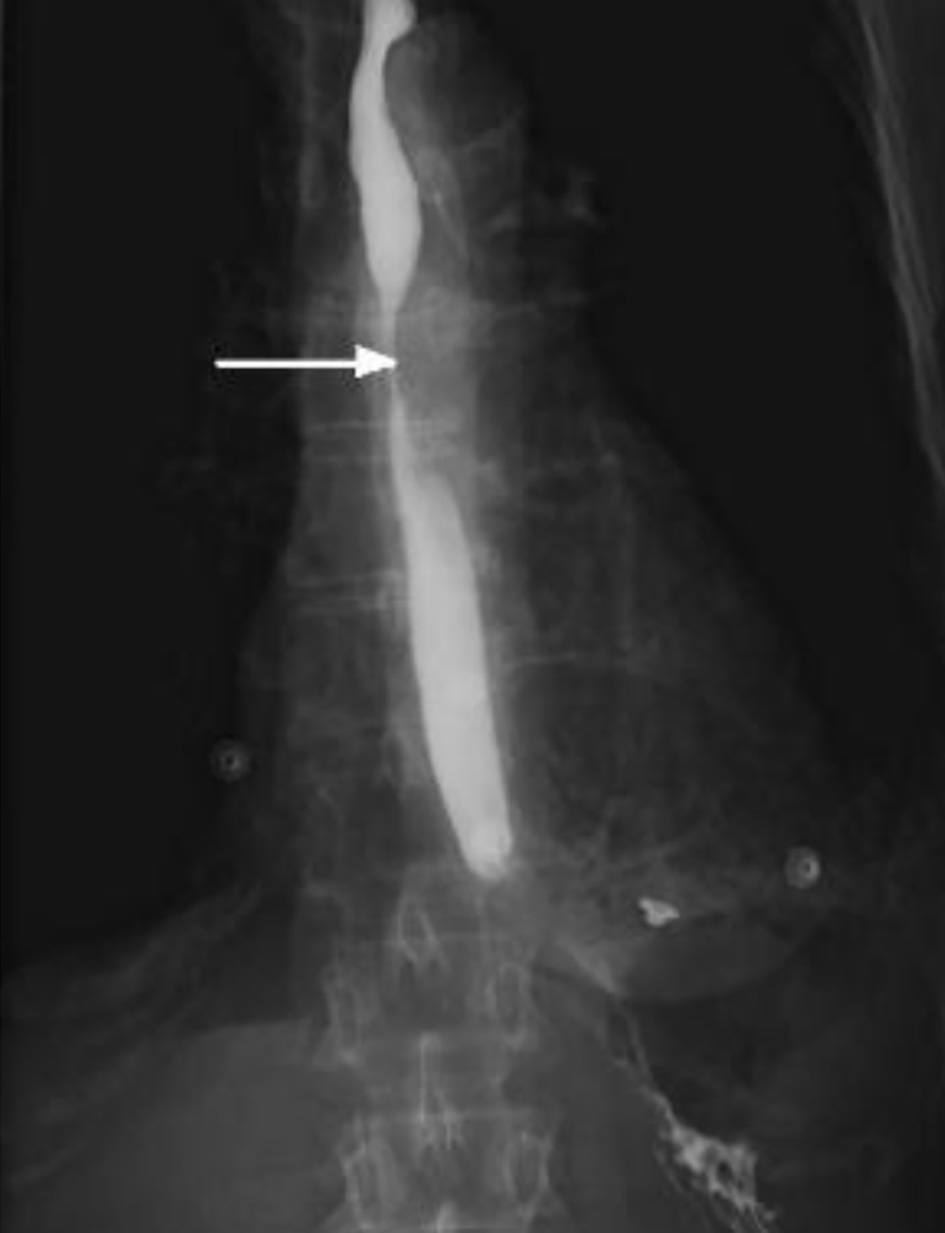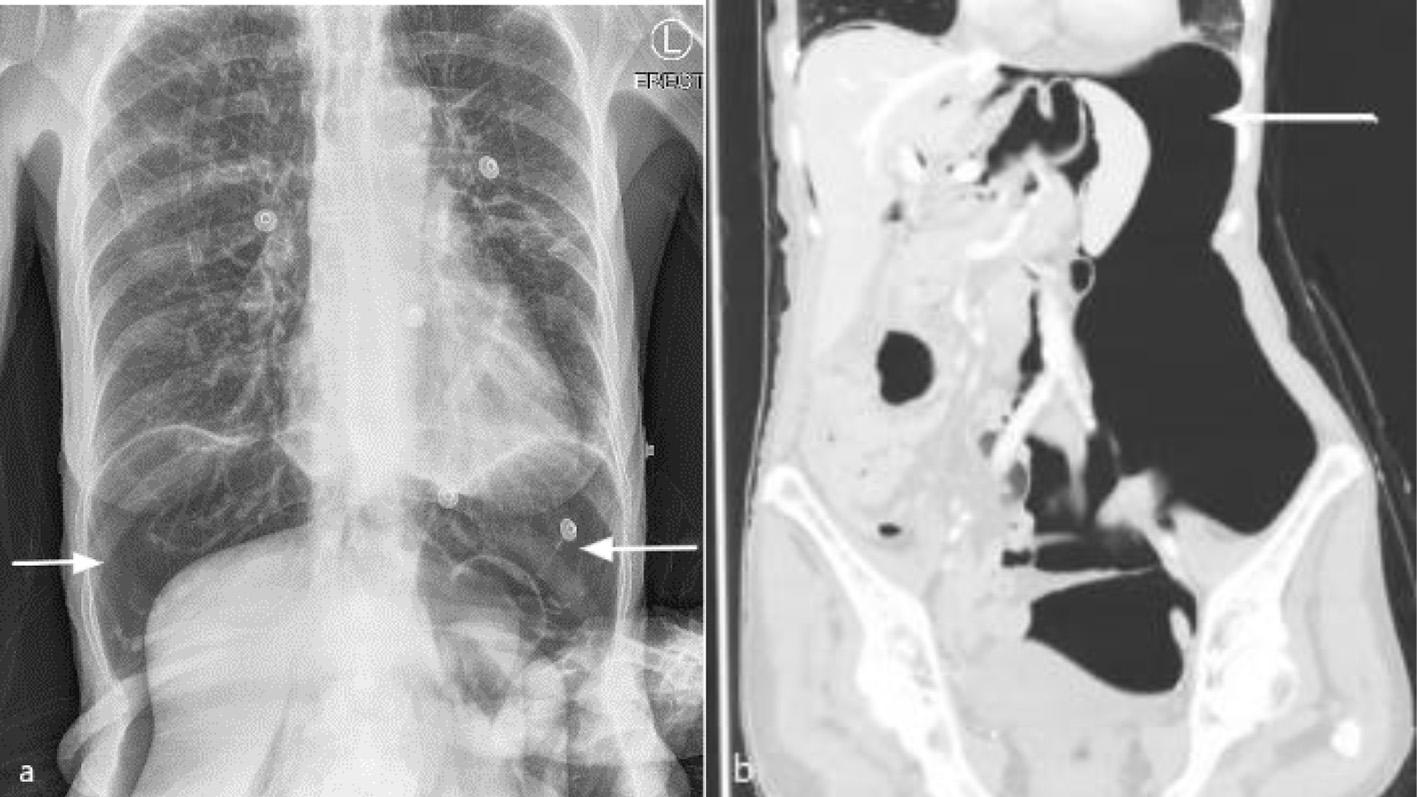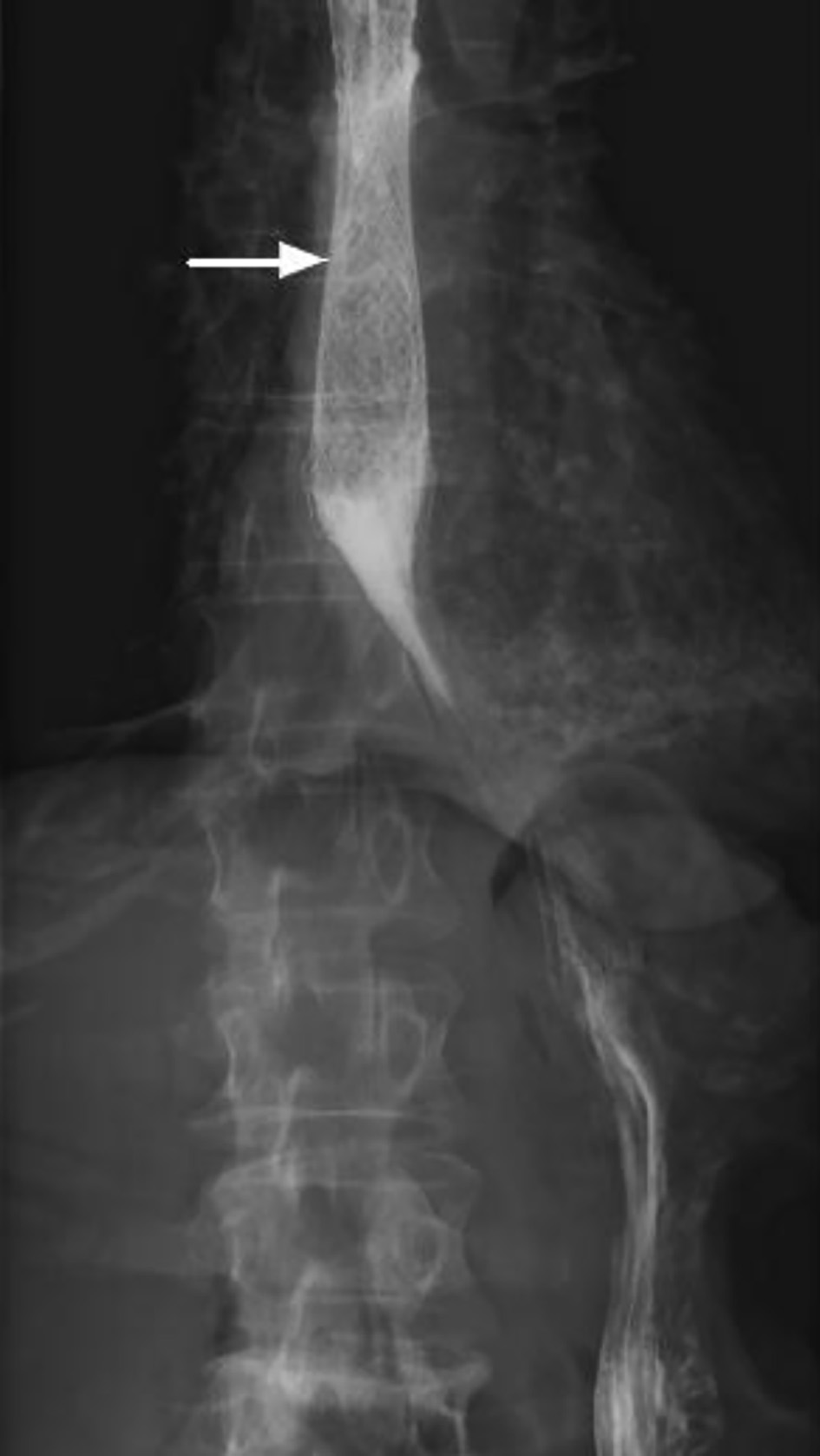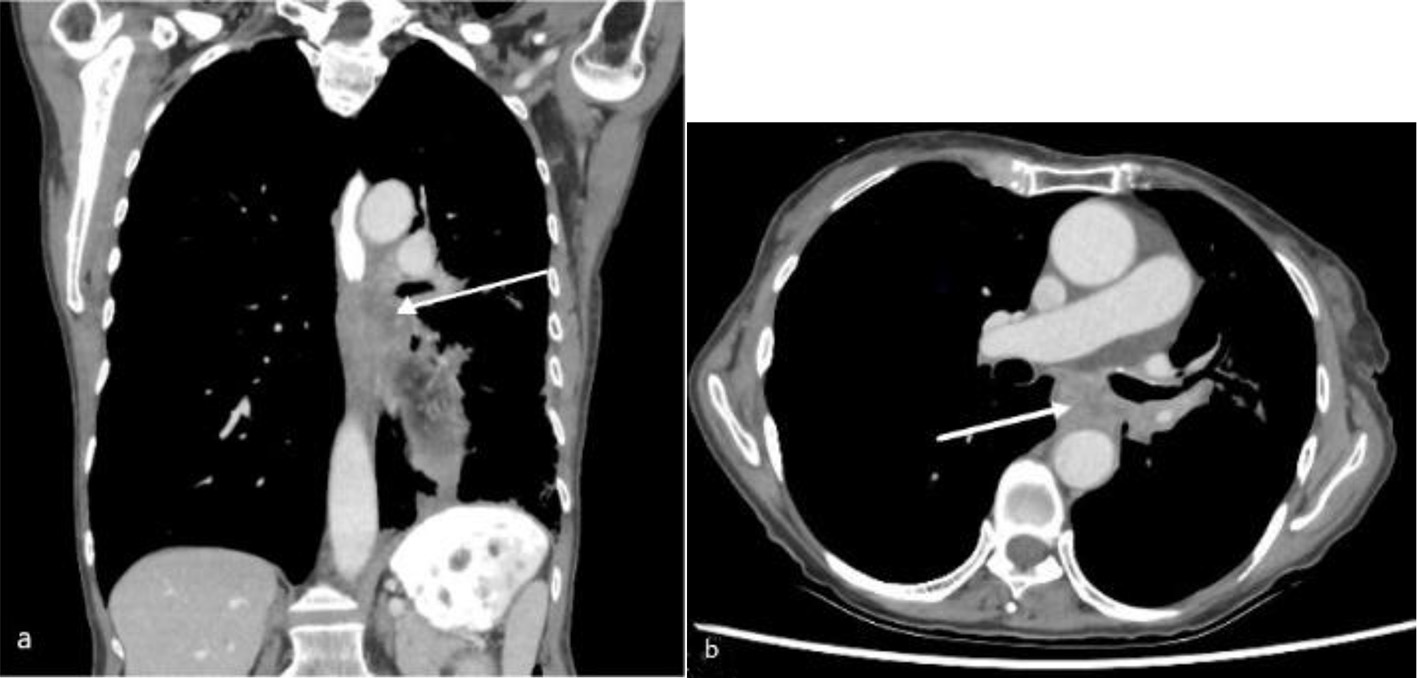
Figure 1. Computed tomography of chest with oral and intravenous contrast in soft tissue window (a: coronal view; b: axial view) showing a subcarinal soft tissue mass (arrow) at the left lung hilum with obstruction of the mid esophagus.
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 13, Number 4, April 2022, pages 178-182
Pneumoperitoneum Post Esophageal Stent Insertion Managed With Paracentesis
Figures