| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 5, Number 6, June 2014, pages 362-365
Mixed Epithelial and Stromal Tumor of the Kidney: A Rare Case Report
Seyma Ozkanlia, c, Pinar Engin Zerka, Ebru Zemheria, Meftun Culpanb, Tulay Zenginkineta, Abdullah Aydina
aDepartment of Pathology, Istanbul Medeniyet University, Goztepe Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey
bDepartment of Urology, Istanbul Medeniyet University, Goztepe Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey
cCorresponding Author: Seyma Ozkanli, Tutuncu Mehmet Efendi Cad. Karanfil Sok. Ugur Apt. No: 16/3 Goztepe-Istanbul, Turkey
Manuscript accepted for publication May 6, 2014
Short title: Mixed Epithelial and Stromal Tumor
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc1797w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney (MESTK) is a rare kidney tumor that is composed of both epithelial and mesenchymal components with solid and cystic architecture. Up to the present, approximately 100 cases have been reported. It was introduced in the World Health Organization 2004 renal tumor classification. Here, we report a 49-year-old female with mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (MEST) in her kidney with no cystic components and no history of hormone use.
Keywords: Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor; Kidney; MESTK; Renal; Tumor
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney (MESTK) is a rare kidney tumor composed of both epithelial and mesenchymal components with solid and cystic architecture [1]. To date, approximately 100 cases have been reported [2]. It was introduced in the World Health Organization 2004 renal tumor classification [1]. Here, we report a 49-year-old female with MESTK with no cystic components and no history of hormone use.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 49-year-old female with a flank pain on left side for 1 year was referred to our urology clinic. She had hypertension and had an operation in the ophthalmology before. There was a history of colon cancer in her mother and renal tumor in her aunt which she did not know the exact diagnosis. On physical examination there was pain and tenderness on left lumbar region. All other findings were normal, and there was no organomegaly. On laboratory tests there was slight leukocytosis with neutrophilic predominance, WBC count was: 12.1 × 103/mL (N: 4.0 - 10.0), Neu% 87.7 (N: 42 - 75.2). RBC and Hb were within normal limits. There was only a slight microcytic anemia, Hct: 36.0 (N: 37-47%), MCV: 75.1 (N: 80 - 100). Platelet count was normal. Urea was within normal limits, but creatinine was slightly higher than normal (1.07 mg/dL, N: 0.5 - 0.9). Electrolytes were also normal. On ultrasonographic examination size and localization of right kidney was normal. No stone or mass was detected. On left kidney, a lobulated solid mass of 26 × 44 mm which was located on the middle zone, extending from renal parenchyma to renal sinus was detected. On MRI size and localization of both kidneys were normal. On coronal plane, on the contrasted, fat-saturated T1 images, 26 × 44 mm lobule contoured mass was seen (Fig. 1). Mass was thought to be either a transitional cell carcinoma or an oncocytoma radiologically. She underwent a surgery. During surgery there was no gross pathology in ureters and urinary bladder. Simple nephrectomy was done.
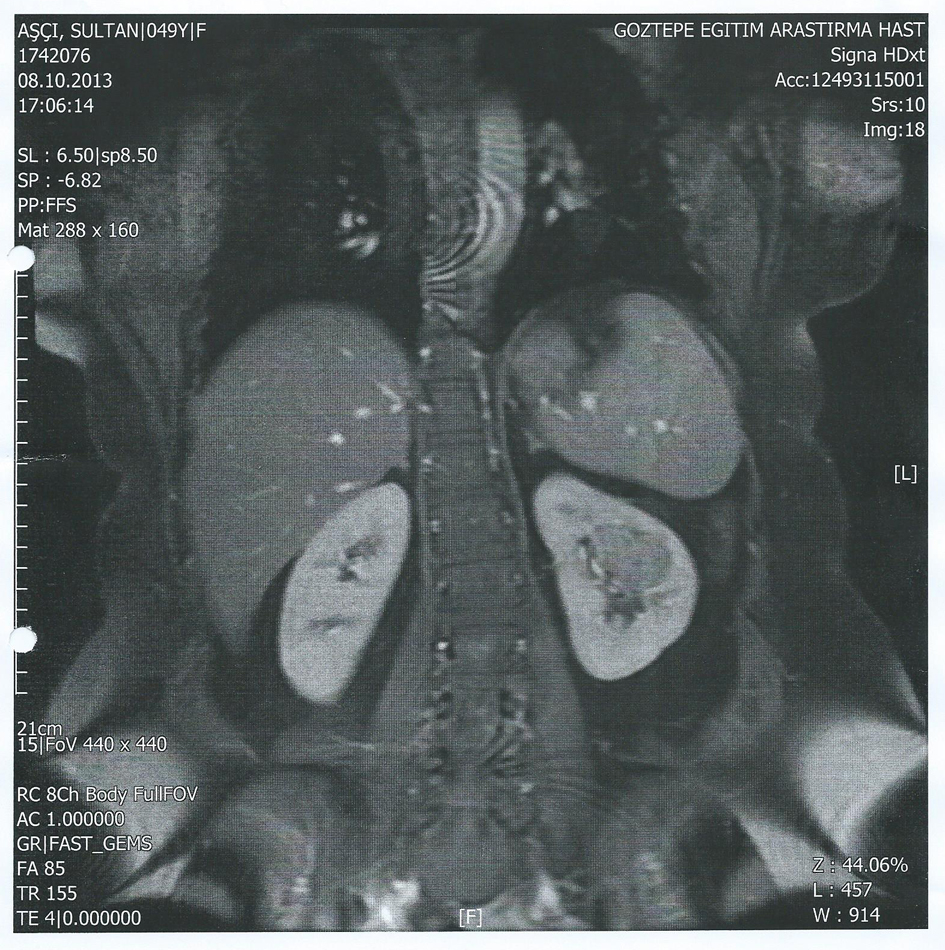 Click for large image | Figure 1. On coronal plane, on the contrasted, fat-saturated T1 images, 26 × 44 mm lobule contoured mass was seen. |
On gross examination, nephrectomy material measured 13 × 6 × 5 cm. On cut surface 3.5 × 3.3 × 3 cm of white-tan colored, well defined, solitary solid mass was seen in the middle zone of kidney adjacent to pelvis. Renal parenchymal invasion was not seen grossly. The mass was composed of only solid areas, and no cystic areas were seen (Fig. 2).
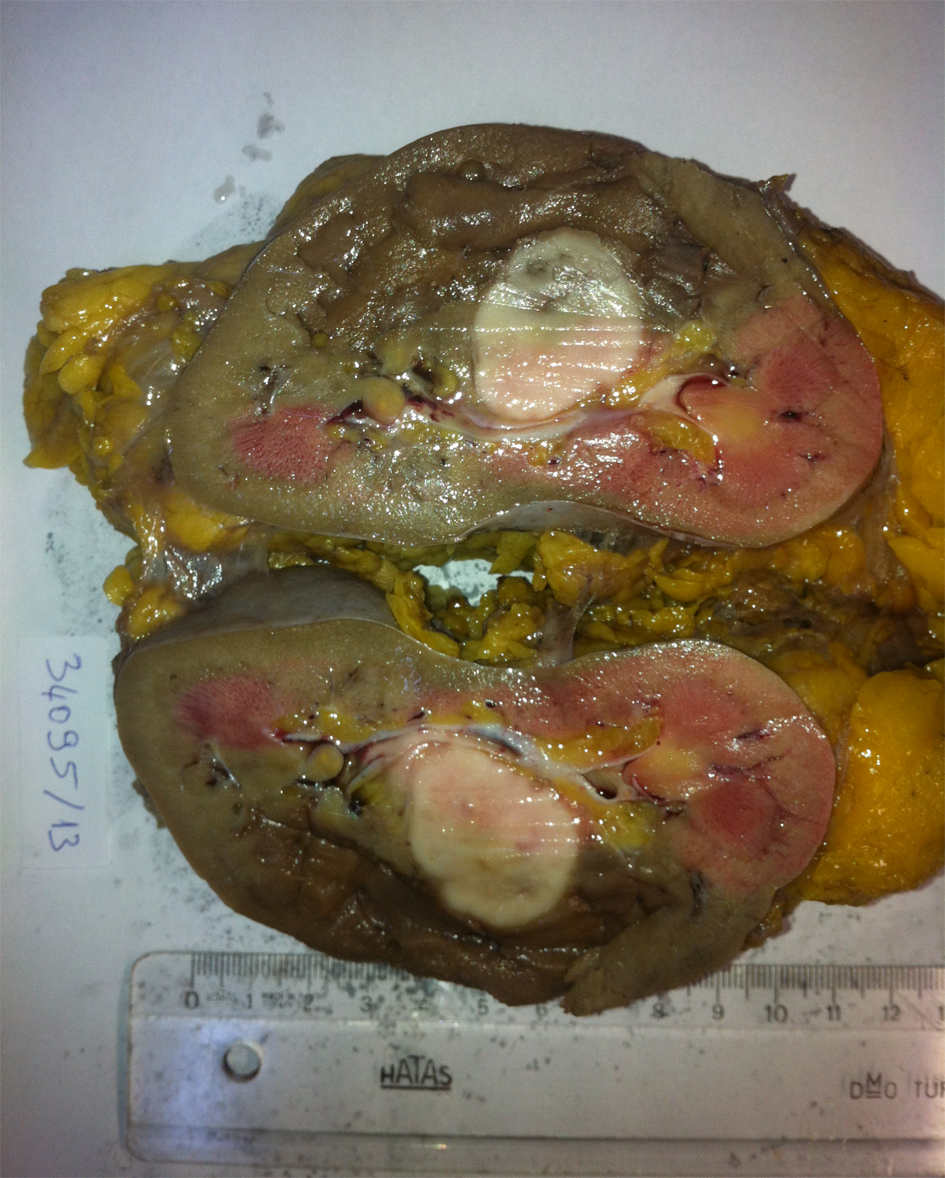 Click for large image | Figure 2. On cut surface 3.5 × 3.3 × 3 cm of white-tan colored, well defined, solitary solid mass was seen in the middle zone of kidney adjacent to pelvis. |
On microscopic examination a spindle cell proliferation was seen. Spindle cell component was arranged in short fascicules and bundles, but there were also areas that were looking like ovarian stroma. Epithelial component was composed of small number of normal appearing tubules with round lumina which scattered throughout the spindle cell component. The spindle cell component was dominant, and only few tubules were seen (Fig. 3). No mitoses or abnormal mitoses were seen in both components. A panel of immunohistochemistry was done: SMA was diffuse positive in the spindle cell component (Fig. 4), and EMA and CK were positive in epithelial component. HMB-45, desmin and S-100 were negative in both components. Progesterone receptor was only focally positive in the spindle cell component (Fig. 5). Both components were also negative for estrogen receptor. Together with these results and morphological pattern of tumor, patient was diagnosed as MESTK.
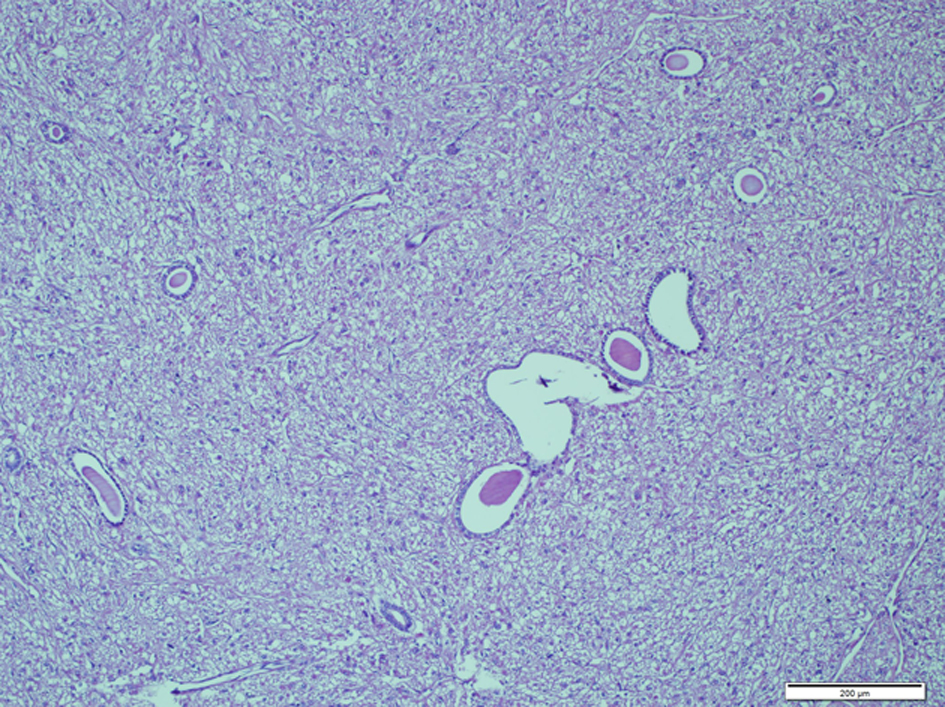 Click for large image | Figure 3. Small number of normal appearing tubules with round lumina which scattered throughout the spindle cell component (H&E × 100). |
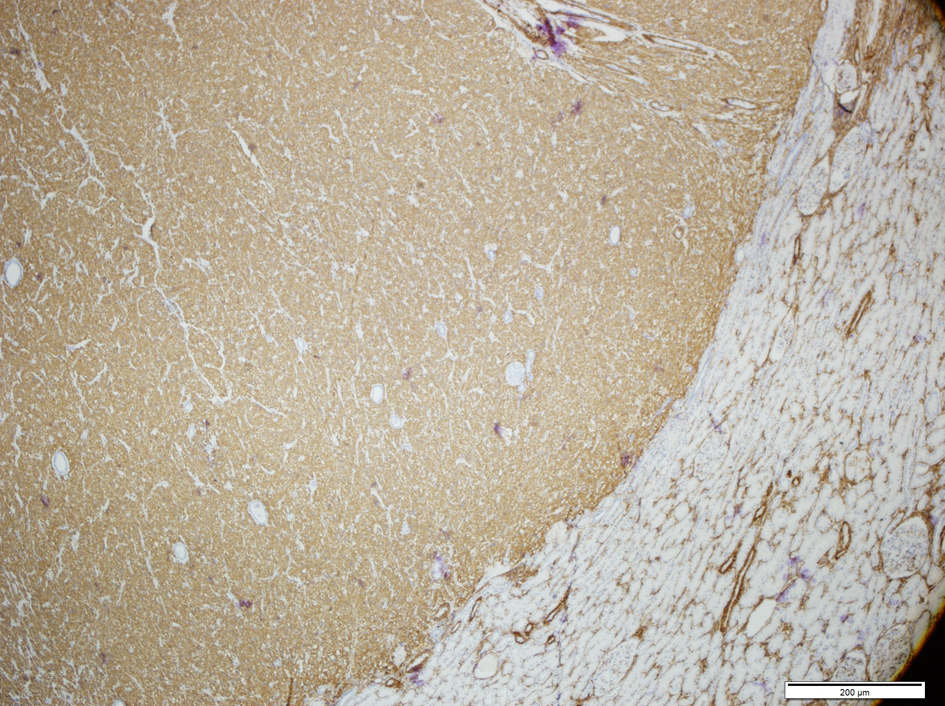 Click for large image | Figure 4. Smooth muscle marker was strongly positive in the stroma of MESTK. |
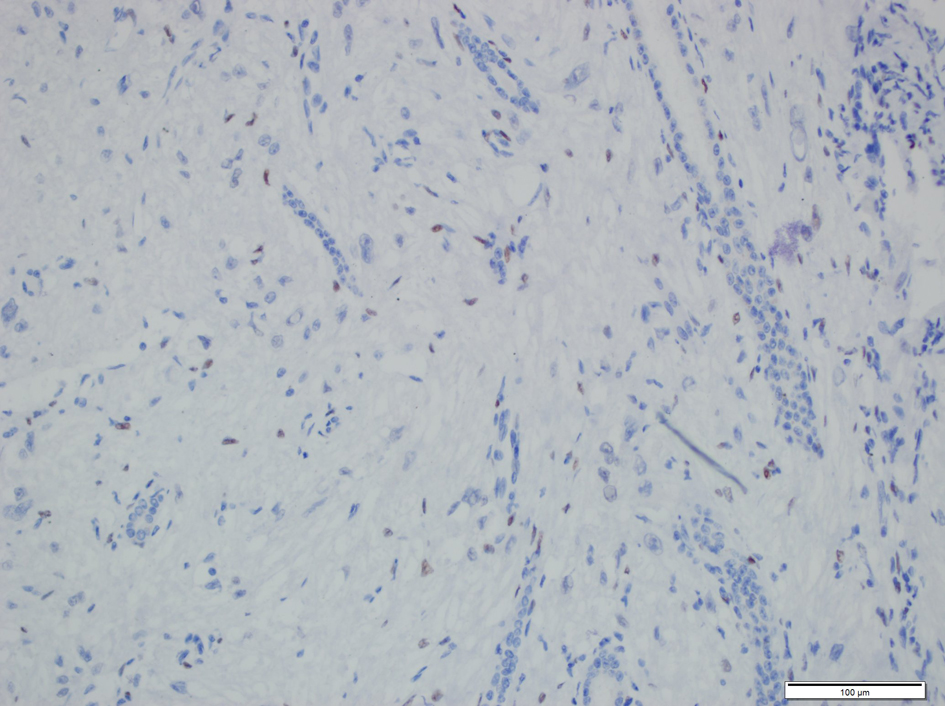 Click for large image | Figure 5. Progesterone receptors were seen in the nuclei of the stromal cells of MESTK. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Mixed epithelial stromal tumor (MEST) is a rare distinctive benign tumor of kidney which is composed of mesenchymal and epithelial elements [3, 4]. It was first described in 1973 by Block et al as congenital mesoblastic nephroma [3, 4]. The term MESTK was introduced by Michal et al in 1998 [5, 6]. These tumors were diagnosed as leiomyomatous renal hamartomas, congenital mesoblastic nephroma in an adult, cystic hamartoma of renal pelvis, solitary multilocular cyst with Mullerian like stroma and adult metanephric stromal tumor in the past [4].
Ages of the patients range from 19 to 78 with a female predominance. It is generally seen in premenopausal woman and the average age is 46 years [4, 5]. Female to male ratio is striking, which is (10:1) [4]. Of the 100 reported cases of MEST, only eight cases are male [7].
History of long term estrogen replacement therapy in females and hormonal therapy in male patients shows that a hormonal mechanism plays role in etiology of these tumors [4, 5].
Most of the patients present with flank pain, palpable mass, hematuria and urinary tract infection as like other renal tumors, but 25% of the cases are identified incidentally and are asymptomatic [4, 5, 8, 9].
Radiologically MESTK can be seen as well described mass in pelvis, can be located in cortex and protrude from cortex and may show multiple septa with solid and cystic components. In contrast, enhanced tomography, solid component generally shows delayed contrast enhancing [10, 11]. MEST can mimic renal angiomyolipomas, adult cystic nephroma, cystic renal cell carcinoma, complex cyst. For that reason most MEST are classified as Bosniak 3/4 [10, 11].
Macroscopically MESTK is a well-defined mass, composed of cystic and solid areas. Dimensions are variable, ranging from 2 to 24 cm [4]. In some cases, cystic component is dominant and solid area may be seen as a mural nodule, it can be seen as multilocular cystic mass and mimic multilocular renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or it can be solid and mimic angiomyolipoma [4].
Microscopically MESTK is a benign biphasic tumor composed of both mesenchymal and epithelial components. The mesenchymal component is characterized by spindle cells arranged in bundles, sheets and fascicules and may show fibroblastic, smooth-muscle or myofibroblastic differentiation in variable degrees. Mesenchymal component may also resemble ovarian stroma. Epithelial component is variable, generally consists of glands scattered throughout the stroma, but sometimes glands can be seen as compact clusters, in a back-to-back pattern, they can show cystic dilatation or may form complex tubulopapillary structures [4, 6, 8]. Mitoses, hemorrhage and necroses are rarely seen in MESTK but malignant cases have also been reported in literature [6, 8].
In our case, diagnosis of MESTK was challenging due to absence of cystic component in the tumor. Generally MESTK are composed of solid and cystic areas grossly [5, 12, 13]. In our case tumor was composed of only solid areas with no cystic component. It was thought to be transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) radiologically. Microscopically there were few tubules scattered between the spindle cell components. Some of tubules showed cystic dilatation. Immunohistochemistry findings were also not typical as with other MESTK. Most of the reported MESTK in the literature showed ER, PR and CD10 positivity in the mesenchymal component [4, 5, 12, 13]. In our case ER was negative and PR was positive only focally. But there is also a fact that estrogen and progesterone receptor positivity are not by themselves diagnostic of MESTK [4]. Another point of conflict in our case is that, there was no history of oral contraceptive use. Hormonal factors are thought to play role in the pathogenesis of MESTK, and long term use of hormonal preparations is shown to be associated with MESTK in literature [4]. Exact pathogenesis is not clear. Also an angiomyolipoma with dominant myomatous component was taken into consideration in differential diagnosis but absence of S-100 and HMB-45 in our case showed tumor was not an angiomyolipoma.
In conclusion MESTK is a rare benign tumor that should be differentiated from other renal tumors. Radiologically it can mimic a variety of tumors for that reason it should be kept in mind in differential diagnosis of a solid tumor in a premenopausal woman. These tumors may consist of only solid areas rather than cystic-solid areas. It must be differentiated from angiomyolipomas and other stromal tumors. ER and PR positivity is not by itself diagnostic of MESTK; it should be kept in mind that these tumors can show only focal or weak positivity as in our case. These tumors generally have good prognosis but recurrence and malignant transformation of these tumors have also been reported. For that reason follow-up of these patients is recommended. A small number of cases were reported in literature as MESTK up to date. For that reason variations in morphology and immunohistochemistry are not known exactly. As number of cases increase, our knowledge about this tumor will also increase and different morphological patterns as our case will be better understood.
| References | ▴Top |
- Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004.
- Moslemi MK. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney or adult mesoblastic nephroma: an update. Urol J. 2010;7(3):141-147.
pubmed - Montironi R, Mazzucchelli R, Lopez-Beltran A, Martignoni G, Cheng L, Montorsi F, Scarpelli M. Cystic nephroma and mixed epithelial and stromal tumour of the kidney: opposite ends of the spectrum of the same entity?. Eur Urol. 2008;54(6):1237-1246.
doi pubmed - Mohanty SK, Parwani AV. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumors of the kidney: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133(9):1483-1486.
pubmed - Zheng S, Yuan HC, Liu LR, Wei Q, Han P. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2013;29(5):280-283.
doi pubmed - Michal M, Syrucek M. Benign mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney. Pathol Res Pract. 1998;194(6):445-448.
doi - Mohd Zam NA, Lau WK, Yip SK, Cheng CW, Tan PH. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumour (MEST) of the kidney: a clinicopathological report of three cases. Pathology. 2009;41(4):403-406.
doi pubmed - Adsay NV, Eble JN, Srigley JR, Jones EC, Grignon DJ. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24(7):958-970.
doi pubmed - Lane BR, Campbell SC, Remer EM, Fergany AF, Williams SB, Novick AC, Weight CJ,
et al . Adult cystic nephroma and mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney: clinical, radiographic, and pathologic characteristics. Urology. 2008;71(6):1142-1148.
doi pubmed - Lang N, Li J, Liu JY, Zeng XZ, Yang Y. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney: an analysis of multidetector computed tomography manifestations and clinicopathologic findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010;34(2):177-181.
doi pubmed - Sahni VA, Mortele KJ, Glickman J, Silverman SG. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumour of the kidney: imaging features. BJU Int. 2010;105(7):932-939.
doi pubmed - Sountoulides P, Koptsis M, Metaxa L, Theodosiou A, Kikidakis D, Filintatzi C, Paschalidis K. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney (MEST) simulating an upper tract TCC. Can Urol Assoc J. 2012;6(1):E23-26.
pubmed - Ekici AI, Ekici S, Gurel B, Altinok G, Erkan I, Gungen Y. Benign mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney. ScientificWorldJournal. 2006;6:615-618.
doi pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


