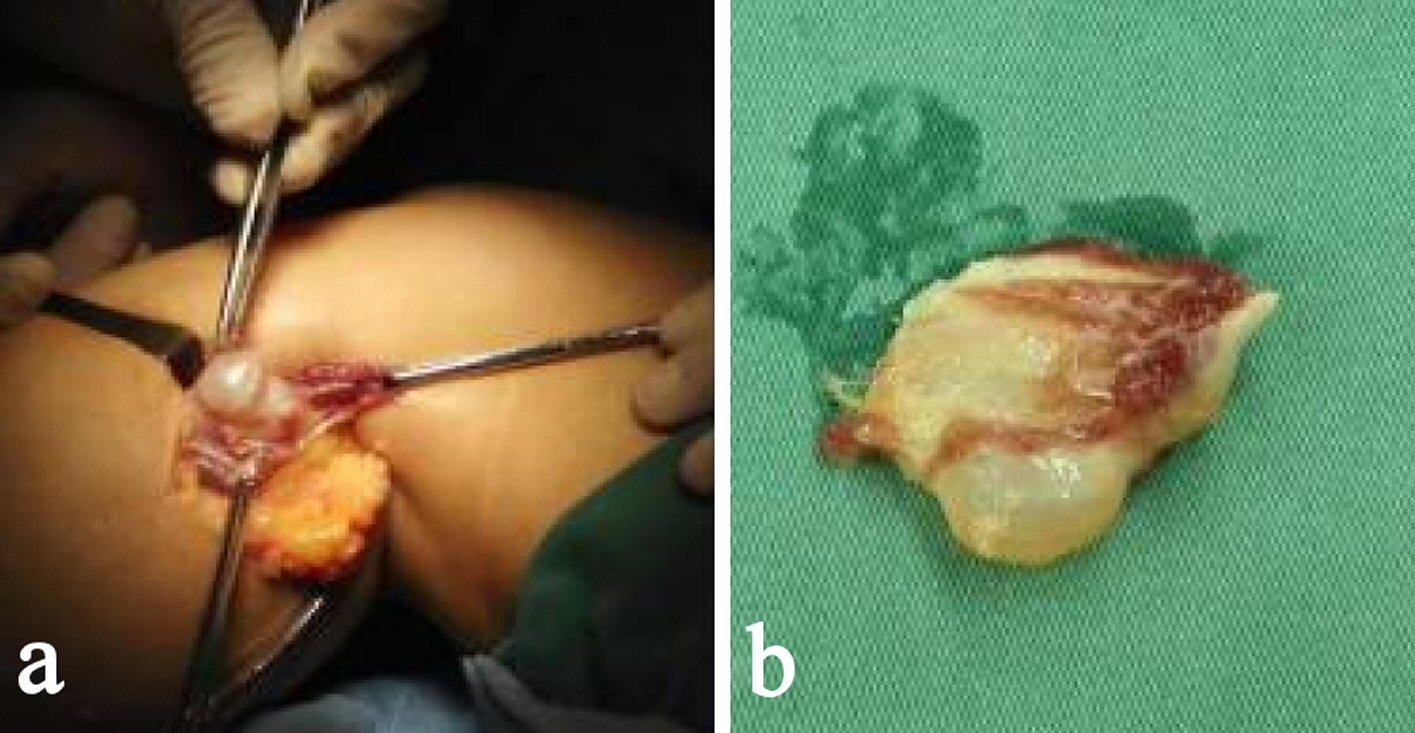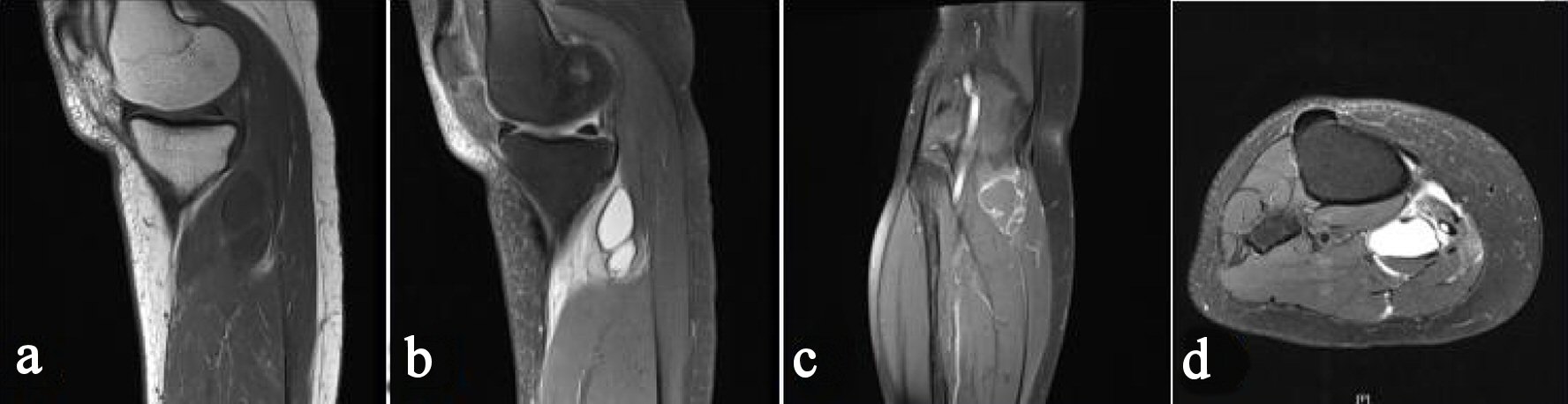
Figure 1. Preoperative magnetic resonance image of the right knee. Sagittal T1-weighted image (a), sagittal T2-weighted image (b), coronal T2-weighted image (c), and axial T2-weighted image (d) reveal a mass in the gastrocnemius medialis muscle, which does not communicate with the articular joint.
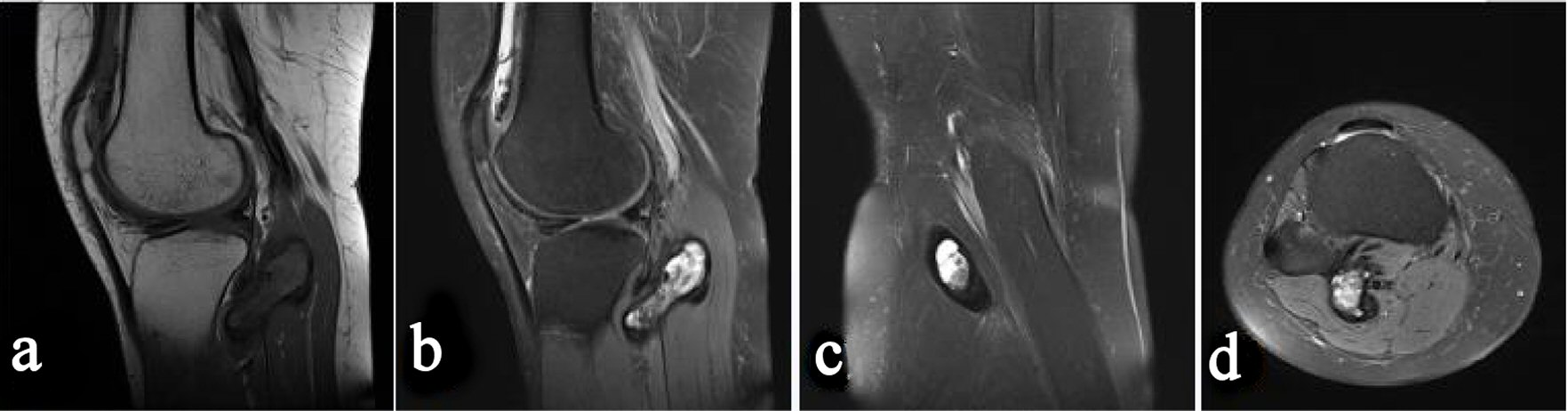
Figure 3. Preoperative magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the right knee. Sagittal T1-weighted image (a), sagittal T2-weighted image (b), coronal T2-weighted image (c), and axial T2-weighted image (d) reveal a mass in the gastrocnemius lateralis muscle. Thickened synovium with low signal intensity on both T1-weighted and T2-weighted images is found in the knee joint.