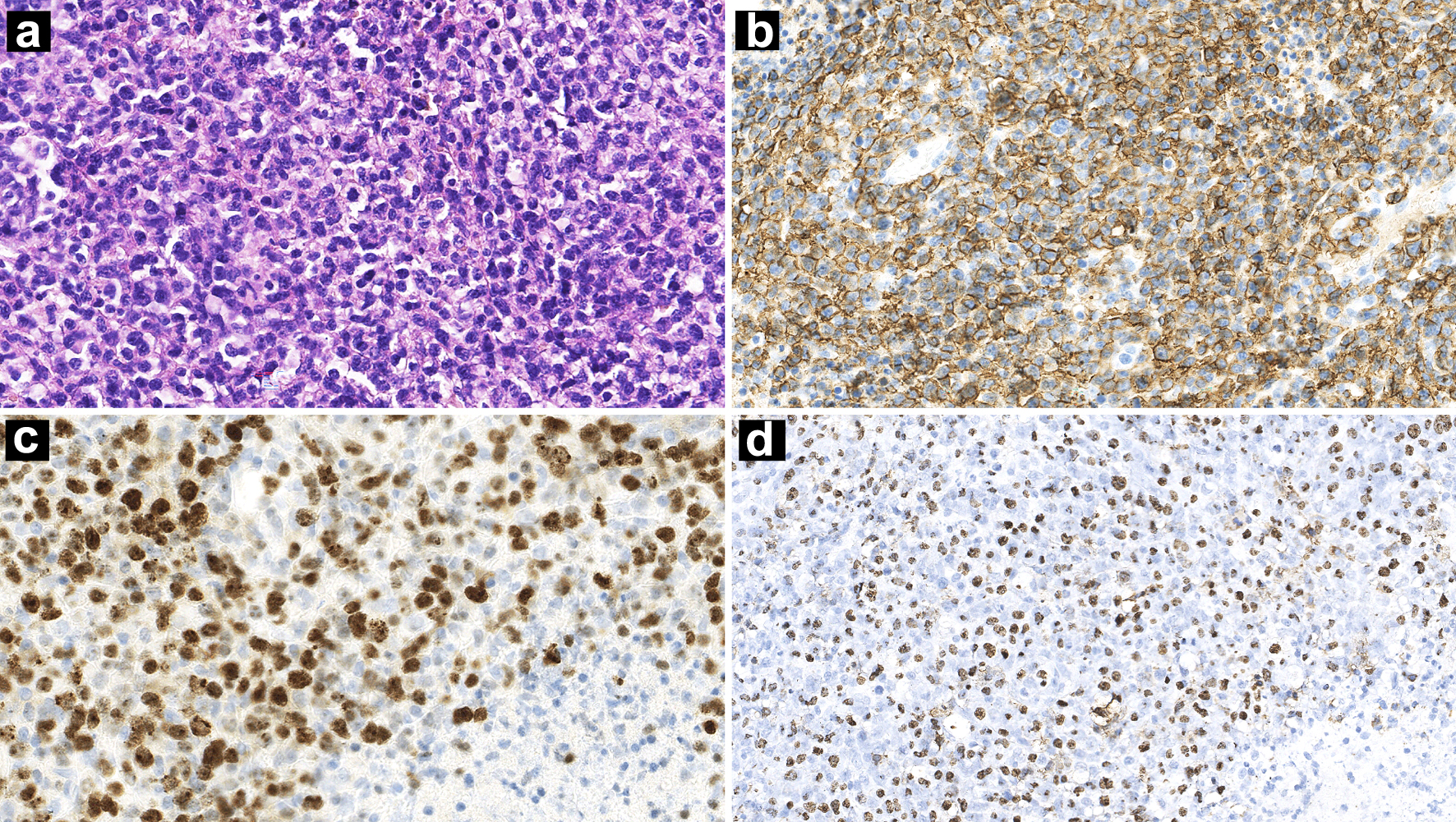
Figure 1. Nasopharynx biopsy showing diffuse infiltration of atypical lymphoid cells (a: H&E, × 100 magnification). IHC stains showing CD20 positivity (b: × 100 magnification) and a high Ki-67 index (c: × 100 magnification). ISH for EBERs was positive (d: × 100 magnification). H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; IHC: immunohistochemistry; ISH: in situ hybridization; EBER: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA.