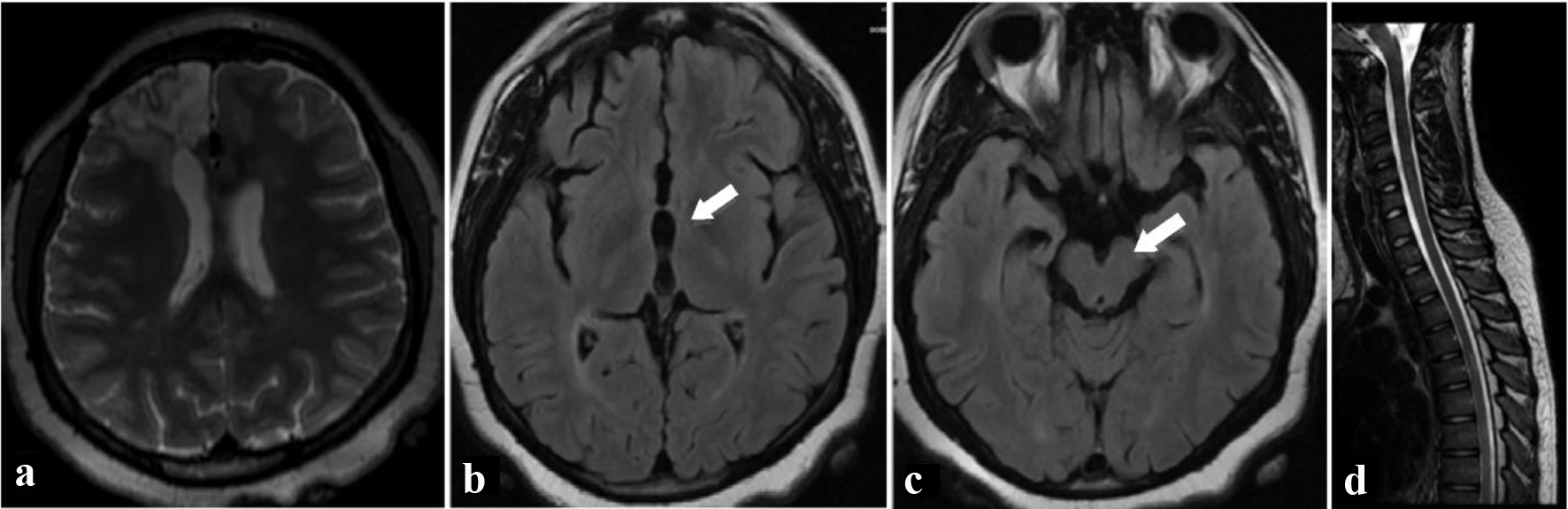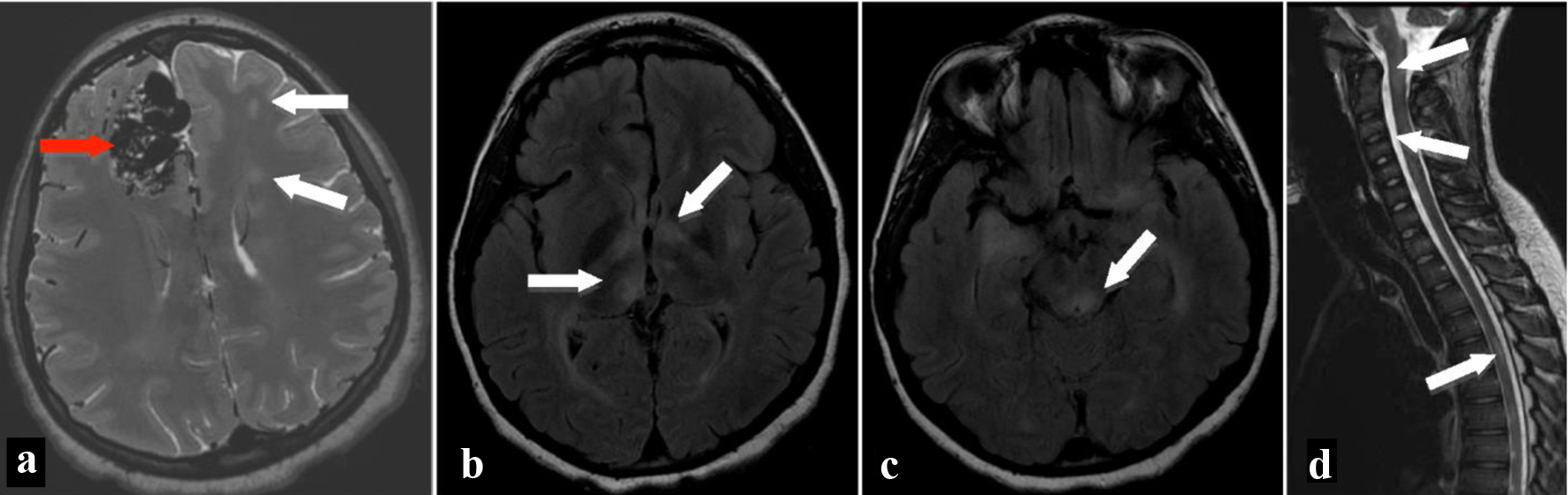
Figure 1. MRI of brain on axial T2-weighted image (a) shows multiple flow voids in the right frontal lobe (red arrow) consistent with arteriovenous malformation as well as multiple hyperintense T2 signal areas (white arrows) in the white matter bilaterally. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery axial images show hyperintensities in the bilateral thalami (b), left globus pallidus, left putamen, bilateral cerebral white matter, and brainstem (c). MRI of the spine shows patchy hyperintense signal areas (arrows) in the brainstem, cervical spinal cord, and thoracic spinal cord on T2-weighted sagittal image (d). MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.