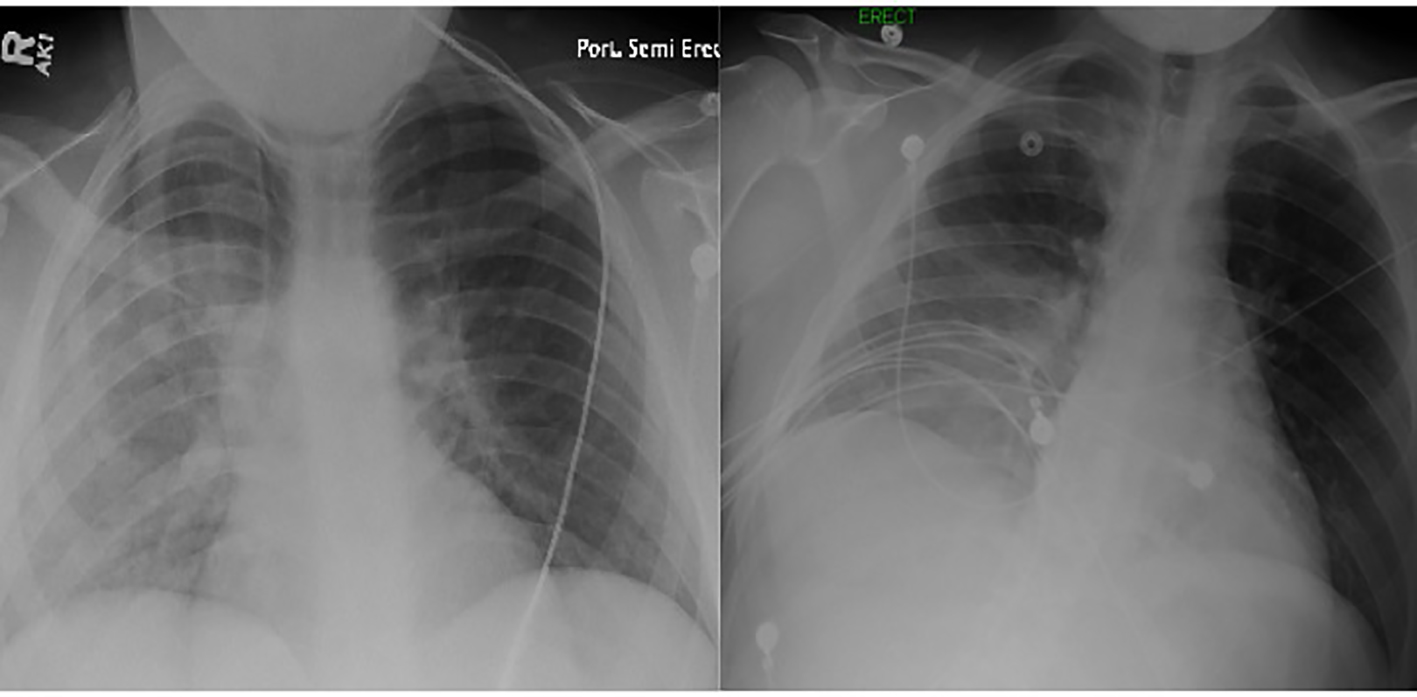
Figure 1. Chest X-ray performed at the time of admission revealing opacification and diffuse infiltrates of the right lung (left image). A repeat X-ray performed the next day demonstrated a significant clearance (right image).
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 8, Number 10, October 2017, pages 305-310
Heroin Epidemic and Acute Kidney Injury: An Under-Recognized but Important Consequence of Opioid Overdose
Figures

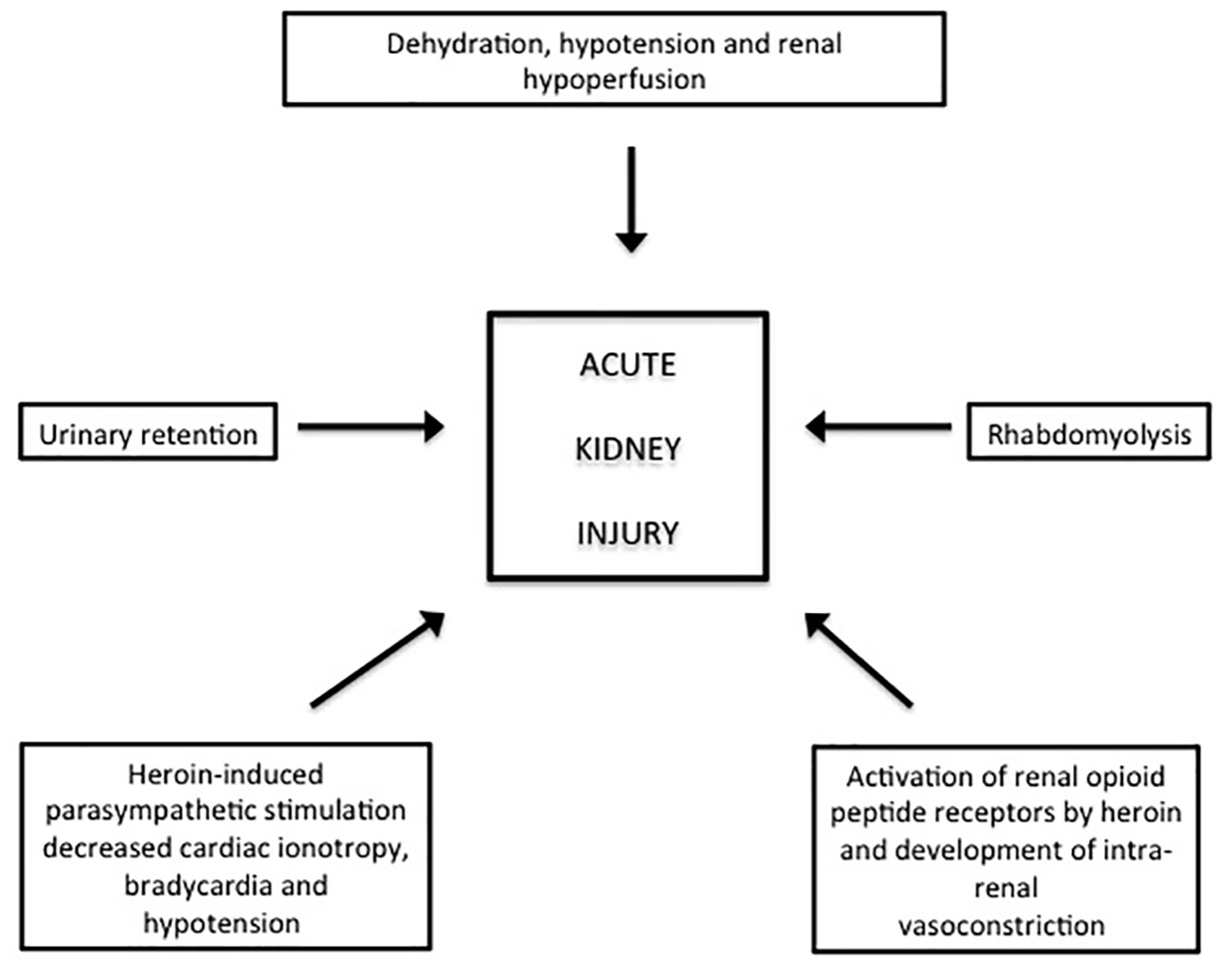
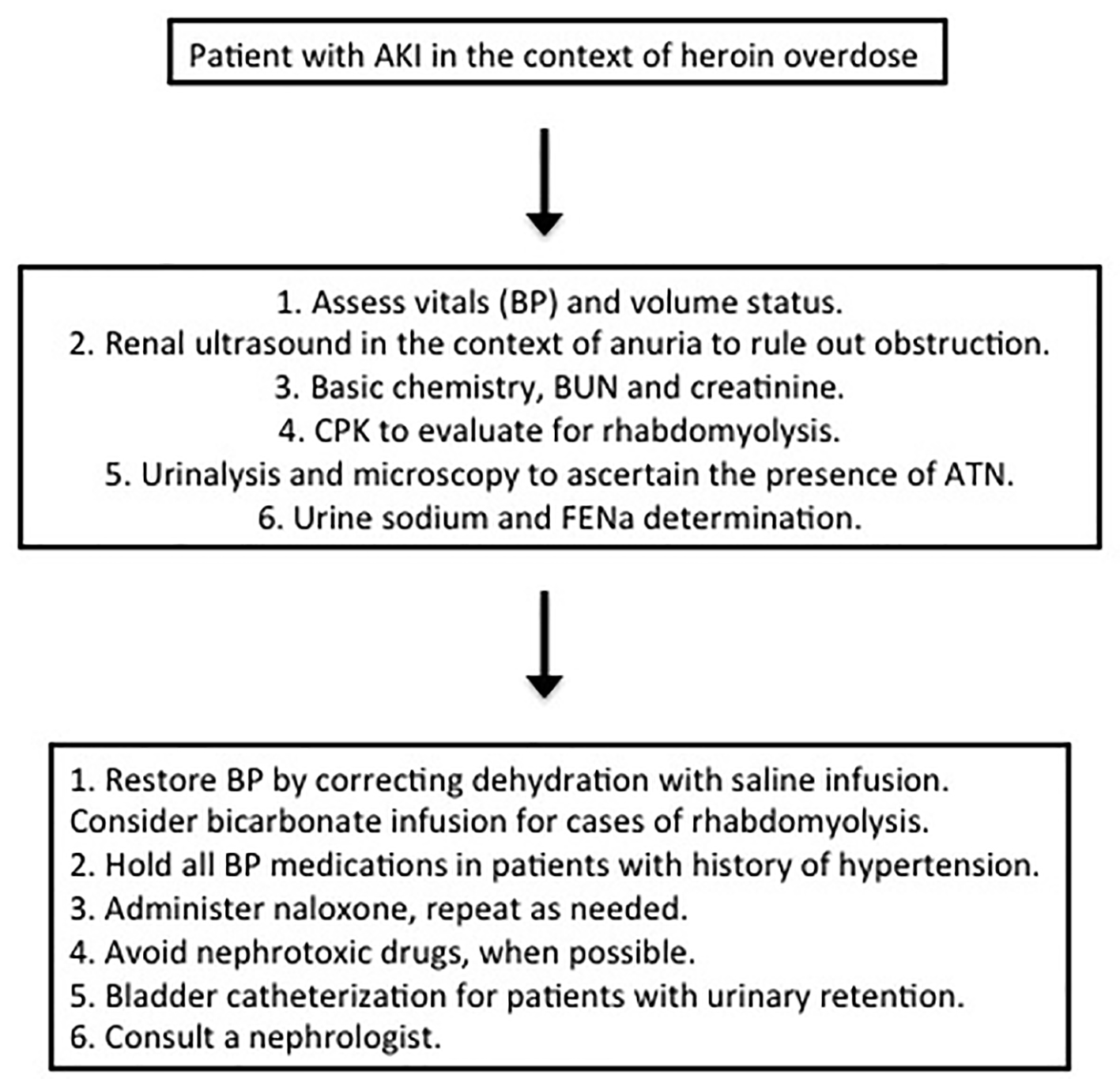
Table
| Laboratory parameter | Patient 2 | Patient 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 1 | Day 6 | Month 7 | |
| WBC: white blood cell; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; CPK: creatine phosphokinase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate (mL/min). | |||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 13.2 | 12.4 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 48.8 | 47 | 47 | 43 | 38 |
| WBC (103/µL) | 29.1 | 8.9 | 7.8 | 7.0 | 7.1 |
| Platelet (103/µL) | 276 | 270 | 256 | 240 | 244 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 93 | 23 | 56 | 38 | 30 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.3 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 5.8 | 2.5 (eGFR = 45) |
| Calcium (mEq/L) | 8.9 | 8.8 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 9.3 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 146 | 144 | 143 | 135 | 137 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.3 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 5.2 | 4.7 |
| Chloride (mEq/L) | 102 | 100 | 97 | 94 | 96 |
| AST (U/L) | 45 | 40 | 39 | 41 | - |
| ALT (U/L) | 38 | 42 | 32 | 34 | - |
| CPK | 300 | 180 | 140 | 120 | - |
| Lactic acid (mg/dL) | 3.4 | 1.4 | - | Normal | - |
| Urine examination | No evidence of hematuria, proteinuria, glucosuria, tubular cells, or granular, tubular, red cell or white cell casts. | - | Numerous tubular cells, granular and tubular casts. | 1+ proteinuria. No evidence of hematuria or glucosuria. | - |