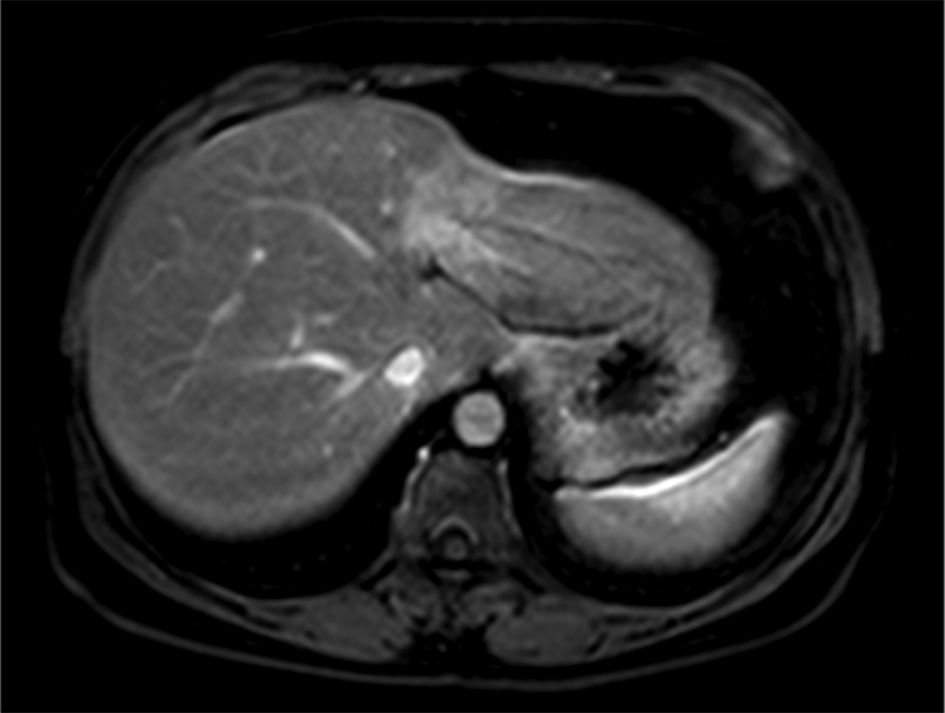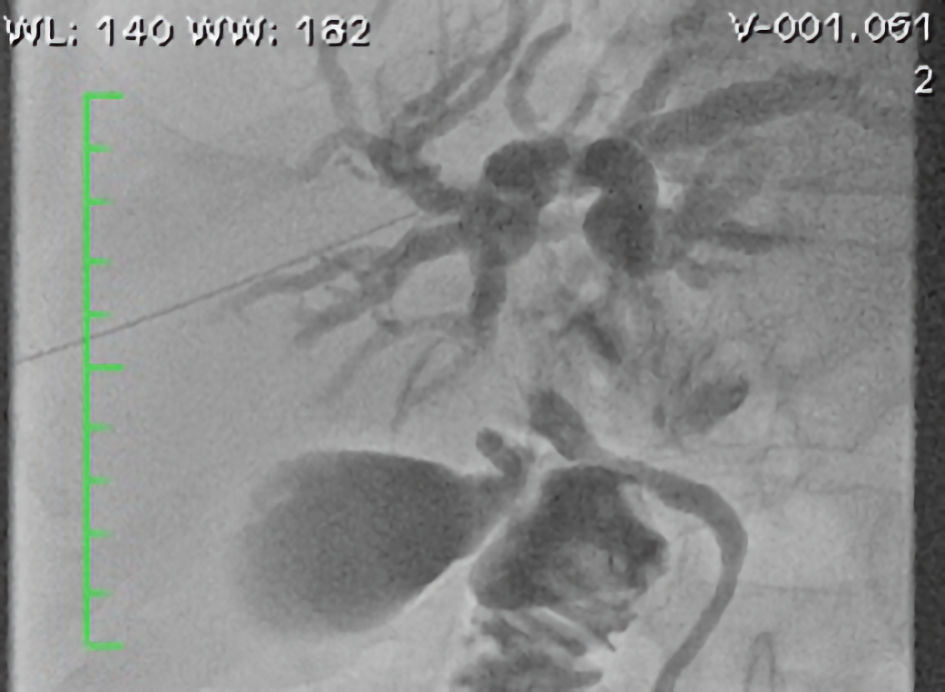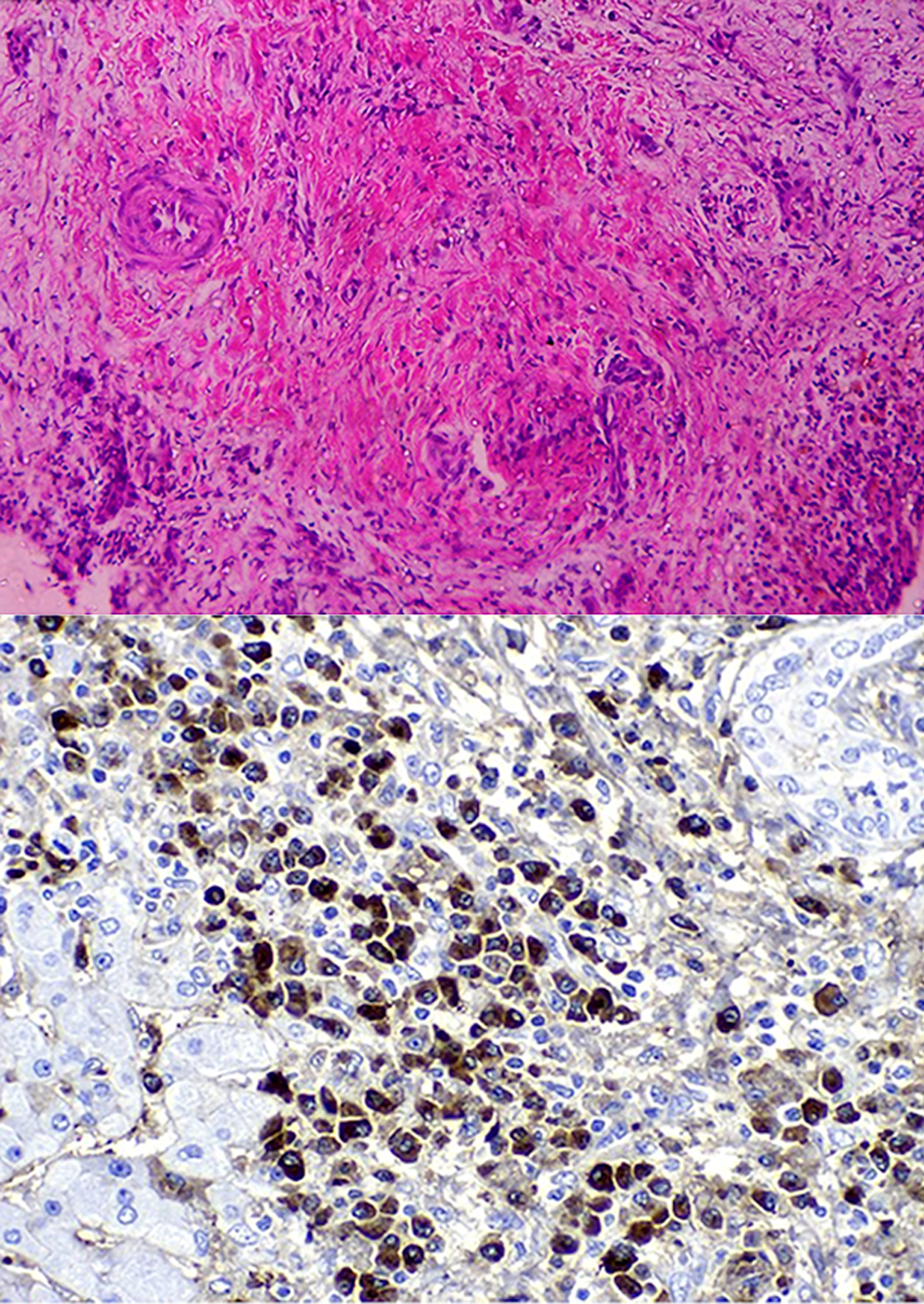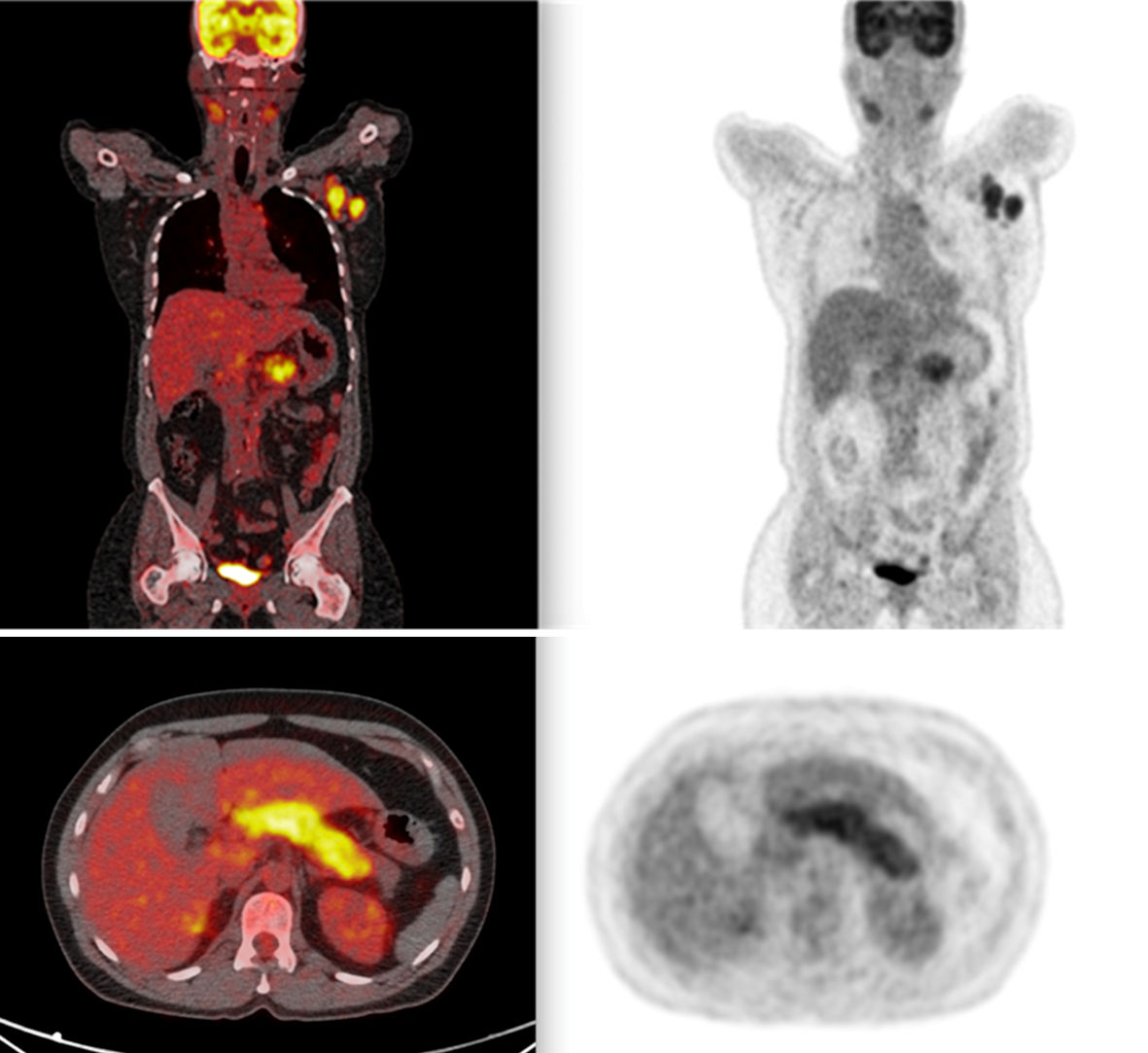
Figure 1. PET scan showing widespread lymph node involvement (pancreatic, submandibular, and hepatic hilum). In the pancreas, in addition to pancreatic enlargement, note the increased FDG uptake. PET: positron emission tomography; FDG: fluorodeoxyglucose.