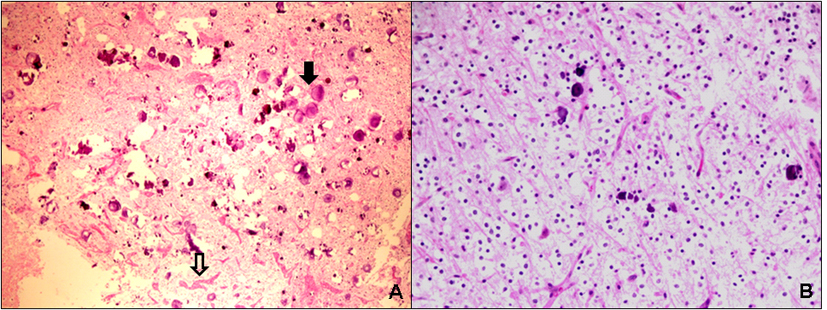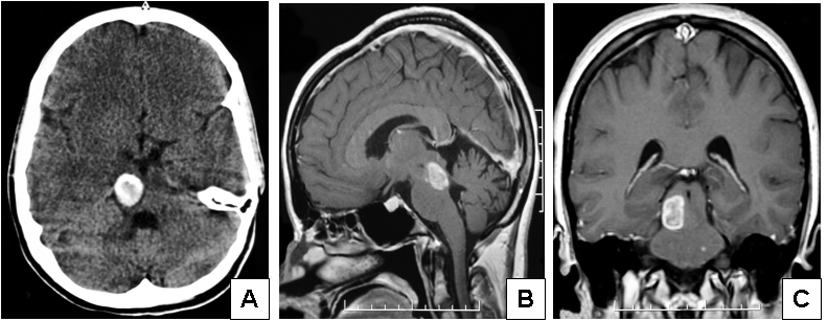
Figure 1. Imaging features of the case of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor presenting in the pontomesencephalic area. (A) Contrast enhanced CT scan showed a large, well-demarcated, subcortical hyperdense lesion in the right mesencephalon with extension into the tegmentum pontis. (B, lateral) and (C, coronal) MRI examination revealed a pontomesencephalic pseudocystic lesion that was hyperintense on T1 weighted images and showed less enhancement on T2 weighted images extending within the brain stem and reaching the red nucleus, the superior colliculi and the superior cerebellar tract.