Figures
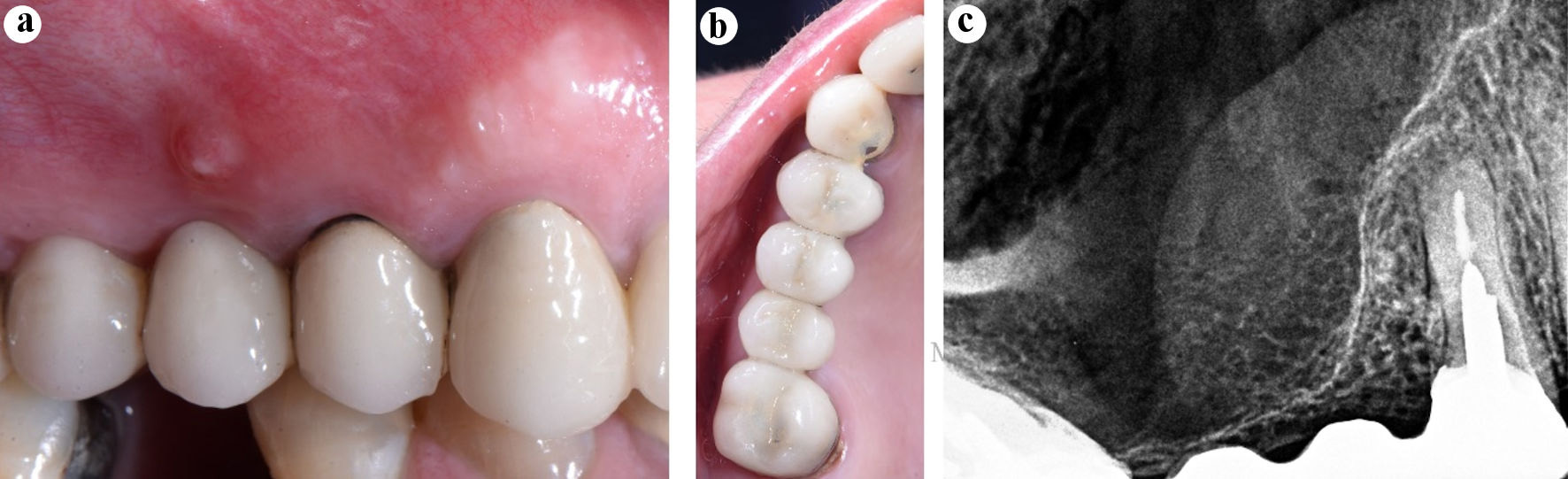
Figure 1. Diagnosis. (a) Preoperative clinical image, the sinus tract in the attached gingiva of the tooth 15 (bridge span). (b) Preoperative clinical image, occlusal view. (c) Preoperative periapical radiograph of the tooth 14.
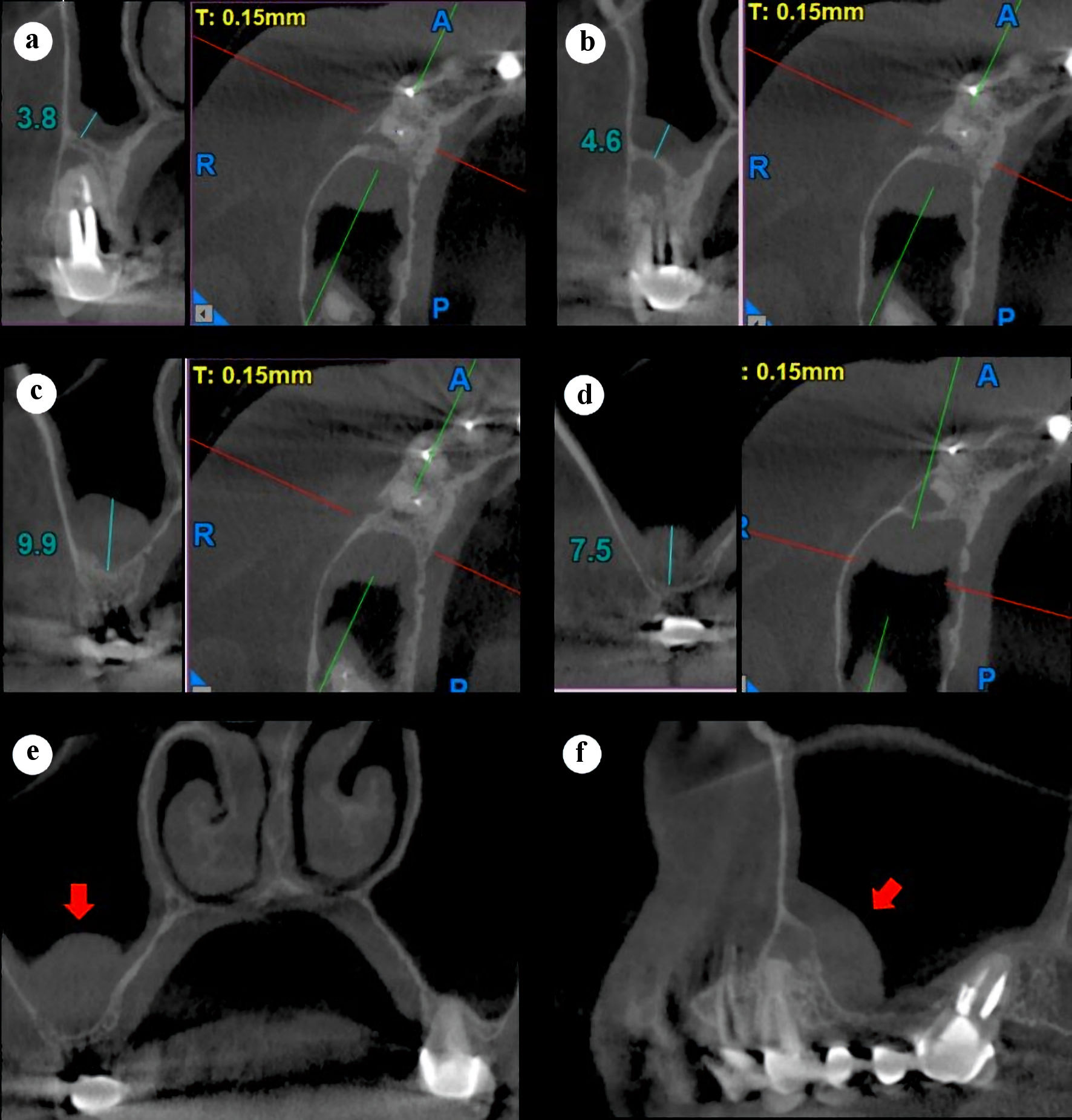
Figure 2. Preoperative right maxillary CBCT scan, sagittal and axial slices (a-d). (a) Center, tooth 14. (b) Distal, tooth 14. (c) 3 mm distal to the tooth 14. (d) Distal of the sinus thickening. (e) Coronal slice showing the thickened sinus membrane (red arrow). (f) Panorex slice showing thickened sinus membrane (red arrow). CBCT: cone-beam computed tomography.
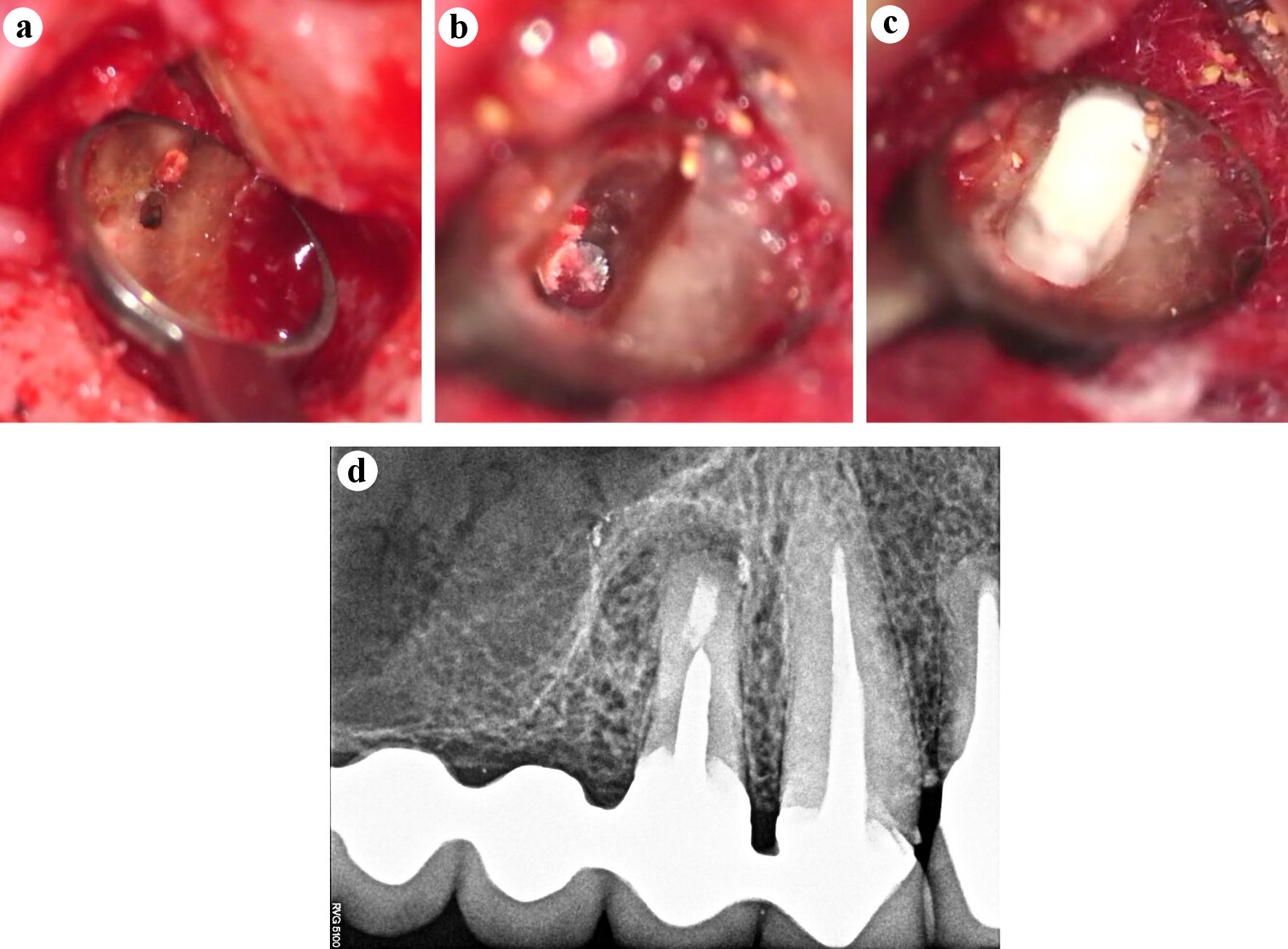
Figure 3. Intra-surgical images documented with operative microscope (Zeiss Extaro 300, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) (a-c). (a) Absence of buccal root canal preparation and filling (× 16). (b) The apical portion of the metal post at the bottom of the ultrasonic root-end preparation is seen (× 25). (c) Apical seal with Bio-C Repair (Angelus, Londrina, PR, Brazil) (× 25). (d) Postoperative periapical radiograph.
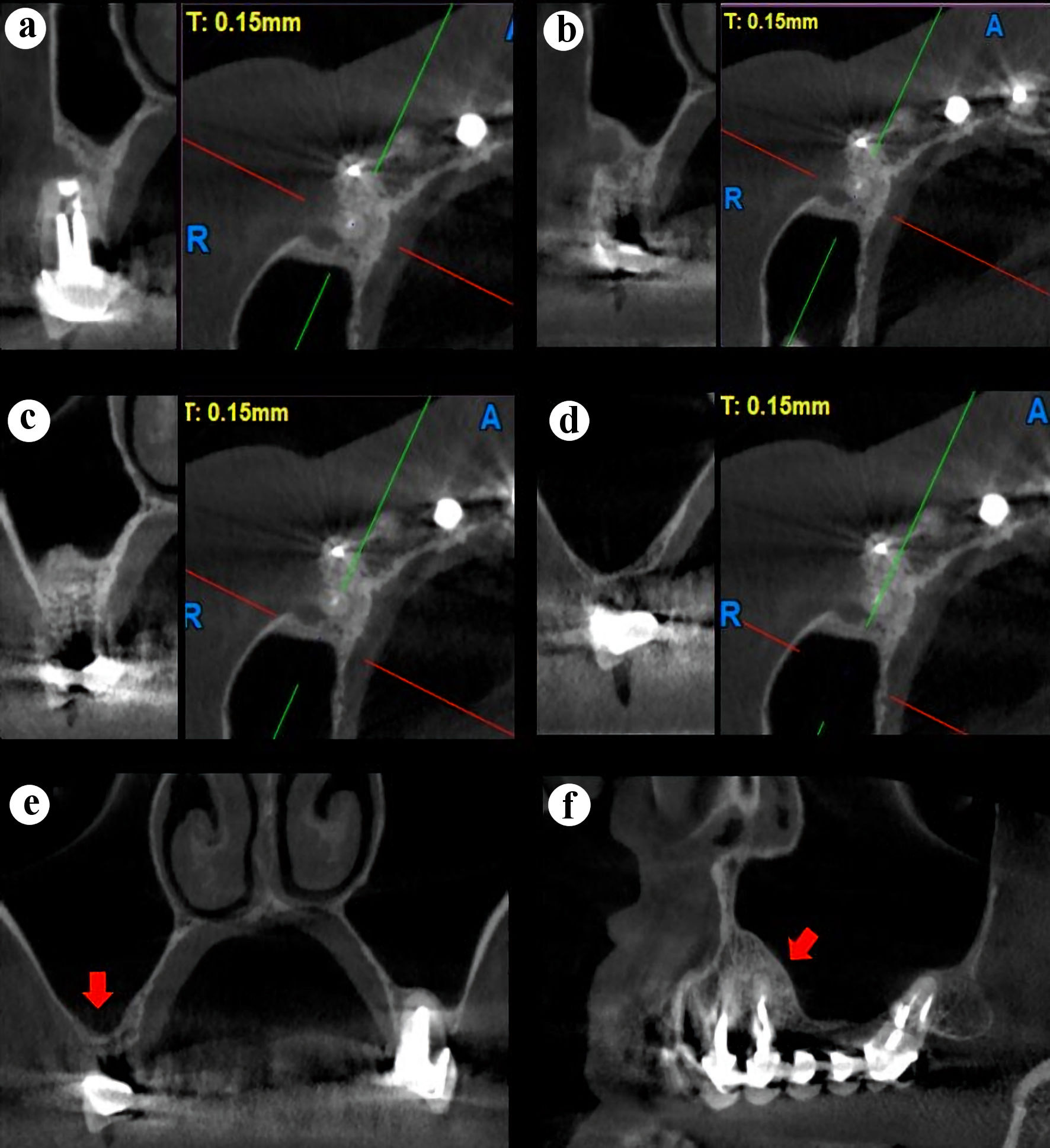
Figure 4. Right maxillary CBCT scan, sagittal and axial slices (a-d). (a) Center, tooth 14. (b) Distal, tooth 14. (c) 3 mm distal to the tooth 14. (d) Total healing of the sinus membrane. (e) Coronal slice showing a normal sinus membrane (red arrow). (f) Panorex slice showing a normal sinus membrane (red arrow). CBCT: cone-beam computed tomography.




