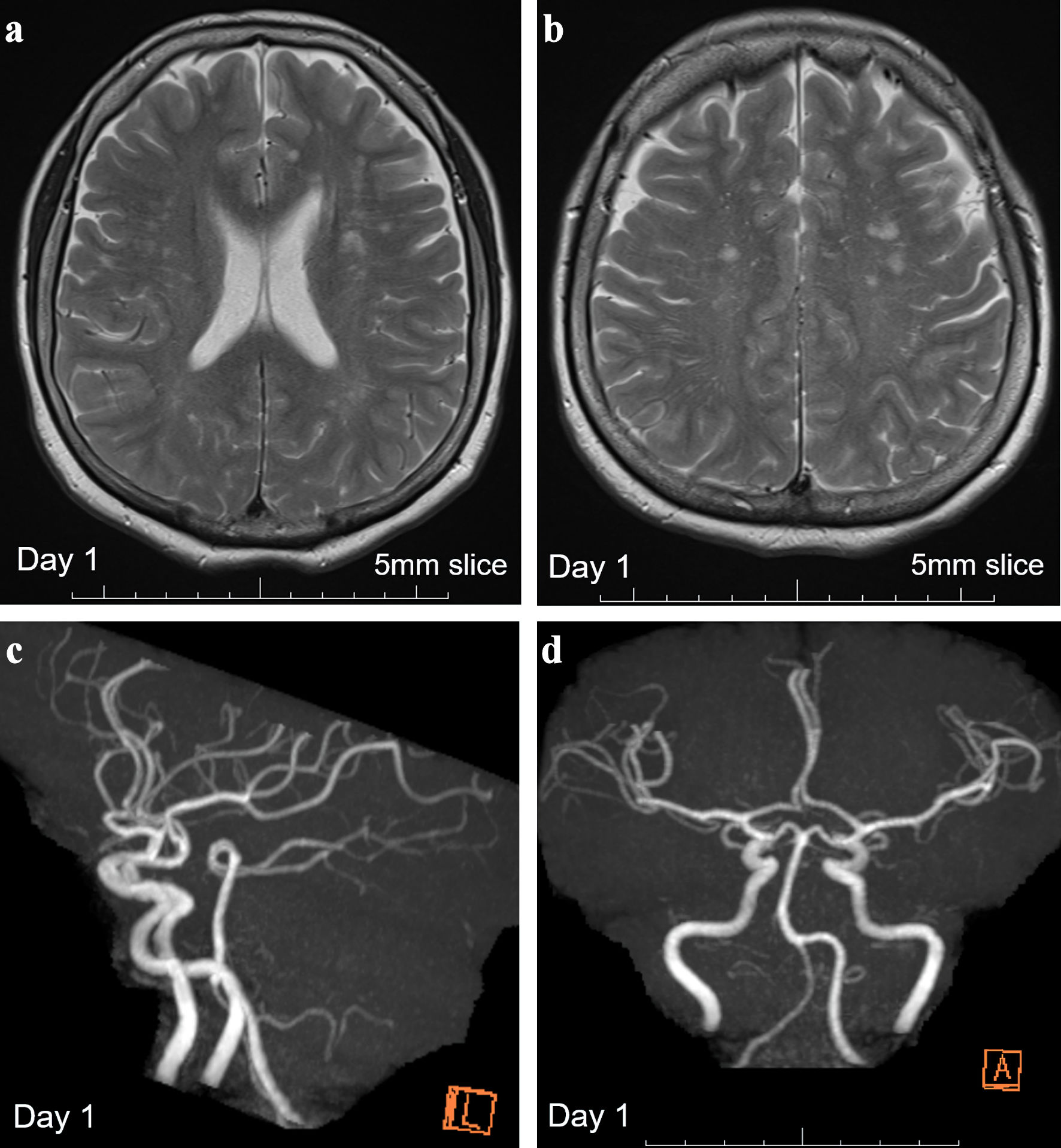
Figure 1. Brain MRI showing multiple old ischemic changes and MR angiography on day 1. (a, b) T2-weighted images with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 1 revealed multiple old ischemic changes in both hemispheres. (c, d) Normal MR angiography findings with a patent posterior circulation system. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; MR: magnetic resonance.
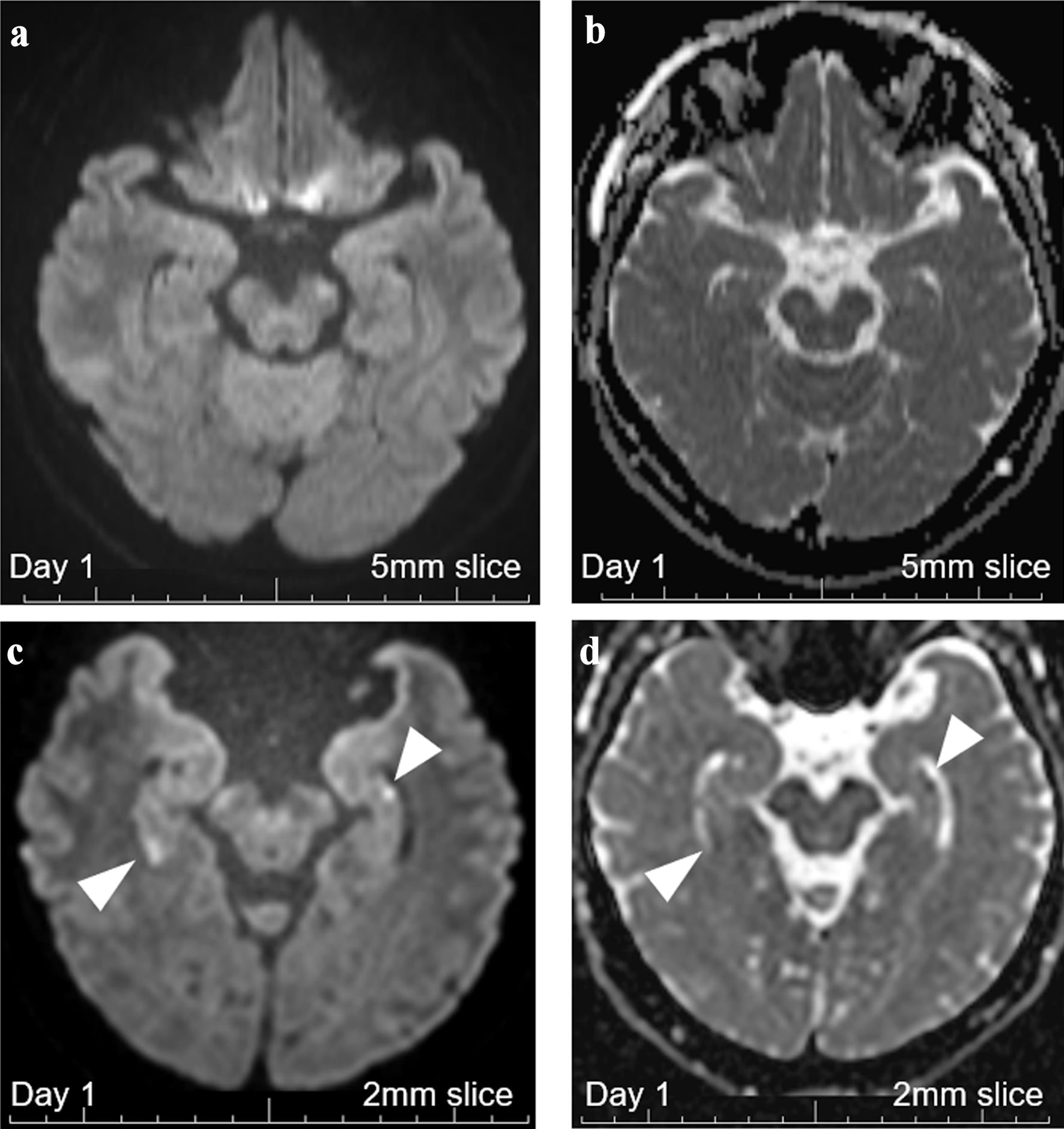
Figure 2. Brain MRI with 5-mm thickness and 2-mm thin-slice on day 1. (a) DWI with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 1 revealed no abnormalities. (b) ADC with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 1 revealed no abnormalities. (c) DWI with 2-mm thin-slice brain MRI on day 1 revealed two hippocampal signal high lesions each on both sides (white arrowheads). (d) ADC with 2-mm thin-slice brain MRI on day 1 revealed signal losses for the two DWI-high hippocampal lesions (white arrowheads). MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; ADC: apparent diffusion coefficient; DWI: diffusion-weighted imaging.
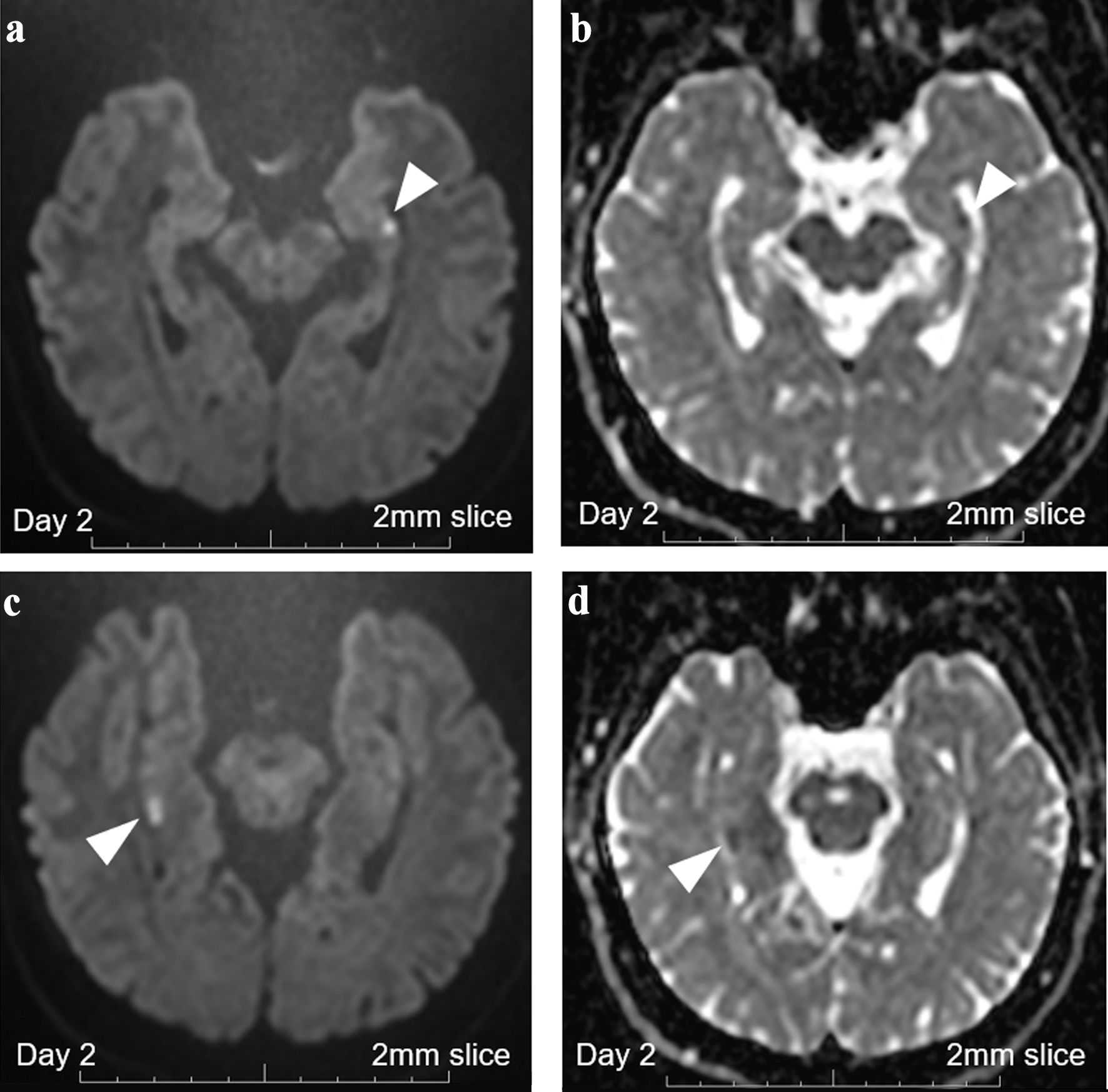
Figure 3. Brain MRI with 2-mm thin-slice on day 2. (a) DWI with 2-mm thin-slice brain MRI on day 2 revealed persistent punctate hyperintense DWI signals in the left hippocampus (white arrowhead). (b) ADC with 2-mm thin-slice brain MRI on day 2 revealed persistent punctate signal loss in the left hippocampus (white arrowhead). (c) DWI with 2-mm thin-slice brain MRI on day 2 revealed persistent high signals in the right hippocampus (white arrowhead). (d) ADC with 2-mm thin-slice brain MRI on day 2 revealed persistent signal loss in the right hippocampus (white arrowhead). MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; ADC: apparent diffusion coefficient; DWI: diffusion-weighted imaging.
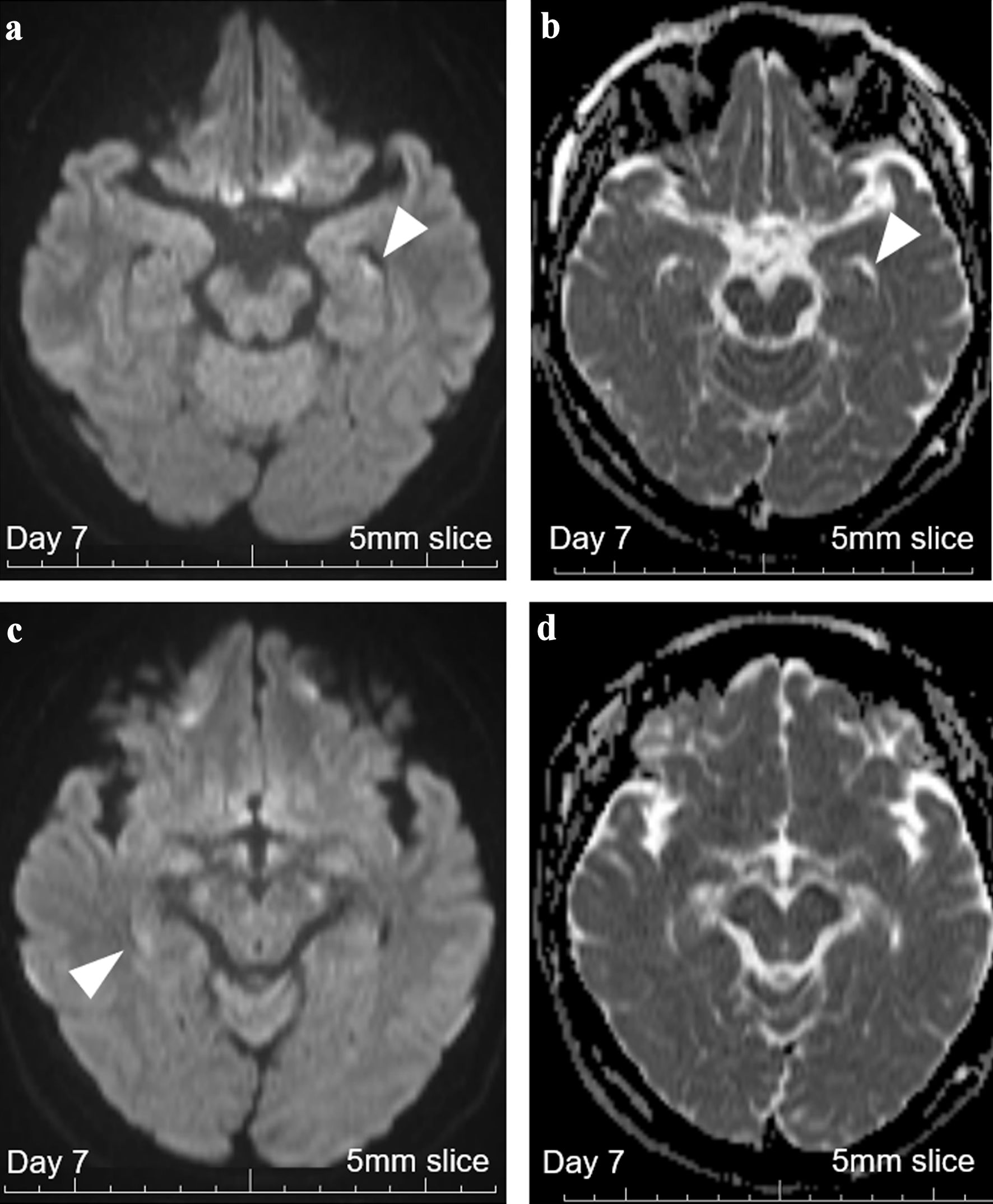
Figure 4. Brain MRI with 5-mm thickness on day 7. (a) DWI with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 7 revealed persistent high signals in the left hippocampus (white arrowhead), increasing the probability of hippocampal infarction. (b) ADC with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 7 revealed persistent signal loss in the left hippocampus (white arrowhead). (c) DWI with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 7 revealed persistent vague high signals in the right hippocampus (white arrowhead). (d) ADC with 5-mm-thick brain MRI on day 7 revealed no apparent signal loss, suggesting that cellular damages were milder on this side. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; ADC: apparent diffusion coefficient; DWI: diffusion-weighted imaging.



