| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 2, Number 4, August 2011, pages 159-161
A Novel Approach to the Removal of a Retained Guidewire
Michael Tucciaronea, b, Hussein Othmana, Melissa Fredericka, Andrew Boguszewskia, Kumara Ramaa
aSt. John Hospital and Medical Center, 22101 Moross road, VEP 2ndfloor cathlab, Detroit MI 48326, USA
bCorresponding author: Michael Tucciarone
Manuscript accepted for publication June 2, 2011
Short title: Approch to removal of retained guidewire
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jmc233w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Retained intravascular foreign body is a rare, but well-documented complication of percutaneous procedures. We present a case of a novel approach of endovascular retrieval utilizing laparoscopic tools of a retained guidewire. A 74-year-old male presents with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator shock secondary to a retained J-wirefrom a prior right heart catheterization. Attempts at percutaneous retrieval were unsuccessful. A transjugular approach with laparoscopic tools was used for successful removal of the J-wire. Percutaneous intervention has made the retrieval of retained foreign bodies feasible, safe and effective in the majority of situations. However, creative endovascular approaches may be required as described in this case.
Keywords: J-Wire; Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD); Superior Vena Cava (SVC); Inferior Vena Cava (IVC); Ventricular Tachycardia; intravascular foreign body; Autosuture Versa step 5mm port; alligator cystoscope forcep
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Retained intravascular foreign body is a well-documented complication of endovascular procedures. Percutaneous approach is currently the method of choice for removal of retained objects. We report a case of transjugular extraction of an old endothelialized retained J-wire due to wire induced symptomatic ventricular tachycardia with the aid of an Autosuture Versa Step 5mm port.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 74-year-old male with ischemic cardiomyopathy and ejection fraction of 20% with an intracardiac defibrillator presented with a defibrillator discharge. He was asymptomatic just prior to his device going off. There were no described palpitations, chest pain or shortness of breath. AICD interrogation showed a successfully aborted ventricular tachycardia. Physical examination revealed good overall general heath. Chest auscultation was unremarkable. Heart sounds were normal. Vascular exam showed good peripheral pulses and no edema.
To rule out coronary ischemia, cardiac catheterization was performed, which revealed stable coronary artery disease. Under fluoroscopy, a J-wire was noted to run from the superior vena cava (SVC) to the right atrium, looped through the right ventricle and into the inferior vena cava (IVC) (Fig. 1). The J-wire was also seen on a prior heart catheterization in 2007, but at that time was seen spanning from the SVC to IVC without looping in the right ventricle (Fig. 2). It was believed that the wire was left over from a right heart catheterization done at an outside institution at least seven years prior to his presentation. At that time, attempts to retrieve the wire using different percutaneous retrieval devices were unsuccessful. It was felt that the wire was endothelialized and/or layered with thrombus, so no further intervention was undertaken at that time. Given these presenting symptoms and migration of the J-wire cephelad, a repeat endovascular approach was attempted.
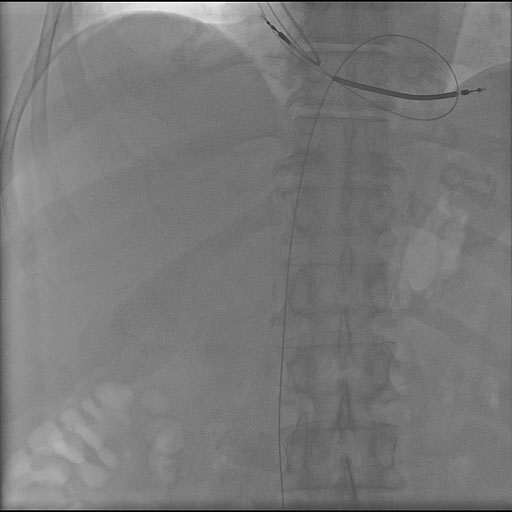 Click for large image | Figure 1. J-wire was noted to run from the superior vena cava (SVC) to the right atrium, looped through the right ventricle and into the inferior vena cava (IVC) under fluoroscopy. |
 Click for large image | Figure 2. J-wire was seen spanning from the superior vena cava (SVC) to inferior vena cava (IVC) without looping in the right ventricle in 2007. |
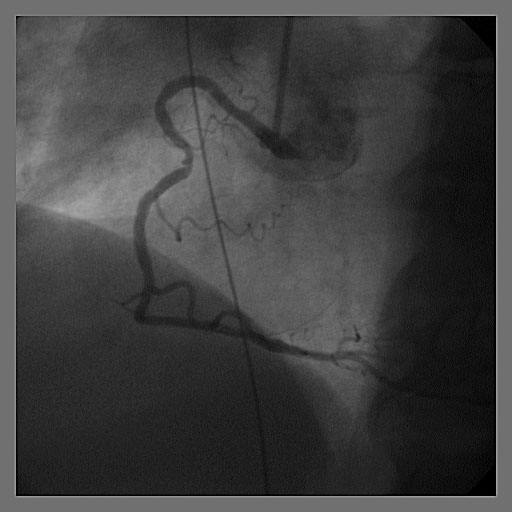
A venogram showed that the distal end of the wire was located 2cm outside the IVC (Fig. 3). The J-wire then tracked up the IVC, where it appeared endothelialized until free floating into the right atrium and right ventricle. After looping inside the right ventricle it extended back into the right atrium up to the SVC. Percutanous approach was attempted with multiple different snaring devices and through both left and right femoral vein access with no success.
 Click for large image | Figure 3. A venogram showed the distal end of the wire outside the inferior vena cava (IVC). |
Recurrent bouts of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia and the J-wire were believed to be the substrate for the arrhythmia. Removal of the wire was deemed necessary.
Vascular surgery was consulted and a right internal jugular approach through a 10 French sheath with different snaring devices was attempted intraoperatively with also no success. An Autosuture Versa Step 5mm port was inserted through the 10 French sheath and then a flexible alligator cystoscope forcep (Fig. 4) was inserted through the port with successful recovery of the J-wire (Fig. 5). The patient tolerated the procedure well and there were no further episodes of ventricular tachycardia. Chest x-ray showed no disruption of the Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) leads post wire removal.
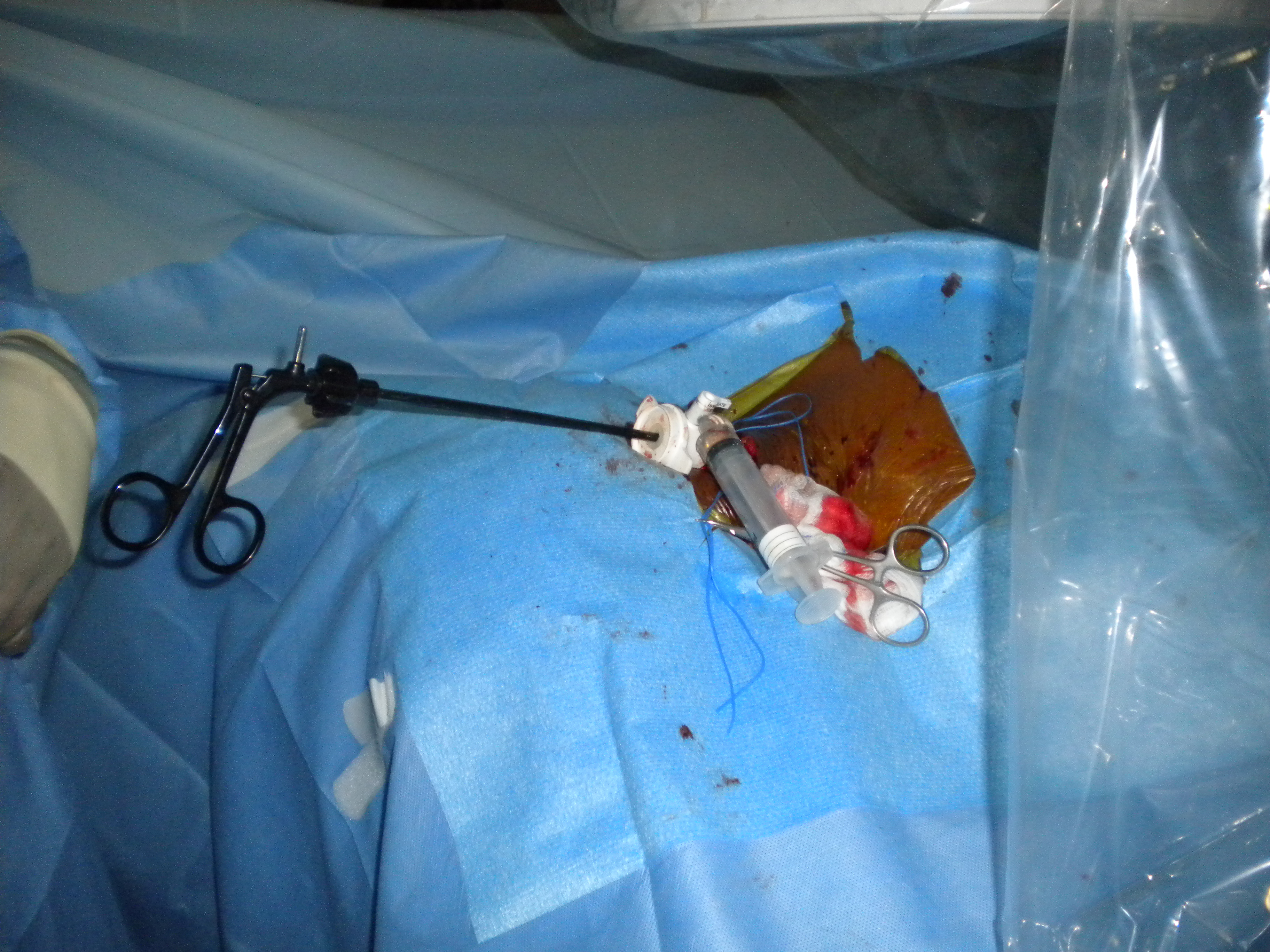 Click for large image | Figure 4. An Autosuture Versa Step 5mm port was inserted through the 10 French sheath. |
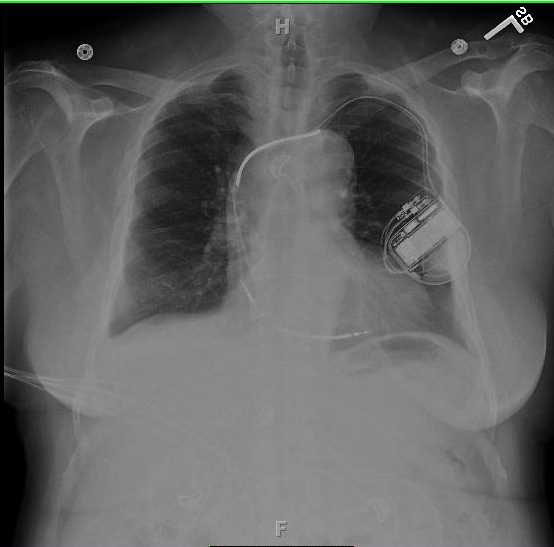 Click for large image | Figure 5. A flexible alligator cystoscope forcep was inserted through the port with successful recovery of the J-wire. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Over the last few decades, there has been an increase in the number of percutaneous cardiovascular interventions. Unfortunately, with this rise has come an increase in the incidence of lost or embolized foreign bodies in the central and peripheral circulation. The true incidence of retained foreign bodies is unknown, however it is estimated at 0.1% to 1.5% [1, 2]. Examples of retained objects include J-wire, stents, Swan-Ganz catheters and pacemaker leads. Most common sites of retrieval are great veins, right heart and coronary circulation.
Although patients with the retained object may remain asymptomatic for many years, serious complications including arrhythmias, myocardial perforation, infection and thrombosis were well-reported [3]. Once symptomatic, removal of the object becomes necessary. The advances in the techniques of percutaneous intervention have made the retrieval of retained foreign bodies feasible, safe and effective, as well as limited the need for the need for surgery [4]. Devices used in percutaneous extraction of retained foreign bodies include loop-snares, retrieval baskets and grasping forceps. Once standard percutaneous tools fail, alternative techniques may prove to be of great use. Laparoscopic devices may sometimes be utilized to facilitate the removal process [5]. Trans-femoral approach is commonly used with the trans-jugular approach as a second line option if the former approach fails [5].
In our case, the patient had the J-wire migrate cephelad over two years until looped within the right ventricle and caused ventricular tachycardia. Because the distal end of the wire was endothelialized into the IVC, the extraction of the J-wire was unsuccessful using the trans-femoral and transjugular approach using conventional snares. The absence of a free wire tip available for snaring is the most common cause of failure [4]. The presence of ICD leads further complicated the procedure. Trans-jugular approach provided a port to the proximal free end of the wire. The fond knowledge of available tools and creative ideas to achieve a good patient outcome is paramount when dealing with endovascular procedural complication. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a novel utilization of laparoscopic tools for retrieval of a retained exchange wire via the trans-jugular approach.
Conflict of interest
No disclosures for any authors.
| References | ▴Top |
- Bonvini RF, Rastan A, Sixt S, Noory E, Beschorner U, Leppanen O, Mach F, et al. Percutaneous retrieval of intravascular and intracardiac foreign bodies with a dedicated three-dimensional snare: a 3-year single center experience. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;74(6):939-945.
pubmed doi - Burri C, Henkemeyer H, Passler HH. [Catheter embolism]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1971;101(44):1575-1577 contd.
pubmed - Fisher RG, Ferreyro R. Evaluation of current techniques for nonsurgical removal of intravascular iatrogenic foreign bodies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978;130(3):541-548.
pubmed - Bessoud B, de Baere T, Kuoch V, Desruennes E, Cosset MF, Lassau N, Roche A. Experience at a single institution with endovascular treatment of mechanical complications caused by implanted central venous access devices in pediatric and adult patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(2):527-532.
pubmed - Mazzetti H, Cichero CF, Tentori MC, Mascheroni O. Transjugular approach for lead extraction. Europace. 2008;10(2):156-160.
doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


