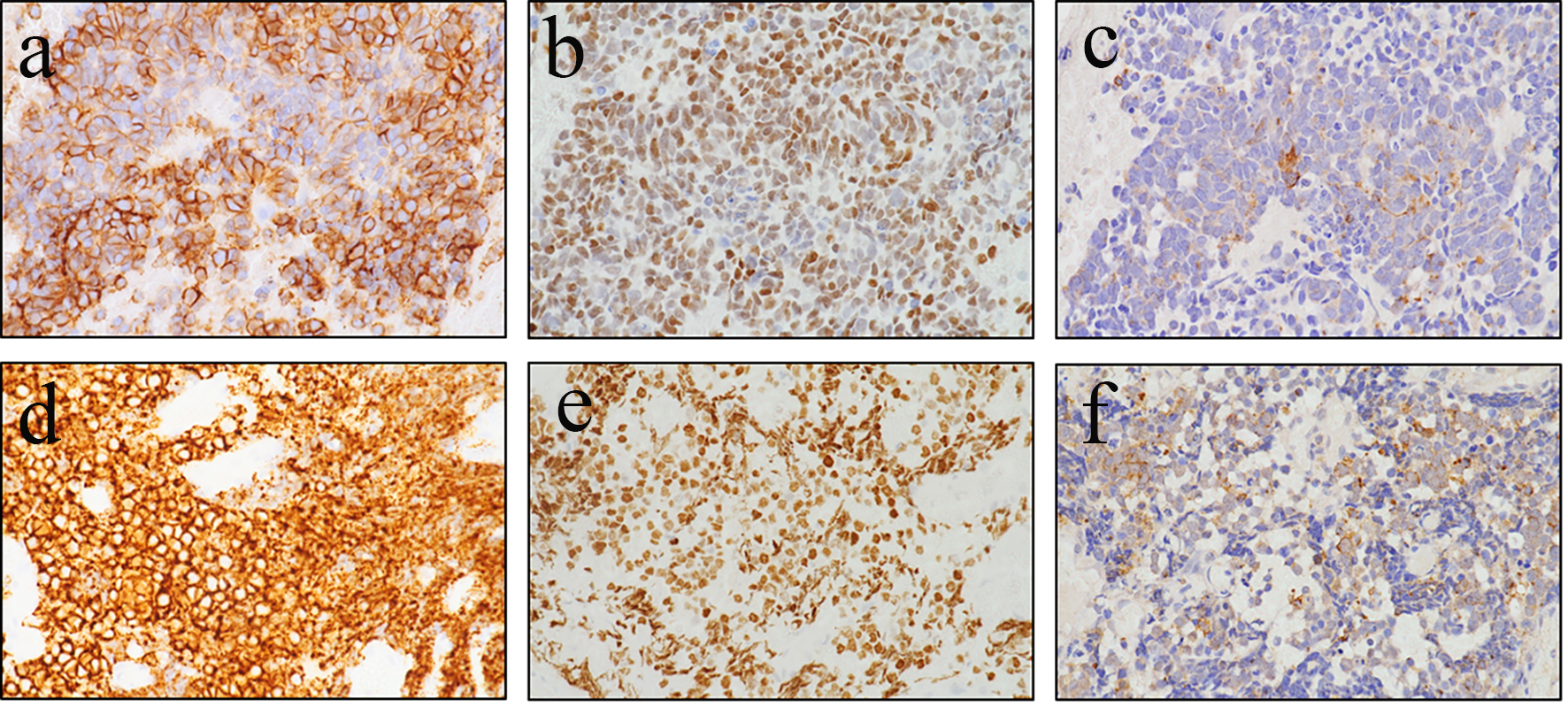
Table
| Case | Year | Author, reference | Age (years) | Sex | Reason for investigation | Condition of small intestine | Tissue sampling | Location | Other metastatic sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET: positron emission tomography; EUS-FNA: endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. | |||||||||
| 1 | 2006 | Yang et al [8] | 57 | M | Abdominal pain | Bowel obstruction | Surgery | Ileum | Brain, peritoneum |
| 2 | 2006 | Kanemoto et al [3] | 71 | M | Anemia | Bleeding | Surgery | Ileum | Adrenal gland |
| 3 | 2009 | Guerin et al [10] | 69 | M | Abdominal pain | Perforation | Surgery | Jejunum | Peritoneum |
| 4 | 2009 | Scabini et al [11] | 76 | M | Abdominal pain, fever | Bowel obstruction | Surgery | Ileum | Unknown |
| 5 | 2012 | Jarmin et al [12] | 75 | M | Anemia, malaise | Bleeding | Surgery | Duodenum, jejunum | None |
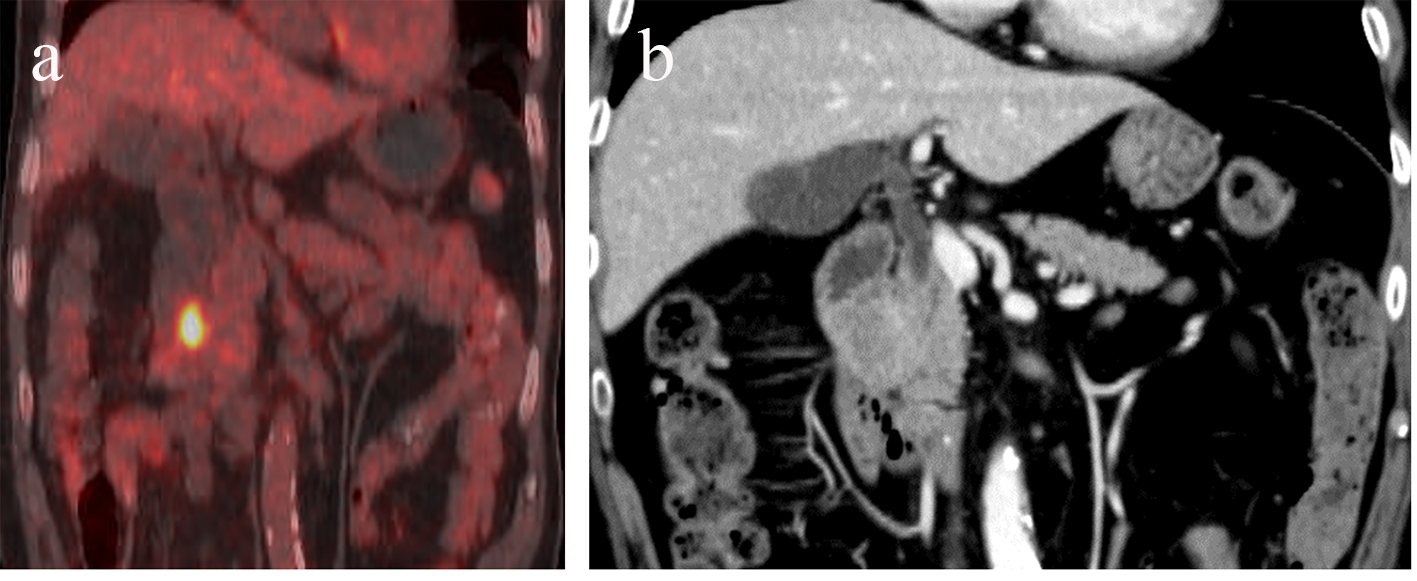
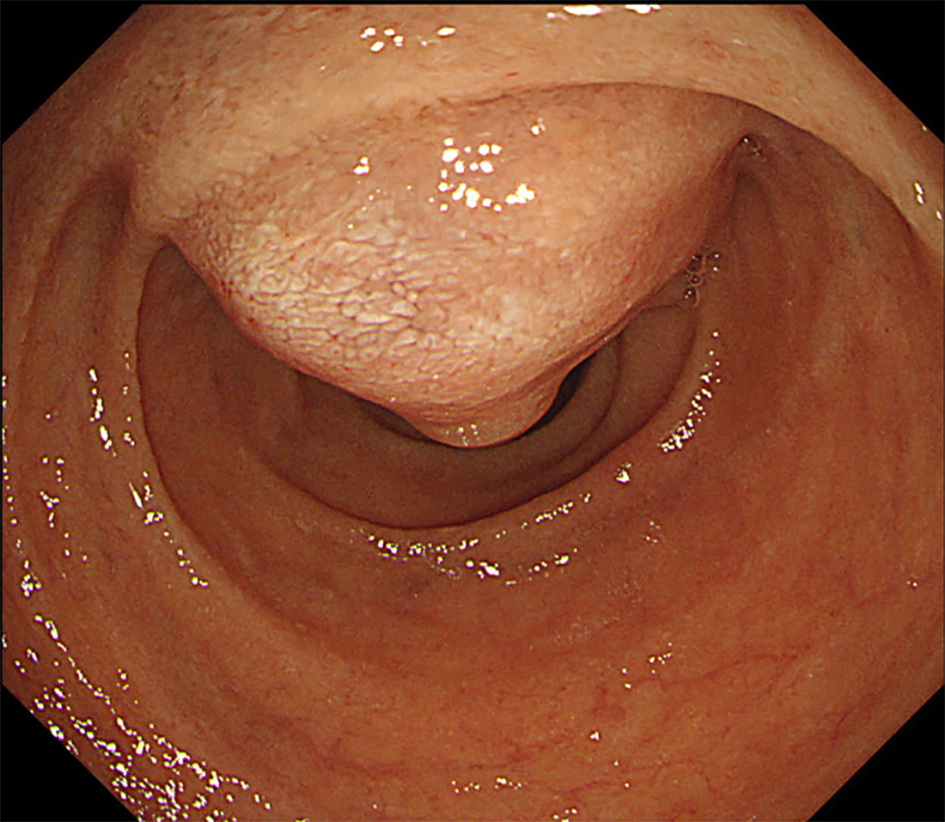
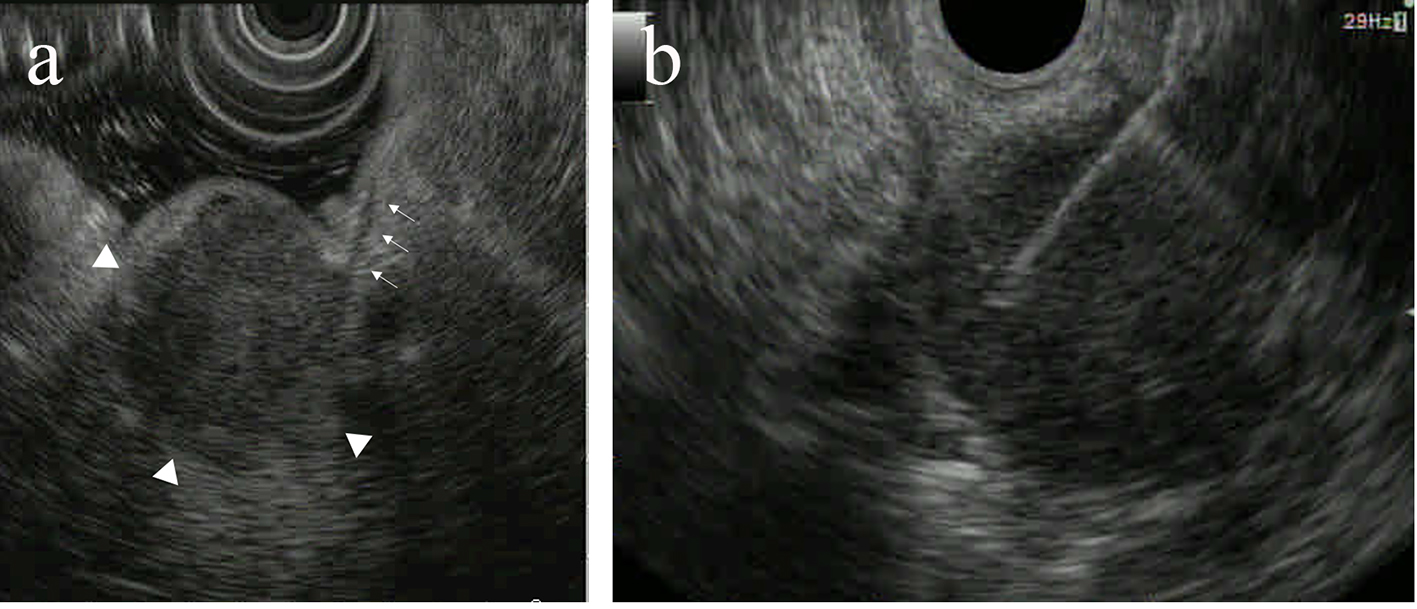
| Our case | - | - | 67 | M | PET | - | EUS-FNA | Duodenum | Bone |