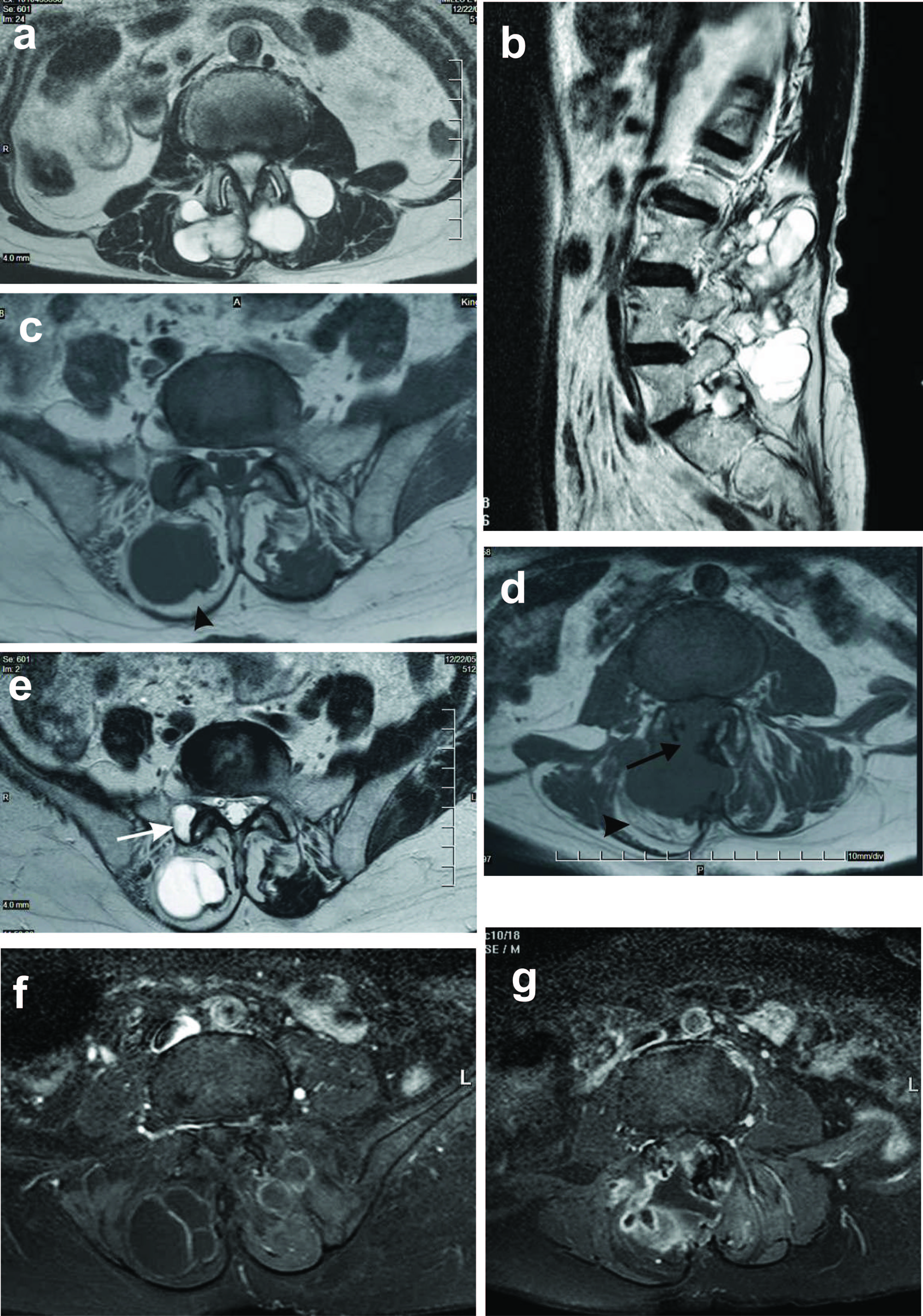
Figure 1. a and b: Axial and sagittal T2 weighted images showing a large, markedly T2 hyperintense multiloculated mass lesion involving the paraspinal muscles bilaterally (1a) and extending from L2 to S1 vertebral levels (1b); c and d: Axial T1 weighted images showing increased signal in the adjacent paraspinal muscles (arrow heads), in keeping with fatty atrophy. There is destruction of the right lamina with extension into the central spinal canal (arrow in d); e: Note is made of involvement of the right facet joint with cystic change as seen by the increased signal on these T2 weighted images (arrow); f and g: Post contrast axial T1 weighted images showing peripheral rim and septal enhancement. In addition there is patchy heterogeneous enhancement of the intraspinal component.