Figures
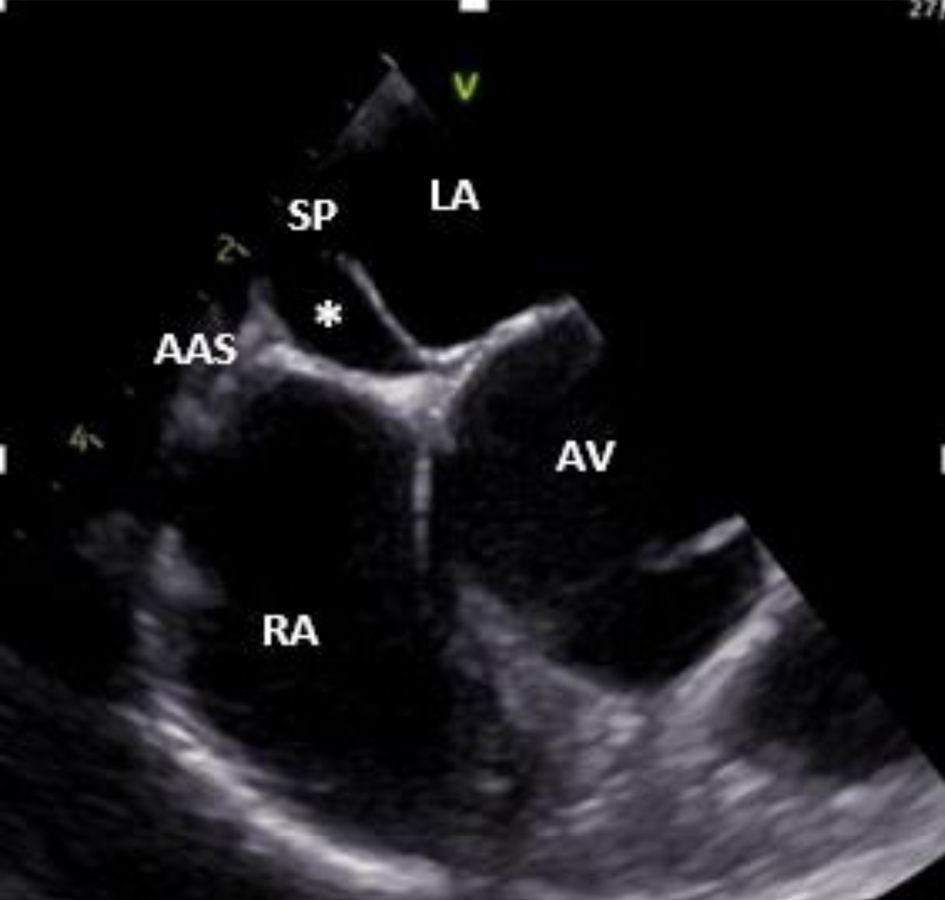
Figure 1. Two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiogram (mid-esophageal short axis view at the level of AV) showing a double interatrial septum with an aneurysmal interatrial SP and an AAS with an echo-free interatrial chamber (asterisk) between them. AAS: accessory atrial septum; AV: aortic valve; LA: left atrium; RA: right atrium; SP: septum primum.
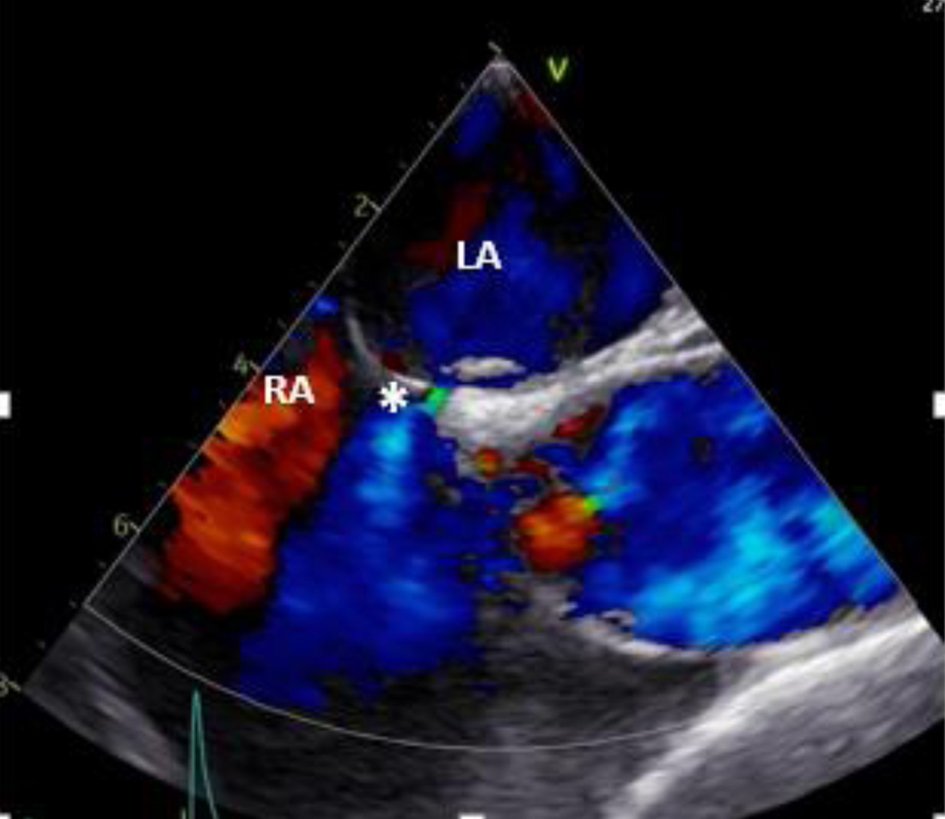
Figure 2. Two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiogram (mid-esophageal) in color Doppler showing flow from LA to the RA through a small-sized ASD (asterisk). ASD: atrial septa defect; LA: left atrium; RA: right atrium.
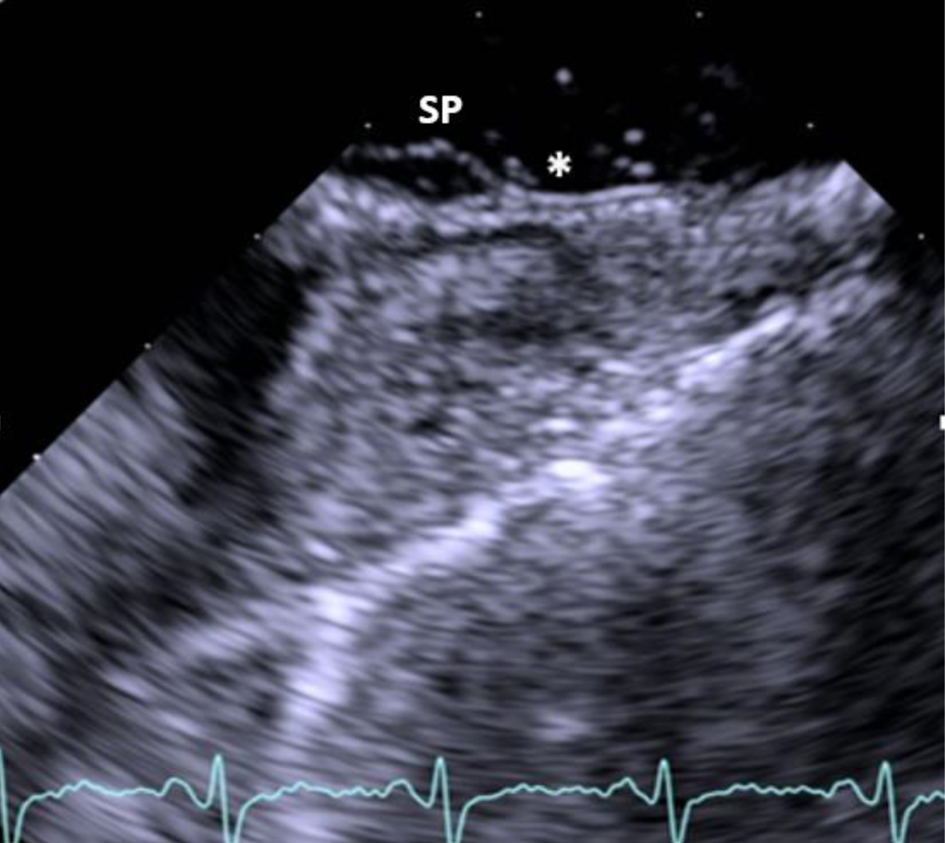
Figure 3. Two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiogram showing the aneurysmal SP and the presence of patent foramen ovale with right to left shunt (asterisk) after injection of agitated saline contrast during Valsalva. SP: septum primum.
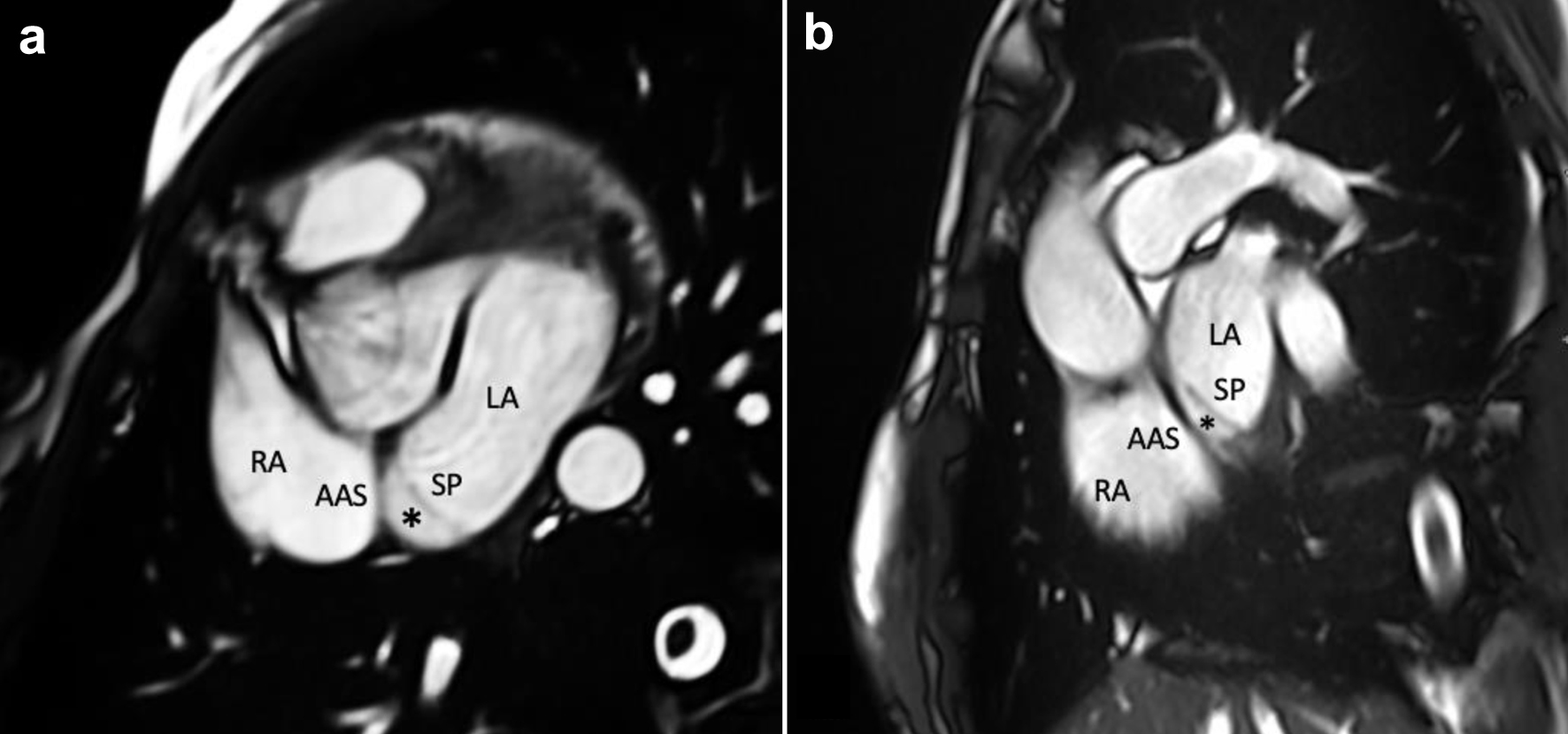
Figure 4. CMR imaging showing an aneurysmatic, mobile interatrial SP, an AAS and an interatrial chamber (asterisk) between them. (a) Trans-axial cine stack using bSSFP sequences. (b) Trans-axial oblique sagittal atrial cine stack using bSSFP sequences. AAS: accessory atrial septum; bSSFP: balanced steady-state free precession; CMR: cardiovascular magnetic resonance; LA: left atrium; RA: right atrium; SP: septum primum.
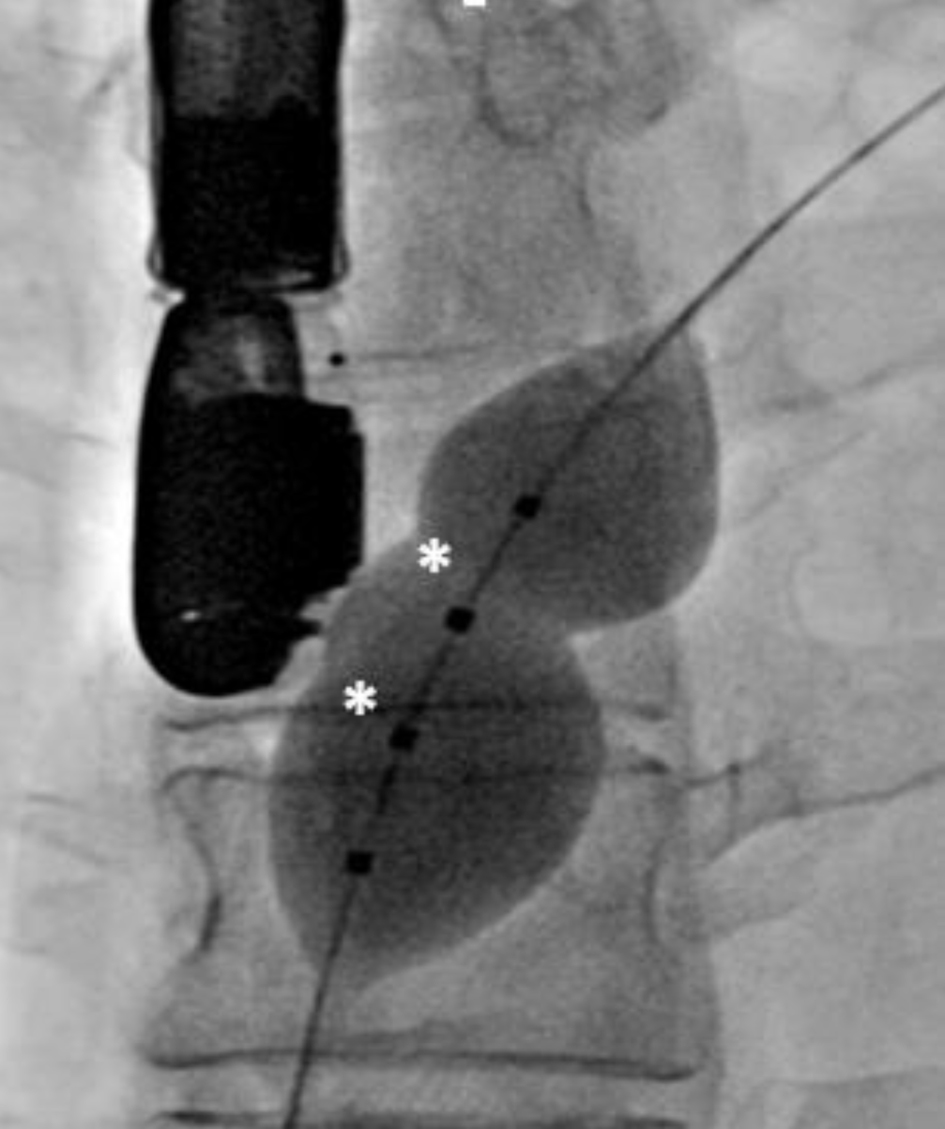
Figure 5. Figure 5. Fluoroscopy shows a dilated 25 mm Occlutech balloon placed through patent foramen ovale with the identification of two balloon waists (asterisks).
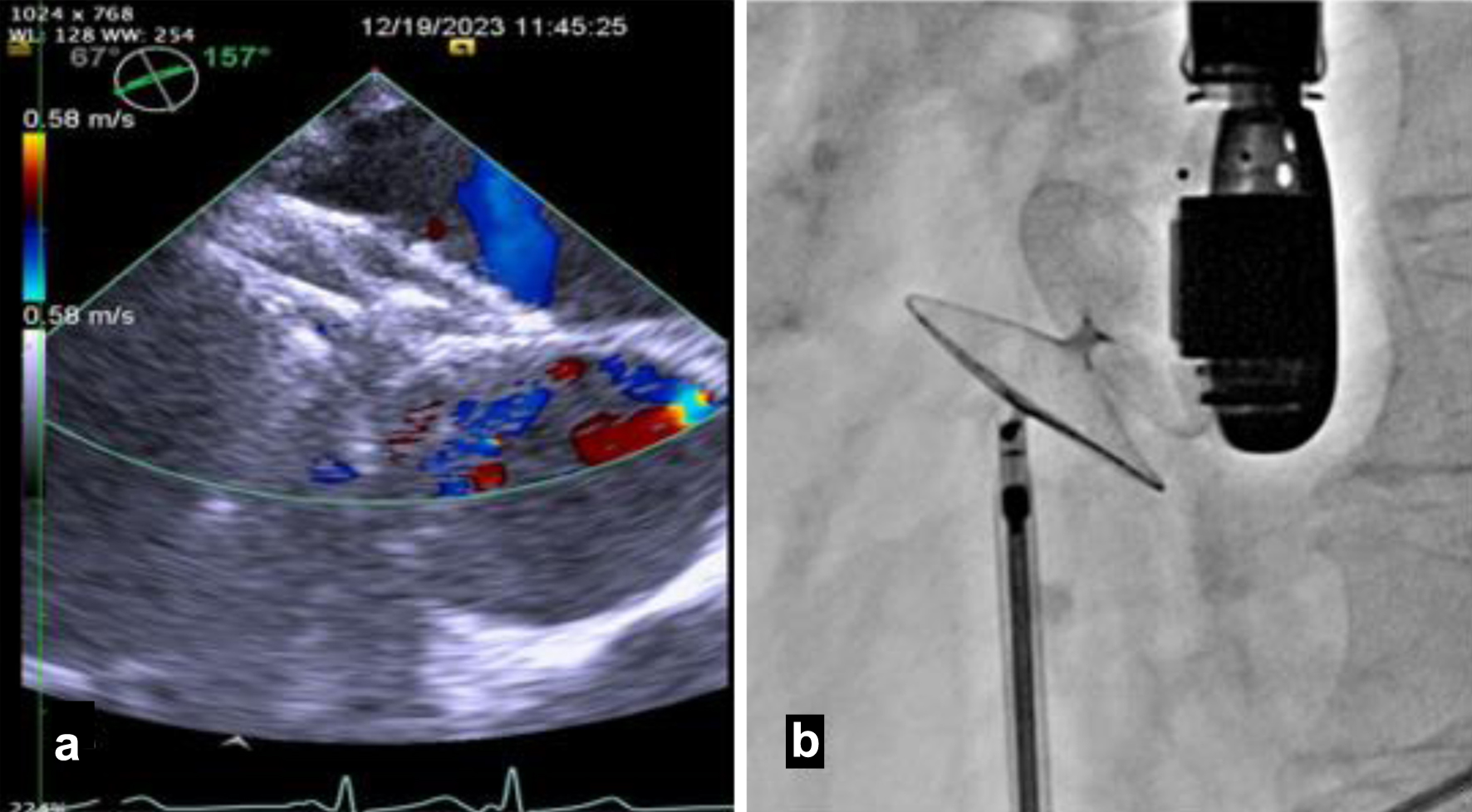
Figure 6. The 30 mm Occlutech Figulla Flex II PFO device was inserted, with the left atrial and right atrial disks appropriately positioned and visualized on transesophageal echocardiogram (a) and fluoroscopy (b). PFO: patent foramen ovale.
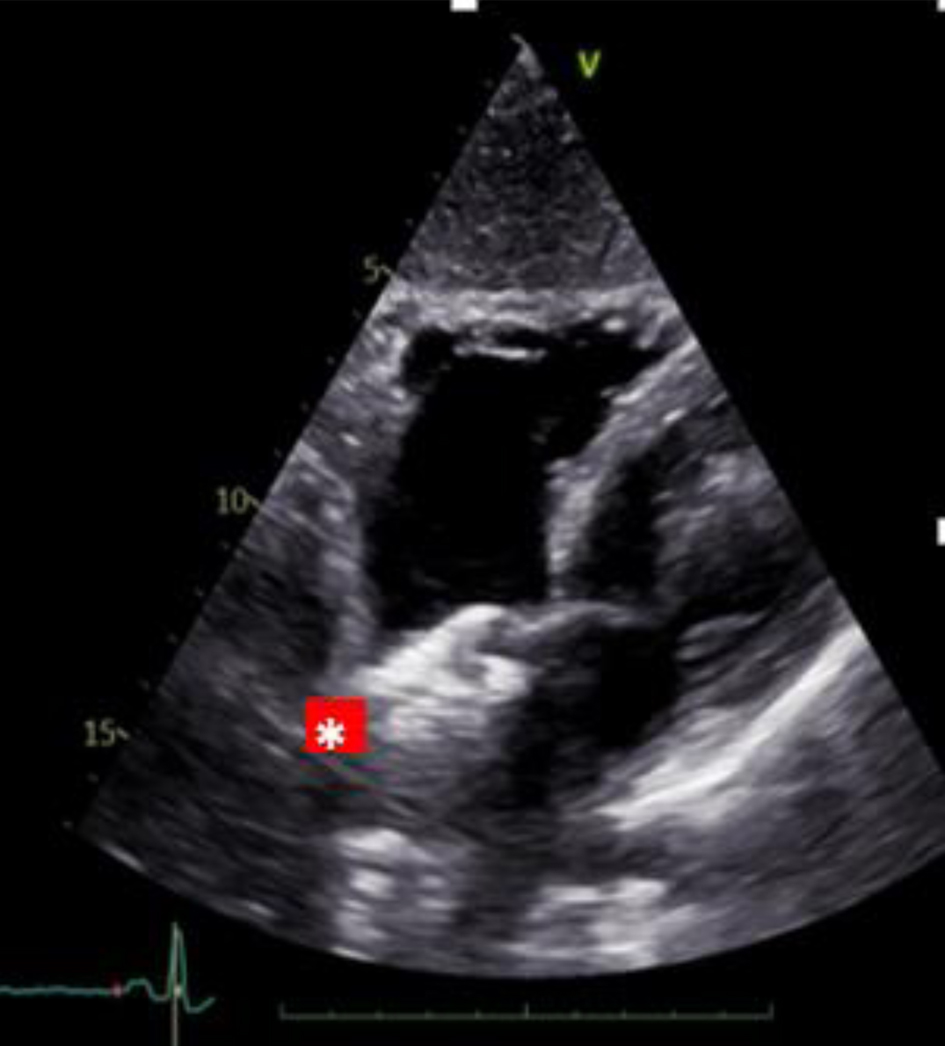
Figure 7. Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiogram (subxiphoid view) shows a well-seated patent foramen ovale closure device (red asterisk).






