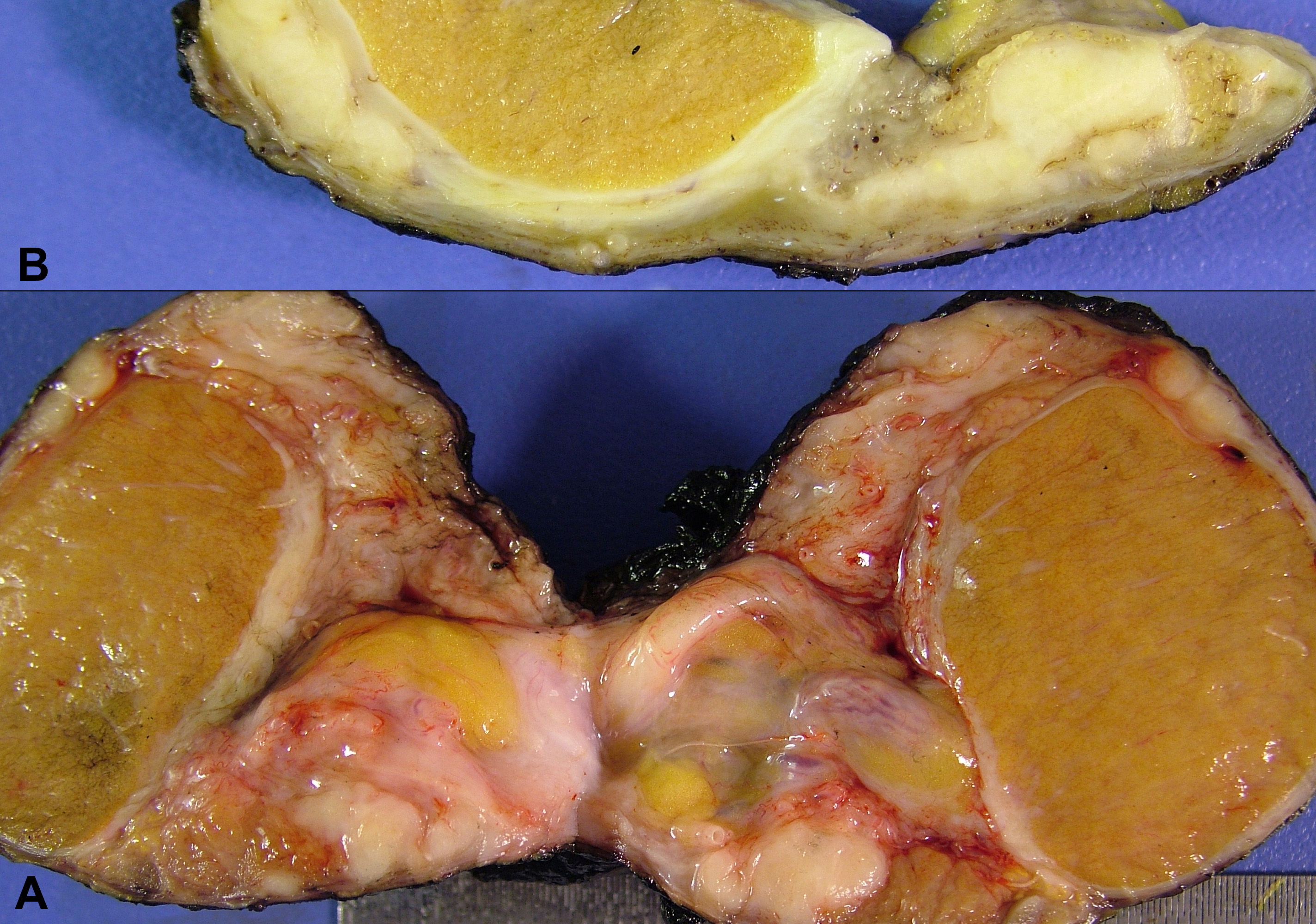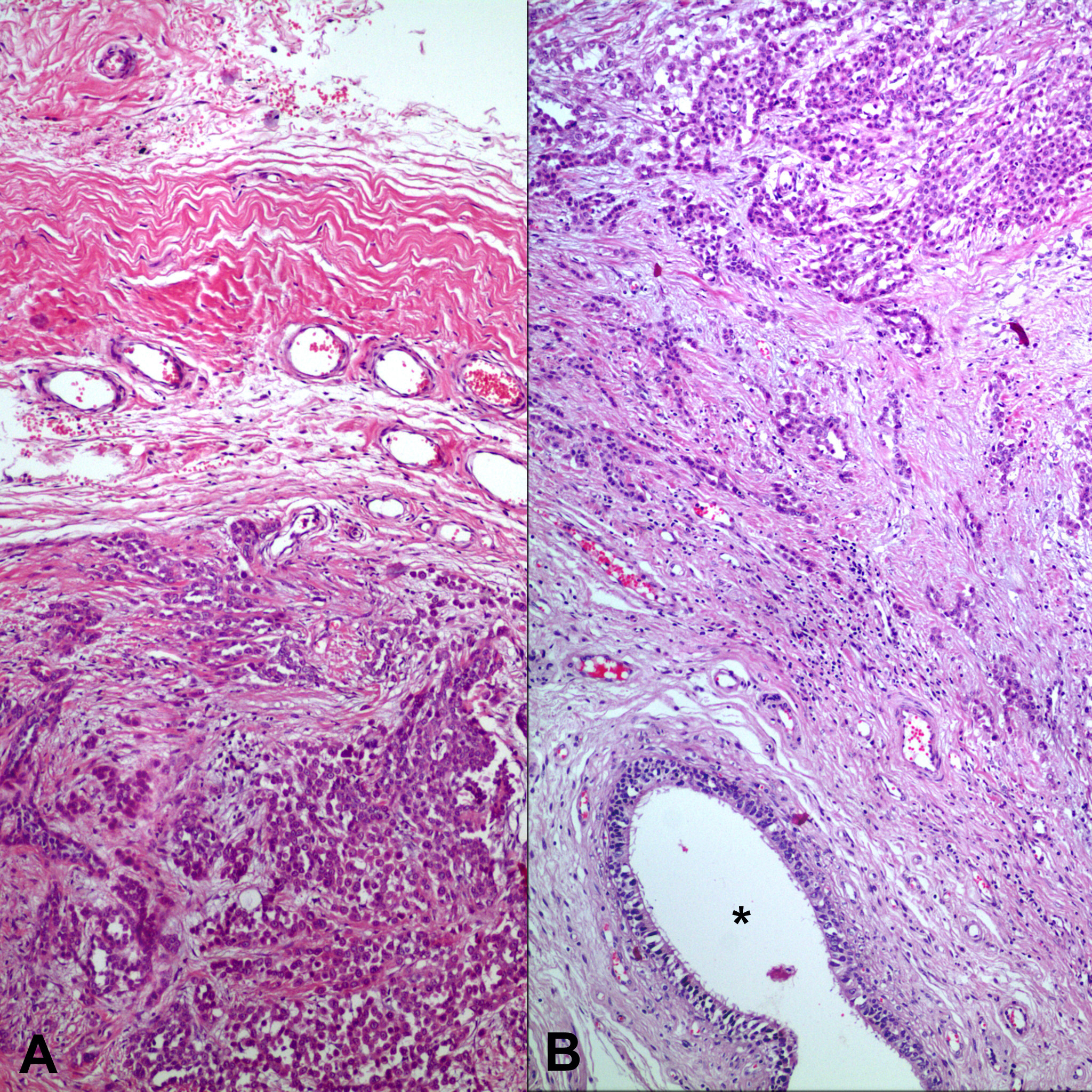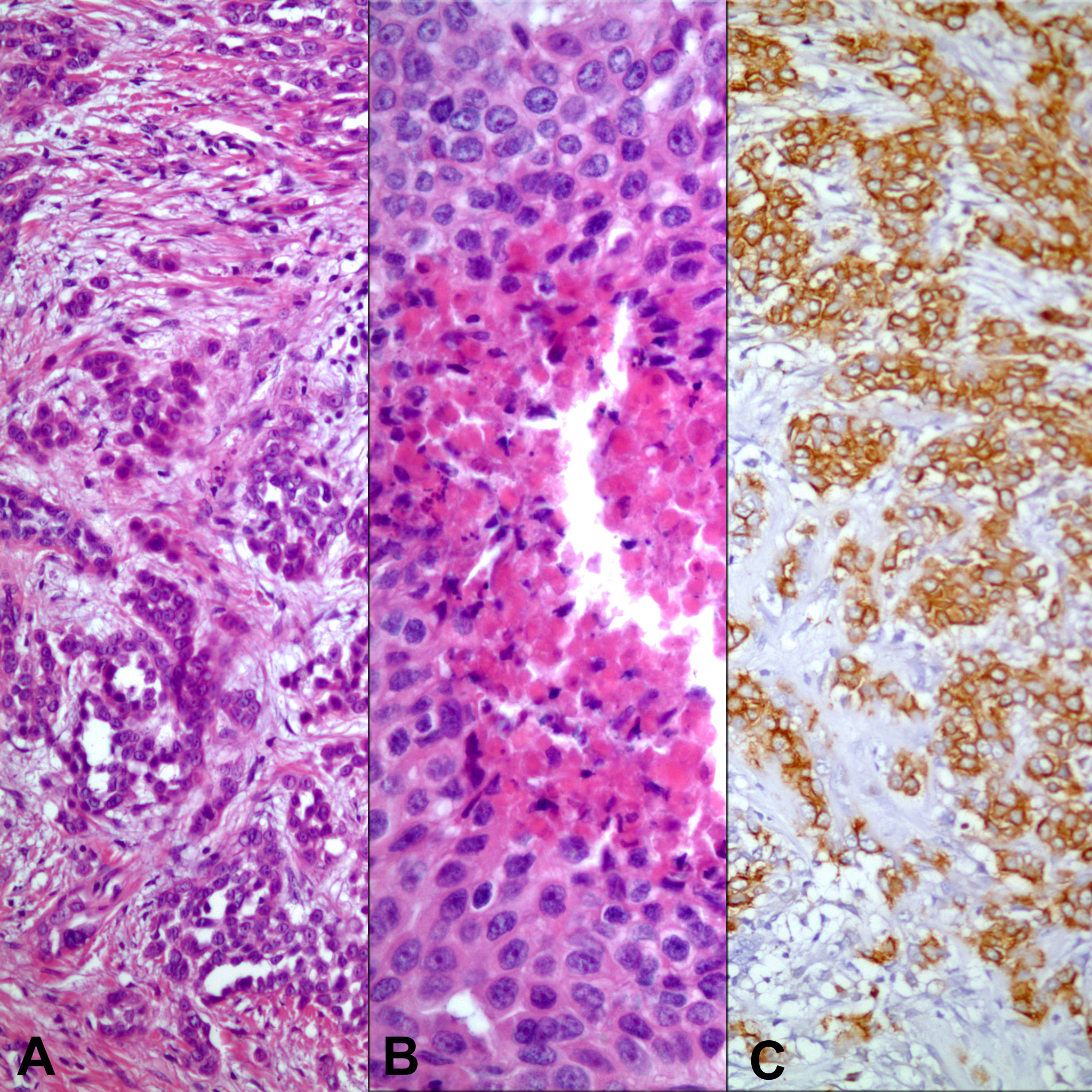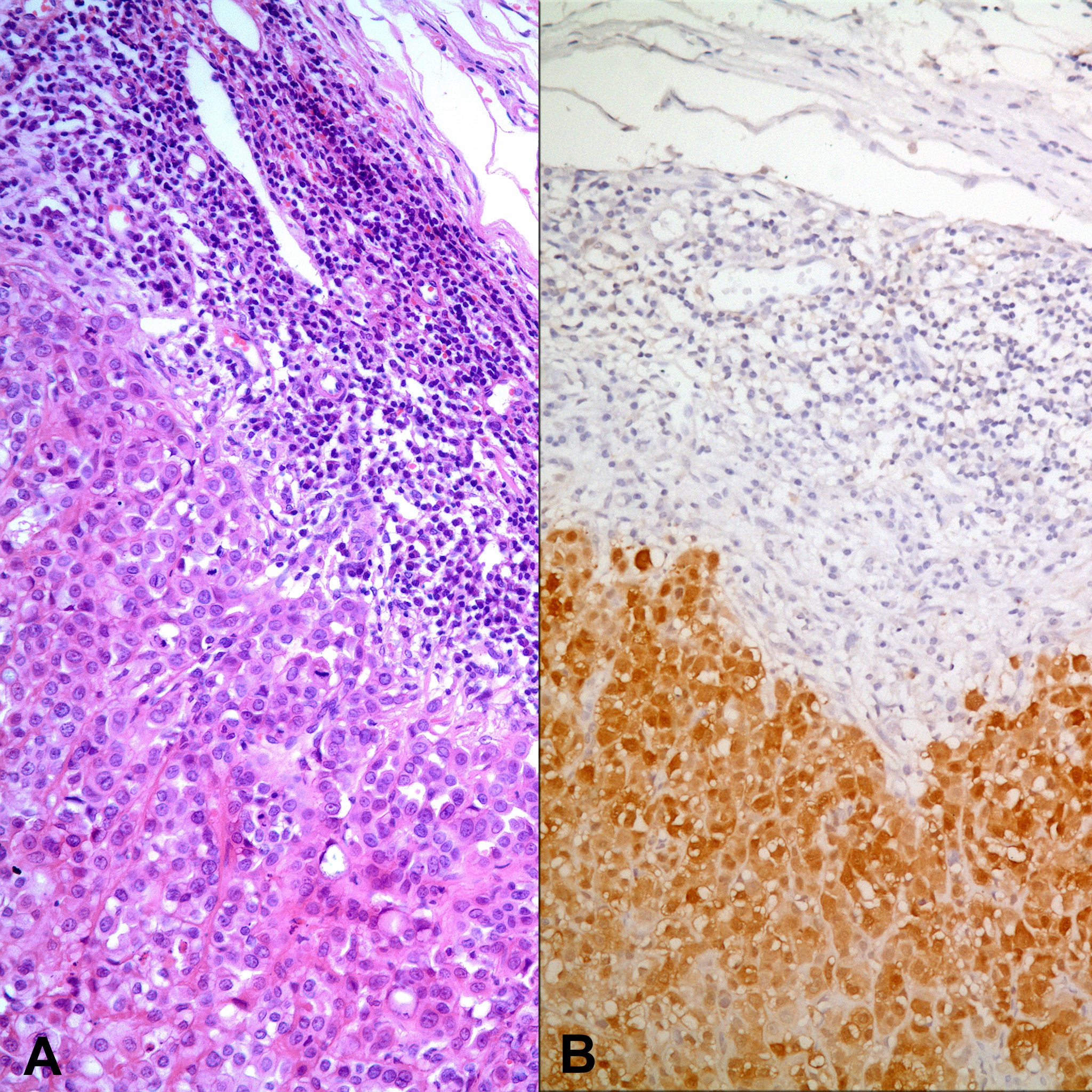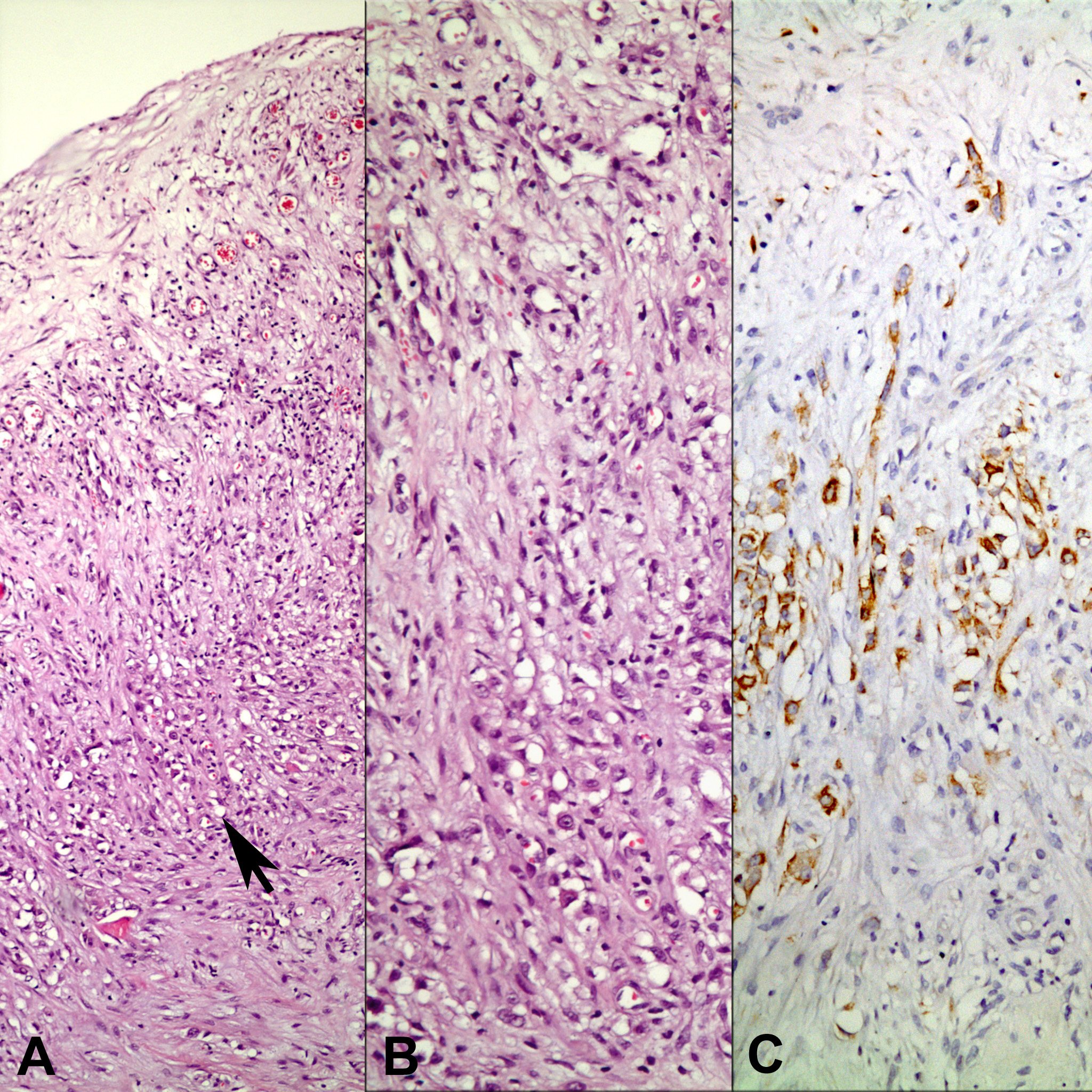
Figure 1. Biopsy from tunica vaginalis showing mesothelial cell proliferation (arrow). Panel B and C represent the area pointed by the arrow (A: H-E x 40; B: H-E x 200; C: Immunohistochemistry, anti-calretinin Ab x 200).
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 2, Number 6, December 2011, pages 275-278
Hydrocele and Unexpected Diagnosis: Malignant Mesothelioma of Tunica Vaginalis Testis
Figures