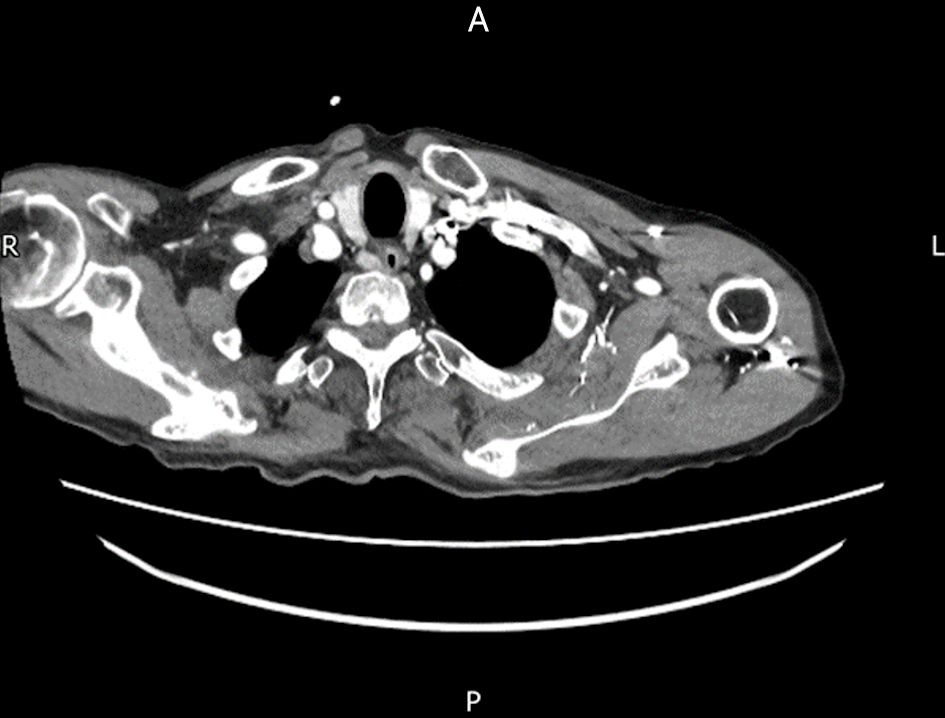
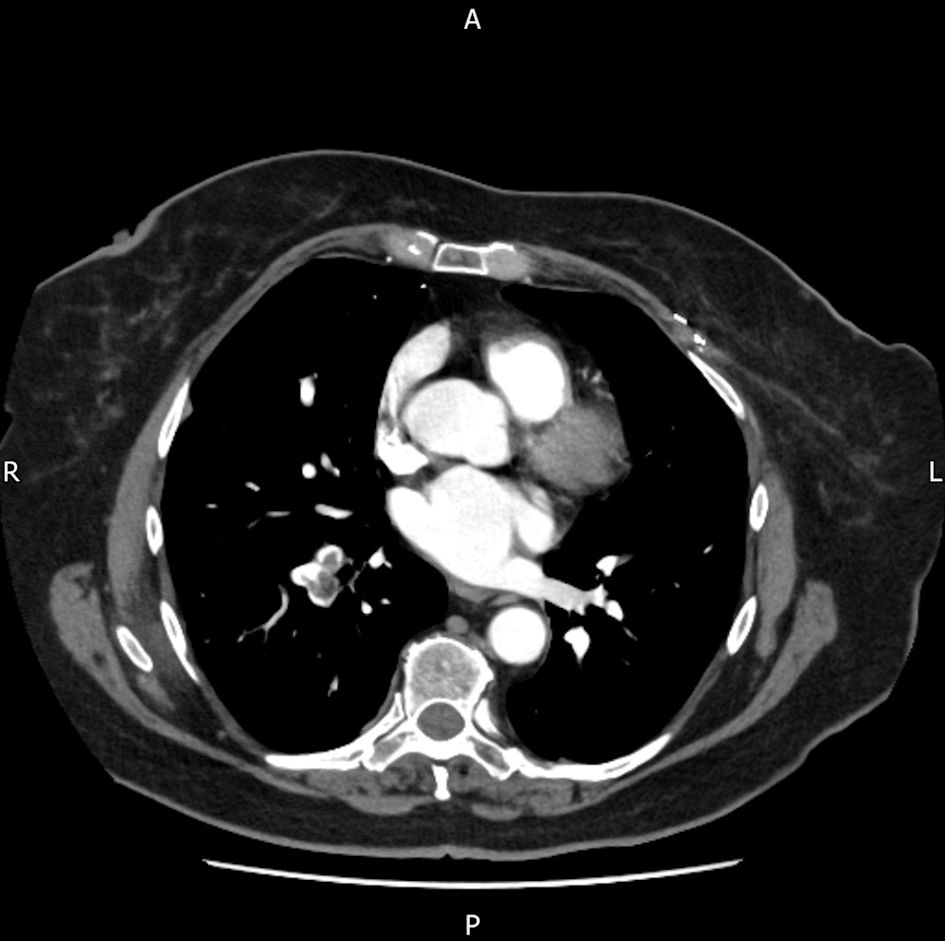
Figure 1. Axial view of computed tomography (CT) scan showing parathyroid nodule suspicious of adenoma.
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 15, Number 8, August 2024, pages 180-185
Primary Hyperparathyroidism and Pulmonary Embolism in Patients With a Fractured Neck of Femur
Figures

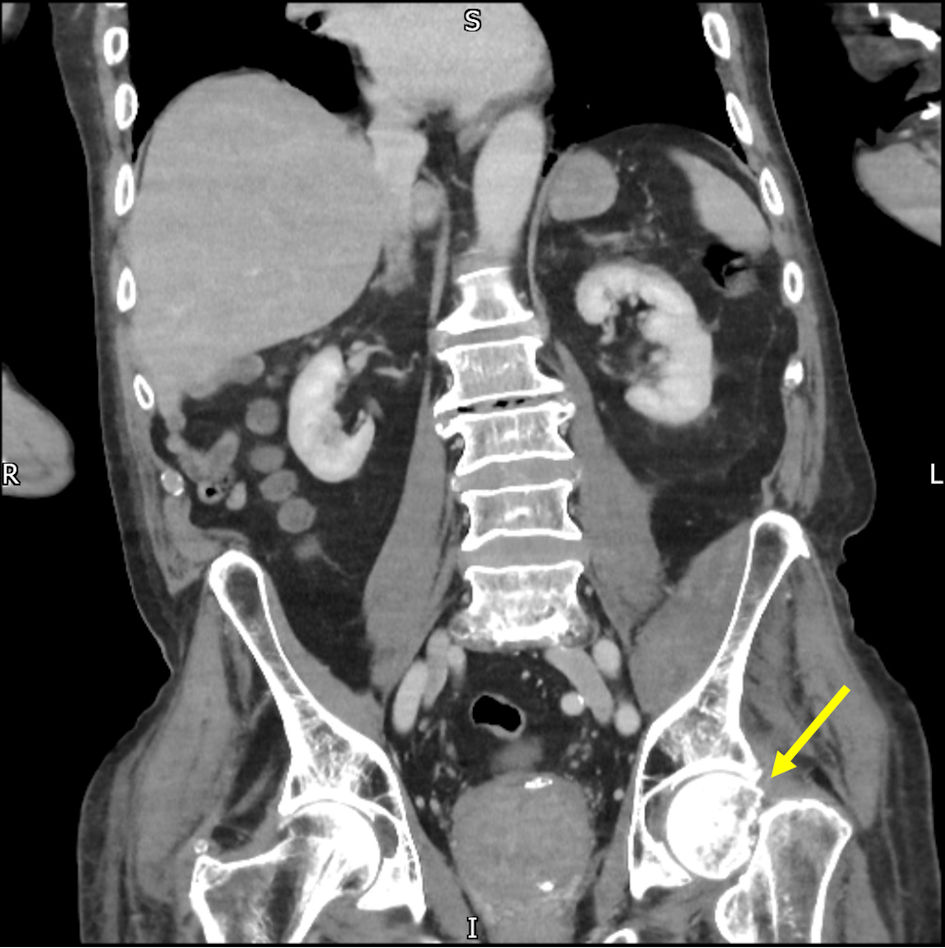
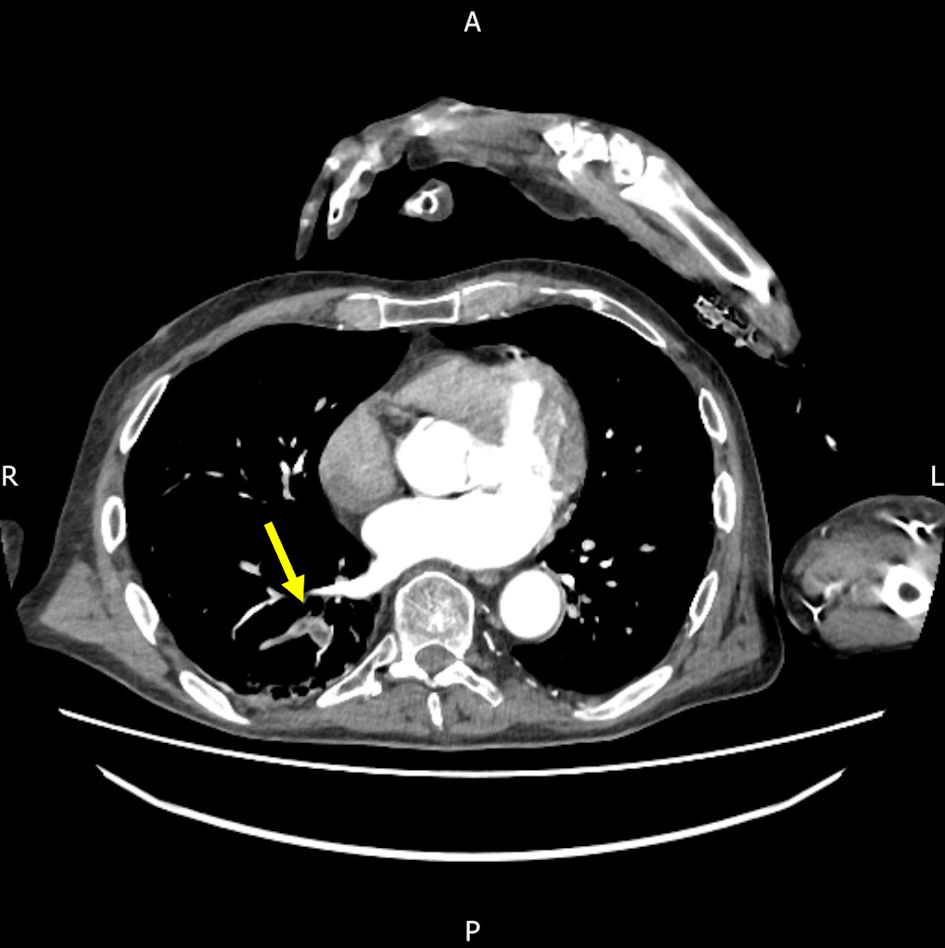
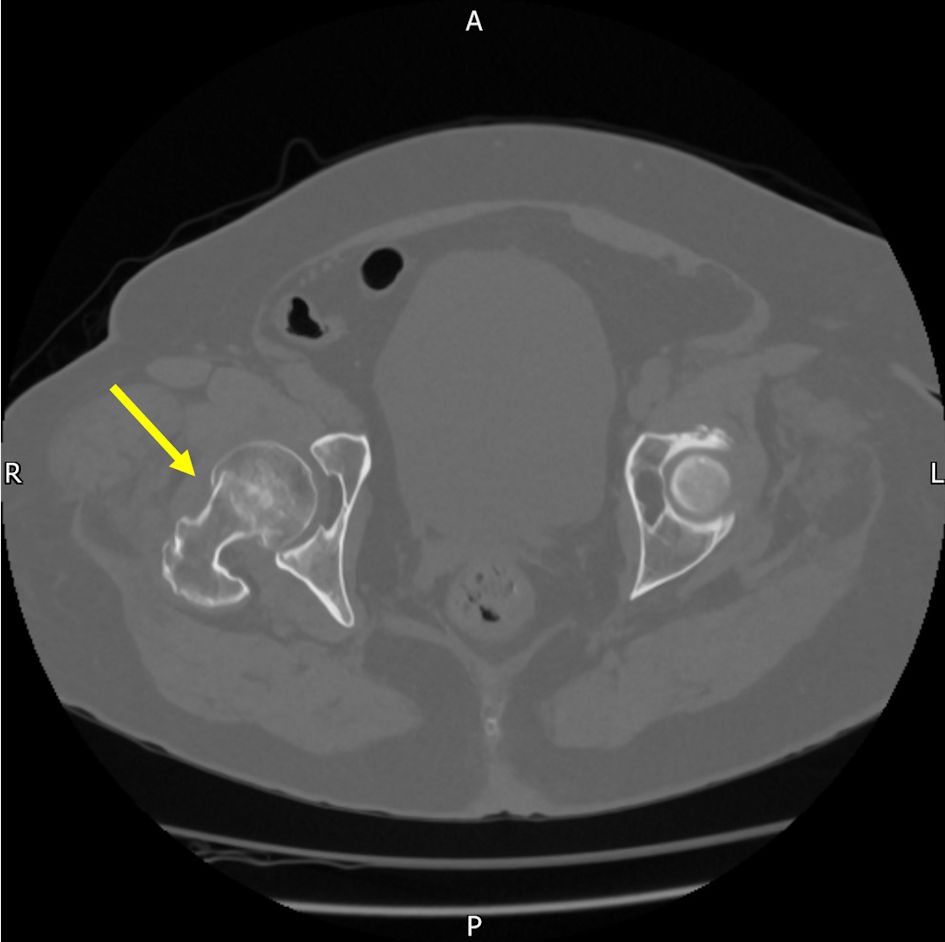
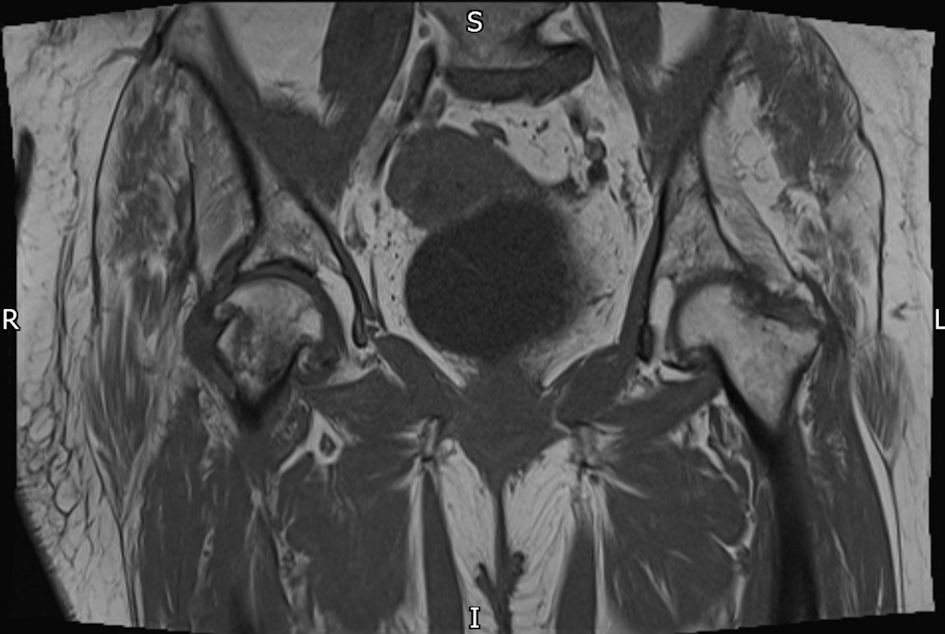
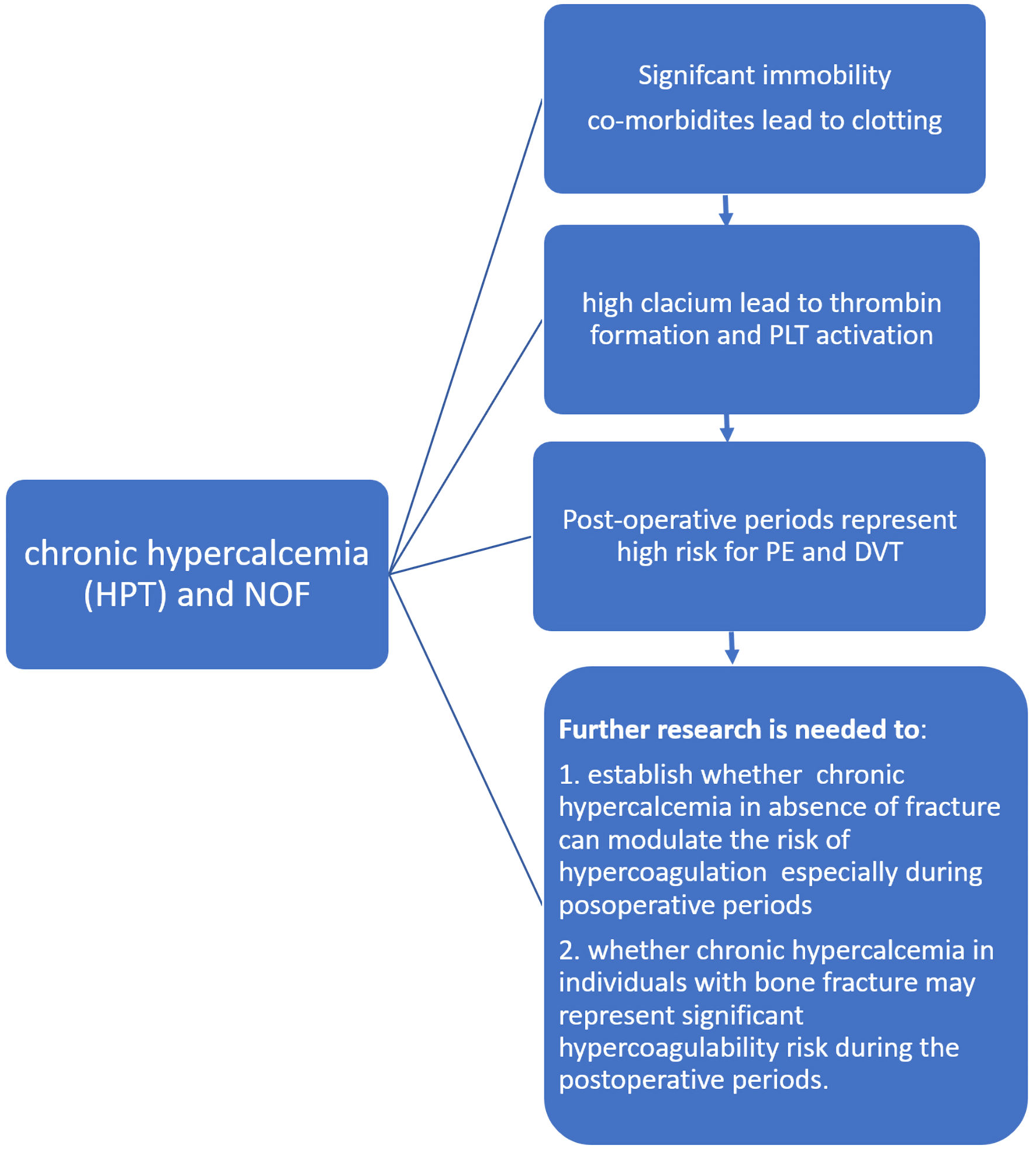
Table
| Parameter | Case 1 (82 years old) | Case 2 (77 years old) | Reference range |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTH: parathyroid hormone. | |||
| PTH | 15.2 | 9.2 | 1.6 - 6.9 pmol/L |
| Adjusted calcium | 2.9 | 3.05 | 2.1 - 2.6 mmol/L |
| Urine calcium/creatinine ratio | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.07 - 0.28 |
| Vitamin D | 50.3 | 55 | 50.0 - 150.0 nmol/L |