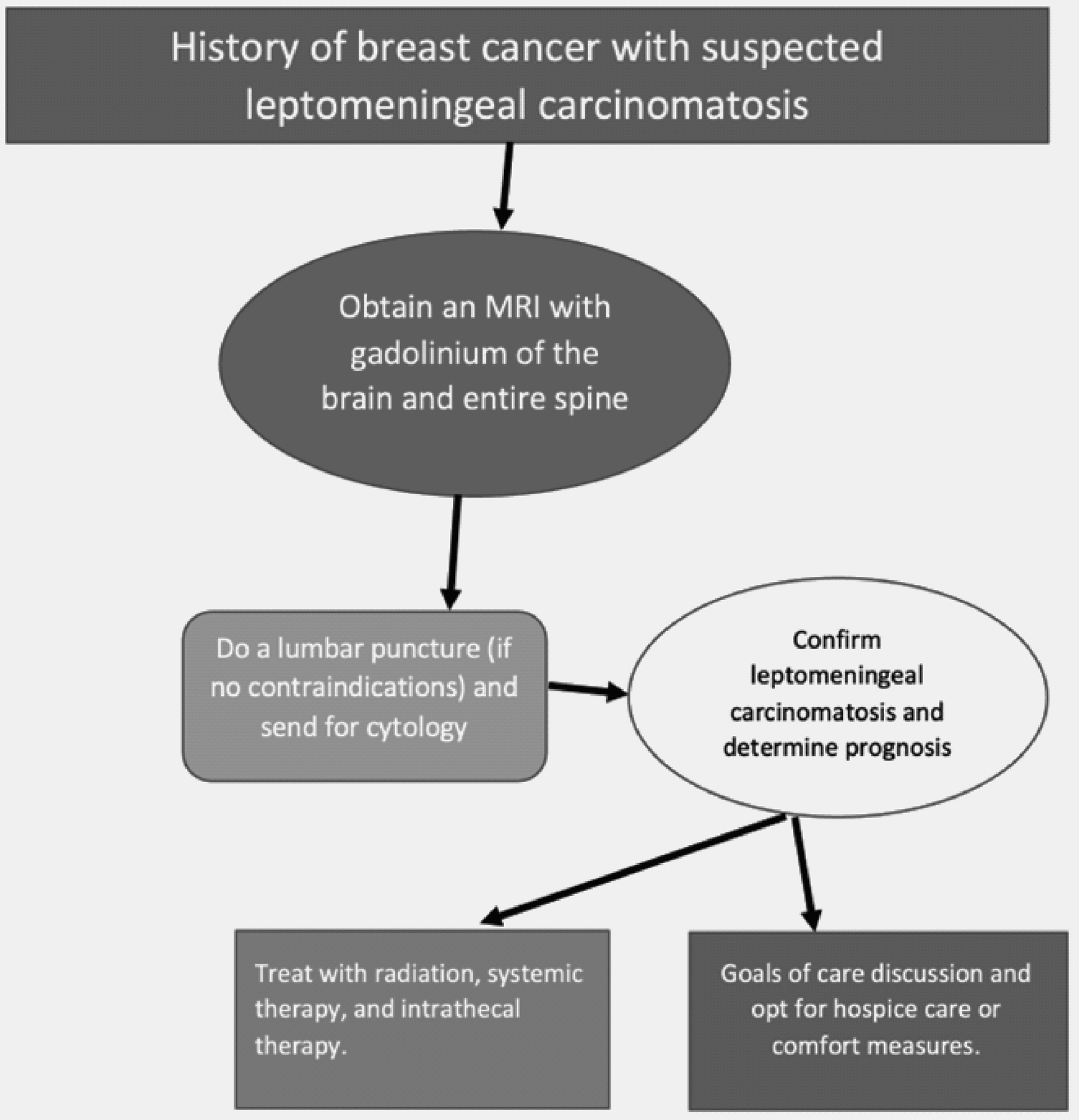
Figure 1. Pathology slides from a breast biopsy. (a) Micro calculi in a ductal pattern from left breast tissue. (b) Stromal sclerosis and infiltrating lobular cancer from left breast tissue. (c) Cells in a single file line, indicating lobular carcinoma from left breast tissue.
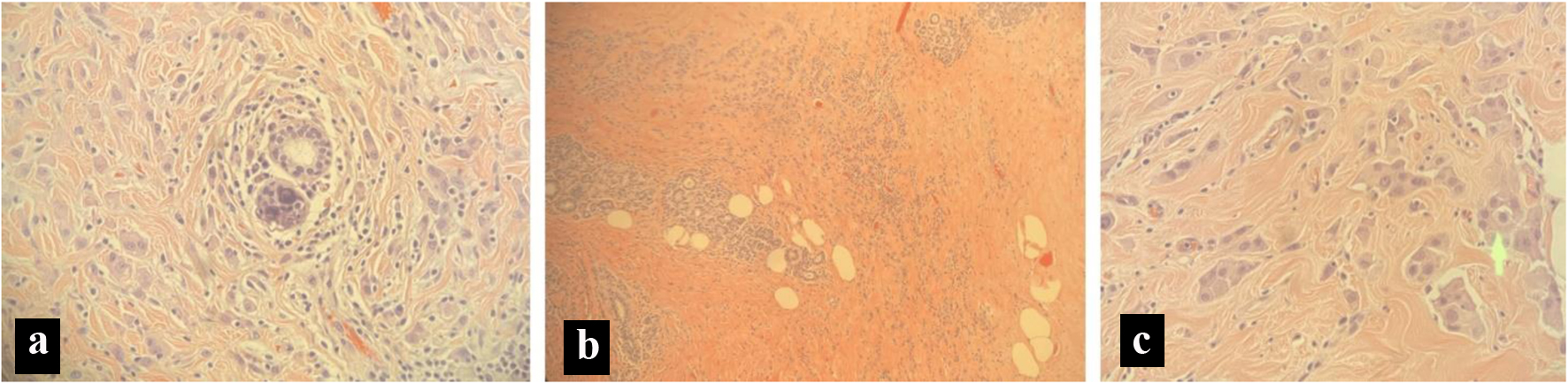
Figure 2. T1-weighted MRI image of the brain. Mild to moderate hydrocephalus (white arrow). T2 hyperintensity consistent with transependymal spread of CSF (red arrow). There is no evidence of mass. There is no abnormal gadolinium enhancement. CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.
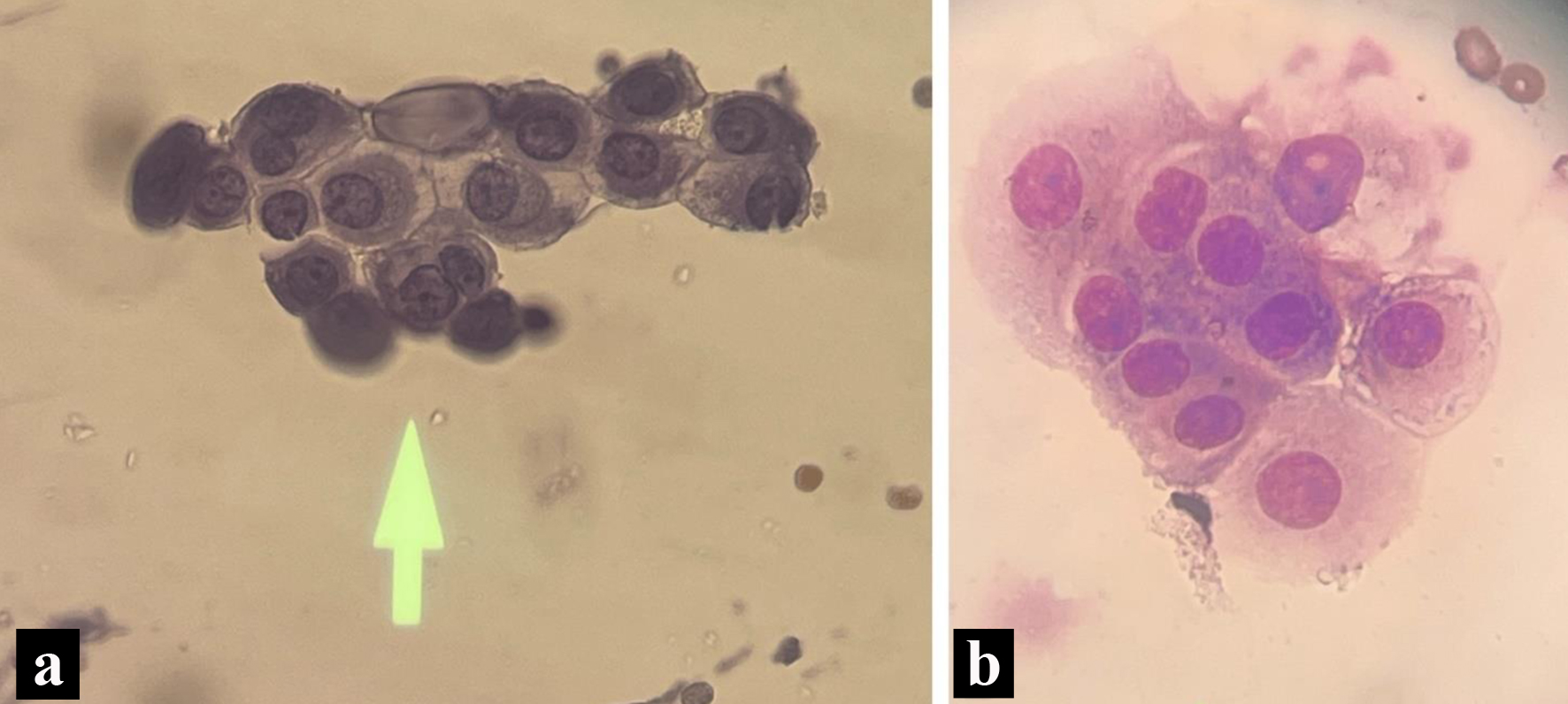
Figure 3. Pathology slides form the cerebrospinal fluid. (a) Enlarged nucleoli with cytoplasmic vacuoles on cerebrospinal fluid cytology (May Grunwald-Giemsa stain). (b) Wright stain indicating a nest of tumors with increased cytoplasm, non-spindled from cerebrospinal fluid cytology.