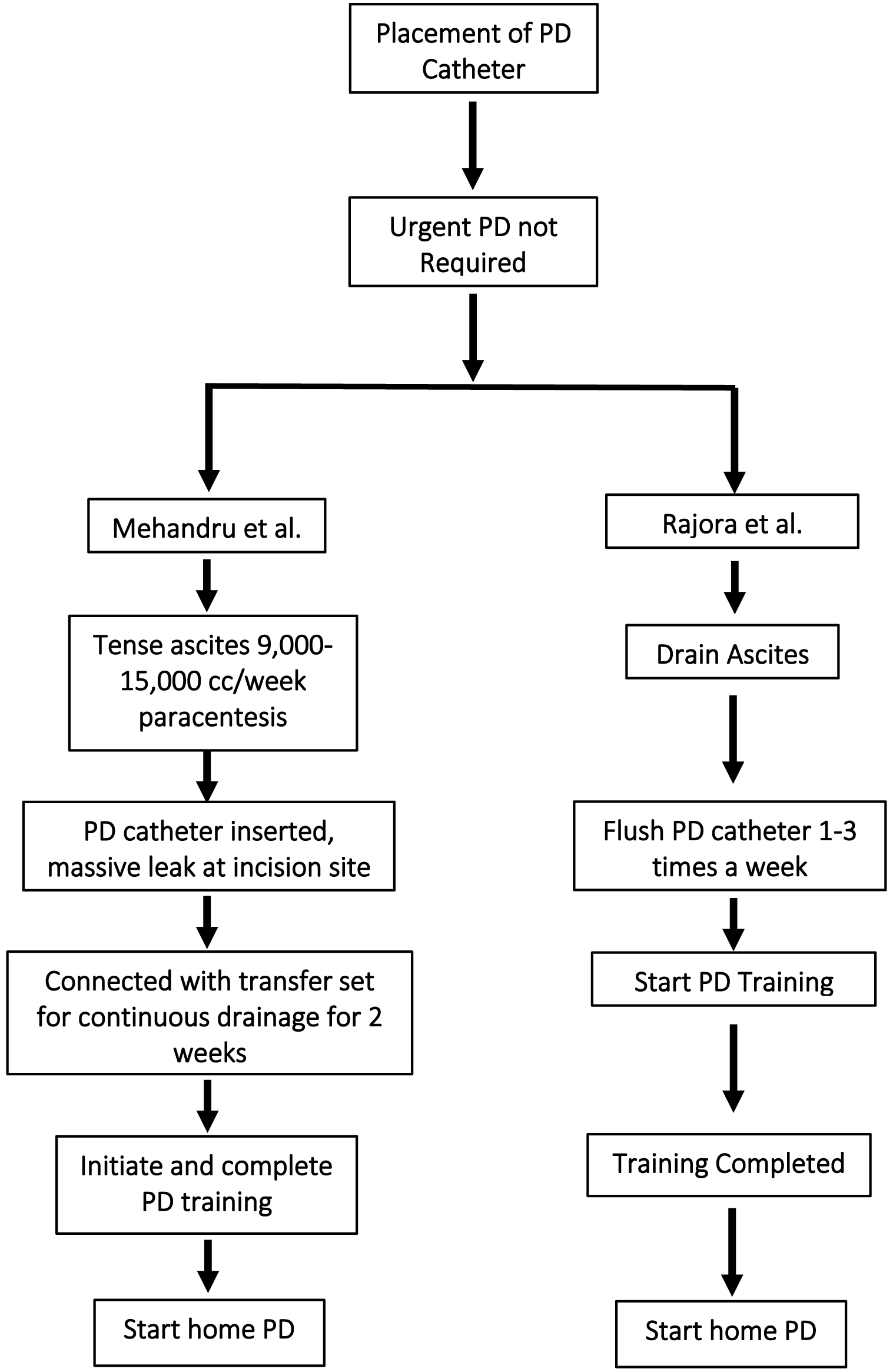
Figure 1. Comparison between Mehandru et al (this study) and Rajora et al study.
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 15, Number 10, October 2024, pages 287-296
Role of Continuous Drainage of Tense Ascites in Peritoneal Dialysis: Mehandru/Masud Technique
Figures


Tables
| Case | Age | Gender | Etiology of liver disease | Etiology of renal disease | Frequency of paracentesis/weekly volume | Systolic blood pressure on ICHD | Systolic blood pressure on PD 3 months after initiation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICHD: in-center hemodialysis; PD: peritoneal dialysis. | |||||||
| 1 | 35 | F | Alcoholic cirrhosis | Hepatic | 2 × weekly/13,000 - 15,000 cc | 80 - 120, symptomatic | 130 |
| 2 | 52 | M | Alcoholic cirrhosis | Diabetes mellitus | 2 × weekly/11,000 -13,000 cc | 90 - 116, symptomatic | 136 |
| 3 | 49 | F | Alcoholic cirrhosis | Hypertensive nephrosclerosis | 2 × weekly/9,000 - 14,000 cc | 93 - 109, symptomatic | 128 |
| Case | Other conditions | Overall conditions on HD | Overall conditions on PD 6 months after initiation | Ascites | Residual renal function, urine output/day | Kt/V on PD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial daily drainage/day | Drainage after 2 years on PD | ||||||
| ESRD: end-stage renal disease; HD: hemodialysis; PD: peritoneal dialysis. | |||||||
| 1 | Alcoholism, anemia, hypoalbuminemia | Wheelchair bound, hospice referral | Ambulatory, able to hold employment, weight gain of 40 lb | 2,050 cc | 350 cc/cycle, three cycles/day with icodextrin | 1,260 cc | 3.5 |
| 2 | Alcoholism, anemia, diabetes mellitus, hypoalbuminemia | Wheelchair bound | Ambulatory, resumed work, stable weight | 1,800 cc | 290 cc/cycle, three cycles/day with 1.5% dextrose | 1,105 cc | 2.9 |
| 3 | Alcoholism, anemia, hypertension, hypoalbuminemia | Wheelchair bound, palliative care consult | Ambulatory, resumed work, gained 15 lb weight | 1,250 cc | 210 cc/cycle, three cycles/day with icodextrin | 1,305 cc | 4.2 |
| Case | Sex (age) | Treatment timeline | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKD: chronic kidney disease; HD: hemodialysis; ICHD: in-center hemodialysis; PD: peritoneal dialysis. | ||||||
| 1 | Female (35 years) | (February 2020) • Admitted to hospital with progressive renal disease requiring dialysis. • HD was initiated. • Patient was hemodynamically unstable, paracentesis and hypoalbuminemia. • Switch to PD was recommended. | (March - April 2020) • Educated on PD and consented for PD. • Decision to initiate PD was made. | (April 2020) • PD catheter was inserted, and continuous drainage initiated. • Transfer set attached to inserted PD catheter helped in controlling leak of ascitic fluid and adequate healing at the site of PD catheter. | (May 2020) • PD training initiated. • Subsequently improvement in hemodynamics, serum albumin and overall health status was observed. | (June 2020) • Stable and independent life style on PD. |
| 2 | Male (52 years) | (June 2020) • Admitted to hospital with CKD (stage 5) and uremia, accompanied with weight loss, nausea, poor appetite and shortness of breath for several weeks. • Abdomen was distended with tense ascites. • Underwent paracentesis and started in ICHD, twice weekly. • Paracentesis to remove ascites fluid continued along with symptomatic hypertension on HD leading to normal saline infusions and worsening fluid overload. | (August 2020) • Counseled on PD modality and consented for PD. • PD catheter was inserted, and continuous drainage initiated. • Transfer set attached to PD catheter helped in controlling leak of ascitic fluid and adequate healing at the site of PD catheter. | (September 2020) • PD training initiated. • Continued successfully with PD modality with stable hemodynamics and overall improvement to health. | (October 2020) • Continued stable and independent lifestyle on PD. | |
| 3 | Female (49 years) | (September 2020) • Admitted to hospital with history of CKD, alcoholism, hypotension, and anemia presented with shortness of breath and abdominal distention. • Was on HD, 3 × weekly along with twice weekly paracentesis, 2 months prior to arrival at hospital. | (October 2020) • Was educated on PD modality. • PD catheter was inserted. • Transfer set attached to PD catheter helped in controlling leak of ascitic fluid and adequate healing at the site of PD catheter. | (November 2020) • Initiated on PD training. • Continued successfully with PD with stable hemodynamics and overall improvement to health. | (December 2020) • Continued stable and independent lifestyle on PD. | |
| Case | Complications after inserting PD catheter | Leaks after attachment of transfer set and drainage bag | Peritonitis for 2-year period | Paracentesis after PD training | Albumin infusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD: peritoneal dialysis. | |||||
| 1 | Leak (++++) | 0 | None | None | None |
| 2 | Leak (++++) | 0 | None | None | None |
| 3 | Leak (++++) | 0 | None | None | None |
| Case | Serum albumin | Albumin in ascitic fluid on PD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD: peritoneal dialysis. | ||||||||
| Before PD | 1 month on PD | 1 year on PD | 2 years on PD | 2 weeks on PD | 1 month on PD | 1 year on PD | 2 years on PD | |
| 1 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 21 g | 9.9 | 200 mg | < 100 mg/day |
| 2 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 23 g | 11.2 | 221 mg | < 100 mg/day |
| 3 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 19 g | 11.5 | 190 mg | < 100 mg/day |