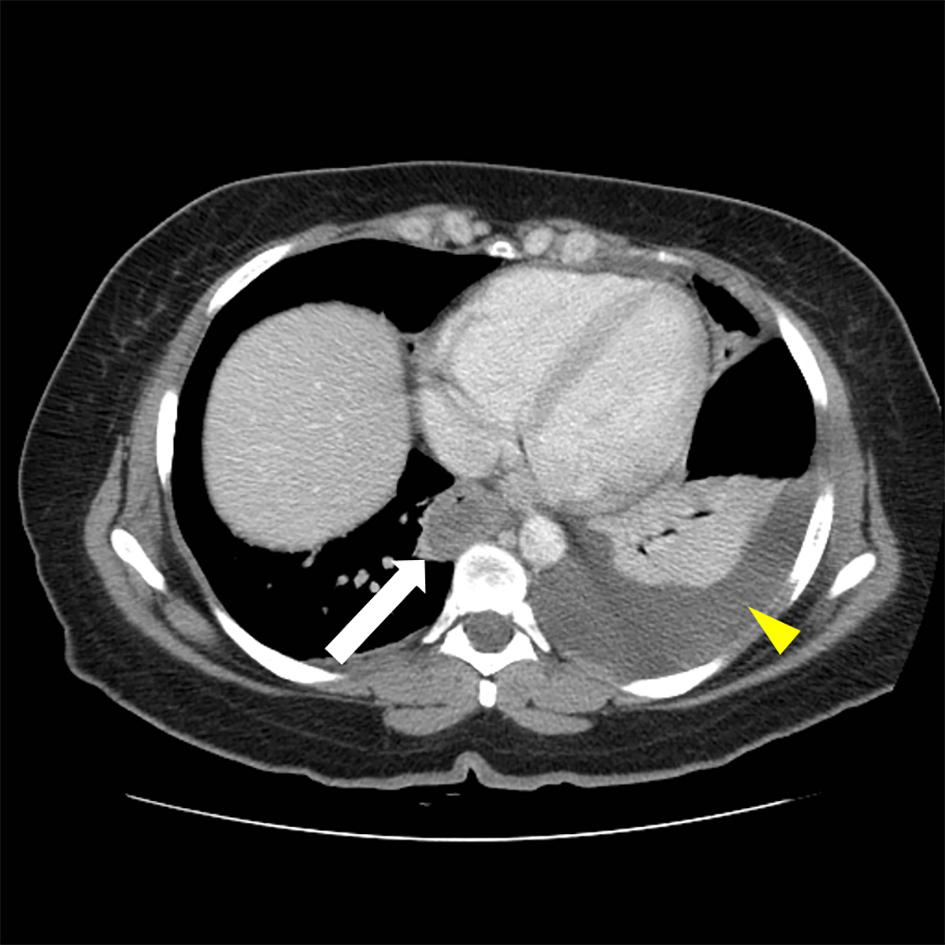
Figure 1. Abdominal CT, thickening of distal esophagus (white arrow) is evident. A left-sided pleural effusion is also seen (yellow arrow head).
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 8, Number 11, November 2017, pages 335-339
A 37-Year-Old Female With Abdominal Pain and Diarrhea: A Case of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
Figures

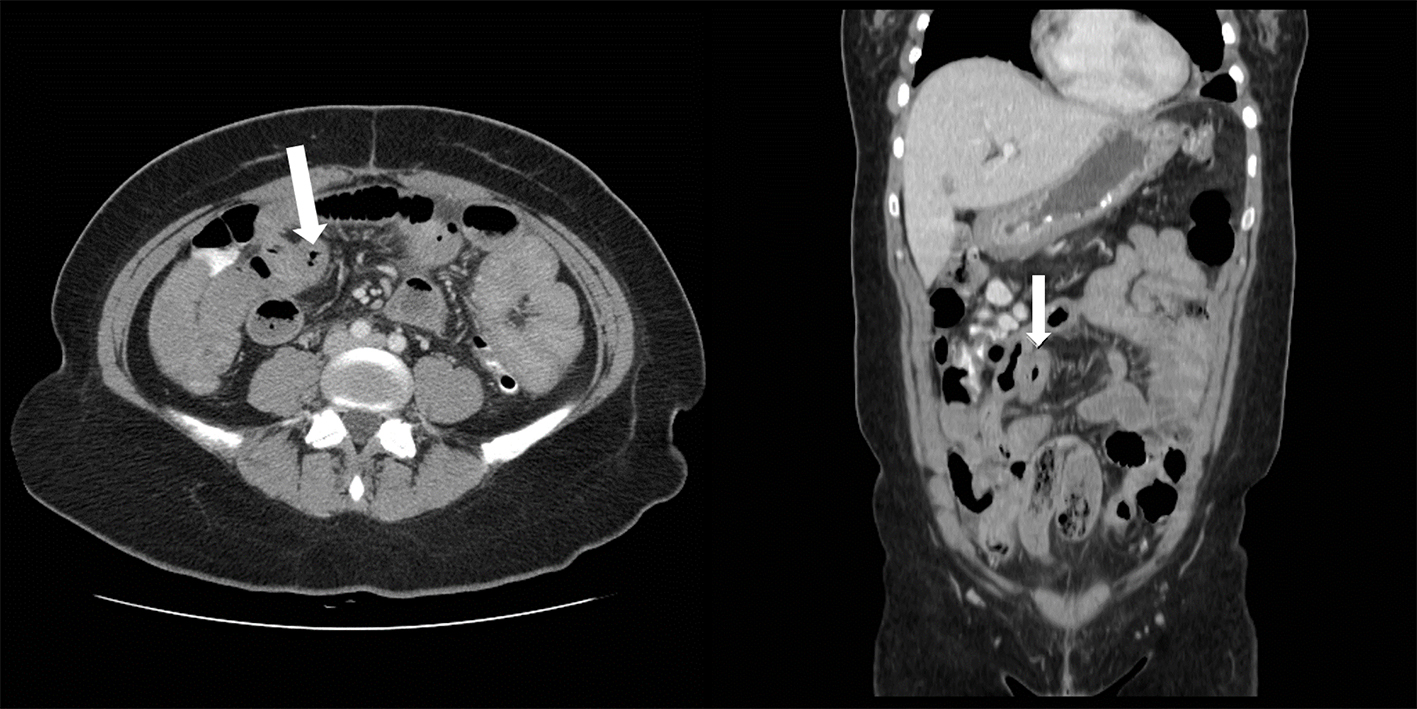
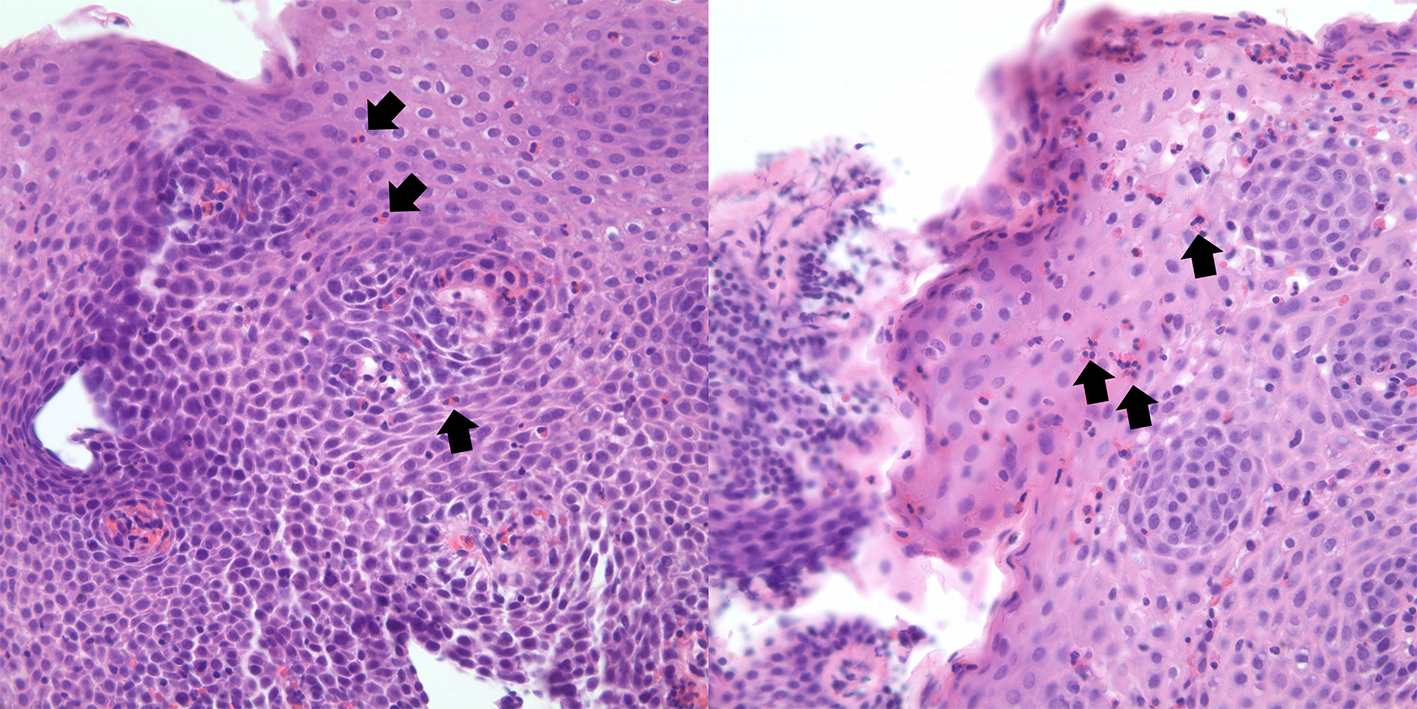
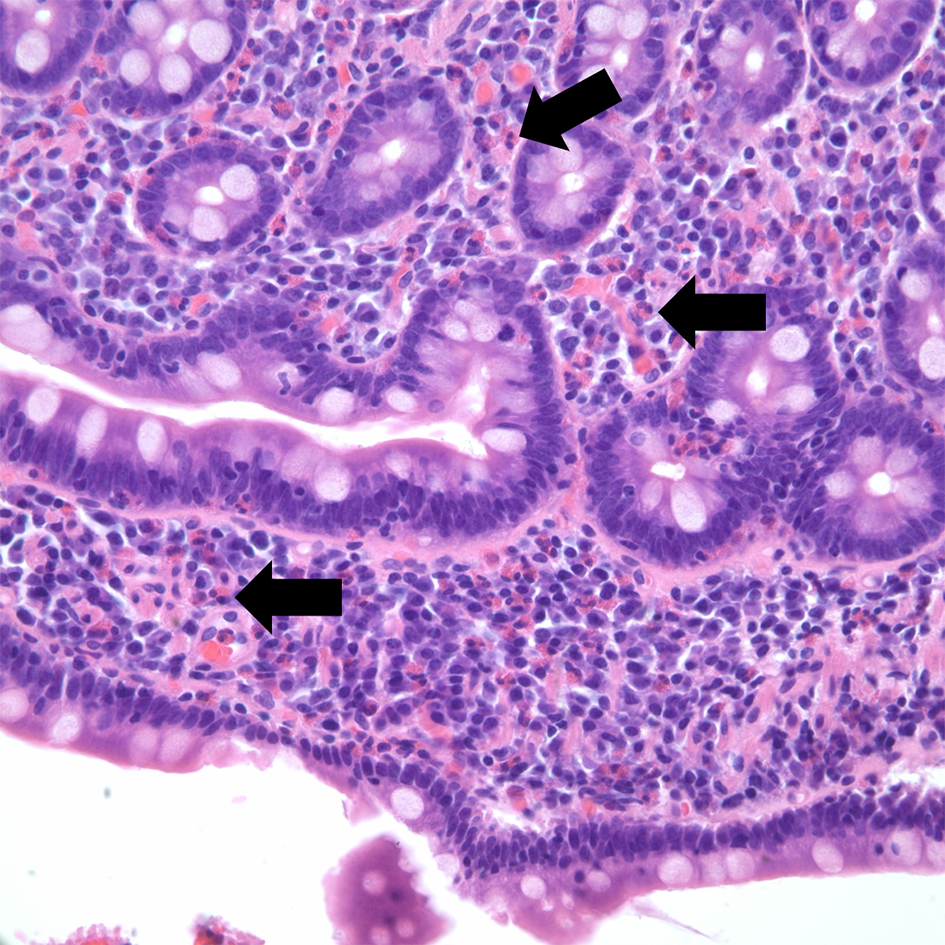
Table
| Modified from [2, 5]. | |
| Infectious | Viral (HIV, HTLV1, EBV) |
| Parasitic (Strongyloides spp, Sarcocystis hominis, Isospora belli, Schistosoma spp., filariasis) | |
| Fungal (Coccidioides spp) | |
| Bacterial (tuberculosis) | |
| Allergic | Asthma |
| Atopic dermatitis | |
| Allergic rhinitis | |
| Malignancies | Solid tumors |
| Systemic mastocytosis | |
| Hematologic malignancies (Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic eosinophilic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia) | |
| Medications | Anticonvulsivants (carbamazepine, valproic acid) |
| Antidepressives (IRSS, amitriptyline) | |
| Allopurinol | |
| Antibiotics (beta-lactam antibiotics, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, quinolones) | |
| Antiretrovirals (efavirenz, abacavir) | |
| Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) | Myeloid HES |
| Lymphocytic HES | |
| Idiopathic HES | |
| Associated HES | |
| Overlap HES | |
| Familiar HES | |
| Immune deregulation | Allergic bronchopulmonar Aspergiliosis |
| HyperIgE syndrome (Job syndrome) | |
| Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis | |
| Gleich syndrome | |
| IgG4 disease | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Others | Adrenal insufficiency |
| Sarcoidosis | |
| Radiation exposure | |
| Cholesterol emboli | |