| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 7, Number 10, October 2016, pages 448-450
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in a Patient With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Interferon Beta-1a
Tsering Gyalpo Lama Tamanga, d, Prabhsimranjot Singhb, Abhinav Binod Chandrac
aDepartment of Internal Medicine, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY, USA
bDepartment of Hematology/Oncology, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY, USA
cDepartment of Hematology/Oncology, Yuma Regional Medical Center, Yuma, AZ, USA
dCorresponding Author: Tsering Gyalpo Lama Tamang, Department of Internal Medicine, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn New York. USA
Manuscript accepted for publication August 30, 2016
Short title: CML Treated With IFN Beta-1a
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/jmc2622w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Hematological problems are commonly associated with the use of beta interferon (INF) such as leukopenia and anemia, which are usually benign and reversible when the drug is stop. We described a case of of a 29 years old patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia who had received INF beta-1a in the recent past for relapsing multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: Myelogenous; Leukemia; Interferon; Multiple; Sclerosis
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by increased proliferation of the granulocytic cell line without the loss of its capacity to differentiate. The diagnosis of CML is based on characteristic histopathological findings and presence of the Philadelphia (Ph1) chromosome in the peripheral blood and bone marrow cells [1]. Interferon (IFN) beta-1a is approved for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) [2]. Hematological abnormalities are common and dose-dependent in patients with MS receiving IFN beta-1a [3]. The events are mild, transient, and reversible when the drug is stopped [3].
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 29-year-old male with MS diagnosed 3 years ago presented with itching throughout his body which was aggravated by warm water showers. Basic laboratory work revealed thrombocytosis for which he was referred to a hematologist. The patient was taking dimethyl fumarate for MS at the time of presentation but had been treated with prednisone, fingolimod, and IFN beta-1a in the past. Physical examination did not reveal any rashes or hepatosplenomegaly. Peripheral smear showed thrombocytosis with manual platelet count of around 800,000, increase in white blood cells (WBCs), eosinophils, and basophils. This was consistent with myeloproliferative disease favoring CML. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for BCR-ABL was positive for Ph1 chromosome (Fig. 1).
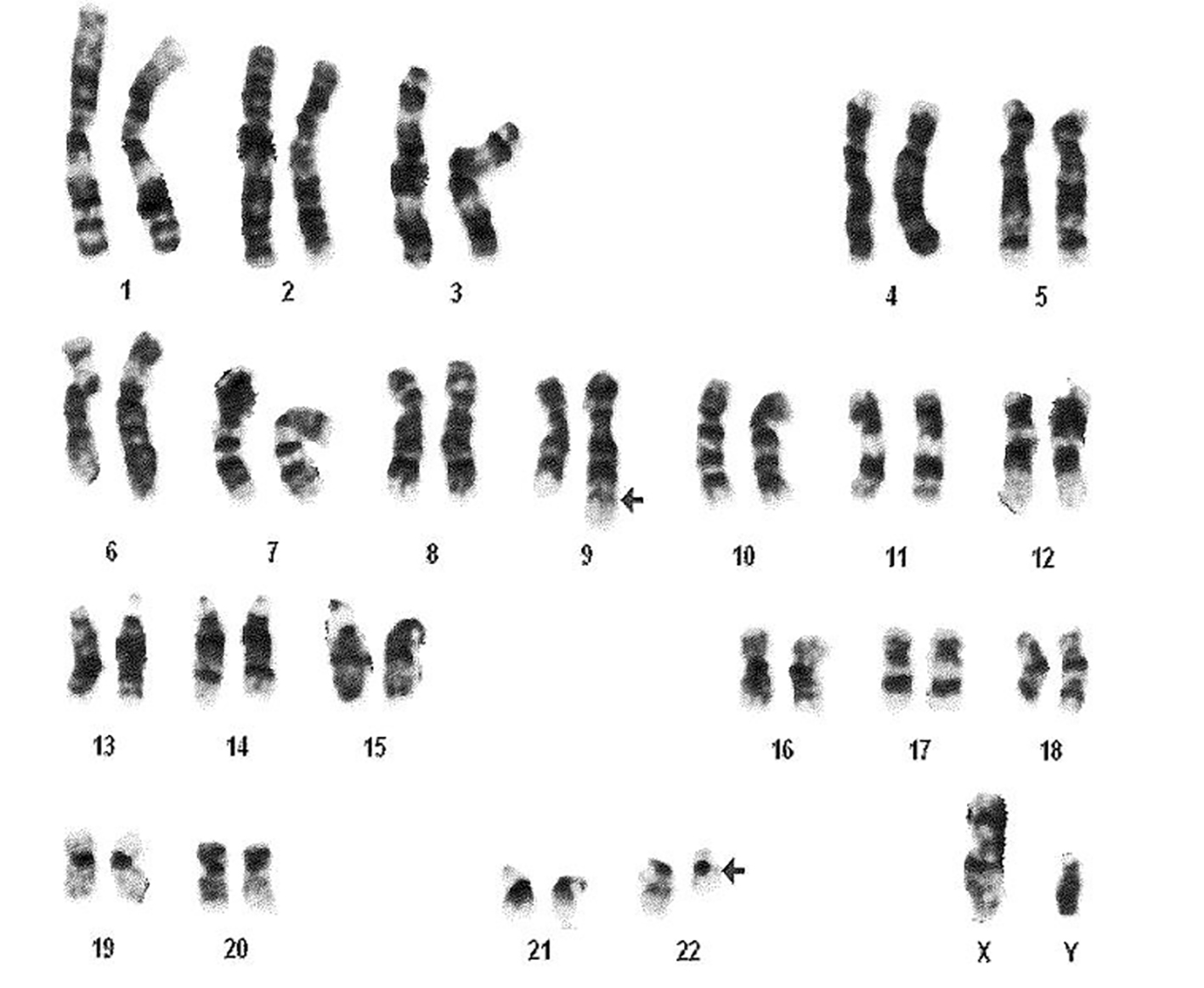 Click for large image | Figure 1. Cytogenetic analysis showing reciprocal translocation t(9:22) (arrows) creating Philadelphia chromosome. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
IFNs are naturally occurring signaling proteins released by host cells to activate immune response in response to the pathogens [4, 5]. They are used for the treatment for a number of solid tumors and hematological malignancies [5]. In general, the type 1 IFNs suppress tumor growth by inhibiting cell proliferation and increasing the susceptibility of cancer cells to cytotoxic immune effectors [4-8]. Thus, the most common hematological side effects experienced by patients treated with IFN beta-1a are leukopenia and anemia [3]. An extensive PubMed search yielded two case reports of patients developing CML during treatment with IFN beta-1a for MS [9]. There were no reports of CML developing after stopping the medication. Among the medications for MS, mitoxantrone has been reported to cause acute leukemia [10]. We report a case of CML in a patient with MS who was treated with IFN beta-1a in the recent past. He had received IFN beta-1a for 8 months prior to the diagnosis of CML.
We do not know the exact mechanism of paradoxical association of leukemia and other cancers with INF therapy. In a cohort study of 69 hairy cell leukemia patients treated with IFN alpha 2b, 13 patients (19%) developed a secondary neoplasm which includes six hematologic tumors over 91 months of median follow-up periods [11]. Tomic et al explained that IFN briefly activates the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) which promotes cell growth though it normally suppresses tumor growth by phosphorylating and activating STAT1 [6]. It can be possible that STAT3 activation contributed to the development of CML in patients treated with INF-B for MS. Also, this might be the delayed association of IFN beta-1a with CML. It is possible that the patient had developed CML earlier than initiation of IFN beta, which had delayed progression of disease for some time.
In conclusion, a regular assessment of complete blood count has been suggested among MS patients receiving IFN beta-1a to monitor for possible leucopenia and anemia. Physicians should also be mindful about the possible association of CML with IFN beta-1a. More larger studies are needed to address this possibility.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Department of Neurology, Division of Hematology and Oncology and Department of Internal Medicine, Maimonides Medical Center.
Author Contributions
TGLT, PS and ABC designed the case report, acquired and interpreted the data and wrote first draft of this case report. All authors contributed to intellectual context and approved the final manuscript. All Authors have read the manuscript and have approved this submission.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained for publication. The IRB has provided permission to publish this case report.
Funding Sources
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose. There was no funding provided for this study or the preparation of this article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Jabbour E, Kantarjian H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2016 update on diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(2):252-265.
doi pubmed - Tsang BK, Macdonell R. Multiple sclerosis- diagnosis, management and prognosis. Aust Fam Physician. 2011;40(12):948-955.
pubmed - Walther EU, Hohlfeld R. Multiple sclerosis: side effects of interferon beta therapy and their management. Neurology. 1999;53(8):1622-1627.
doi - De Andrea M, Ravera R, Gioia D, Gariglio M, Landolfo S. The interferon system: an overview. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2002;6(Suppl A):A41-46; discussion A55-48.
- Jonasch E, Haluska FG. Interferon in oncological practice: review of interferon biology, clinical applications, and toxicities. Oncologist. 2001;6(1):34-55.
doi pubmed - Tomic J, Lichty B, Spaner DE. Aberrant interferon-signaling is associated with aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2011;117(9):2668-2680.
doi pubmed - Takaoka A, Hayakawa S, Yanai H, Stoiber D, Negishi H, Kikuchi H, Sasaki S, et al. Integration of interferon-alpha/beta signalling to p53 responses in tumour suppression and antiviral defence. Nature. 2003;424(6948):516-523.
doi pubmed - Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(11):836-848.
doi pubmed - Almeida L, Neves M, Cardoso E, Melo A. Chronic myeloid leukaemia in two multiple sclerosis patients on interferon beta-1a. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2009;34(1):125-127.
doi pubmed - Pielen A, Goffette S, Van Pesch V, Gille M, Sindic CJ. Mitoxantrone-related acute leukemia in two MS patients. Acta Neurol Belg. 2008;108(3):99-102.
pubmed - Kampmeier P, Spielberger R, Dickstein J, Mick R, Golomb H, Vardiman JW. Increased incidence of second neoplasms in patients treated with interferon alpha 2b for hairy cell leukemia: a clinicopathologic assessment. Blood. 1994;83(10):2931-2938.
pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


