| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 10, Number 6, June 2019, pages 168-170
Cauda Equina Syndrome: A Rare Presentation in Burkitt Lymphoma
Muhammad Idreesa, b, Haisam Abida, Timothy Korytkoa
aBassett Medical Center, Cooperstown, NY 13326, USA
bCorresponding Author: Muhammad Idrees, Bassett Medical Center, Cooperstown, NY 13326, USA
Manuscript submitted May 4, 2019, accepted June 10, 2019
Short title: A Case of CES Due to Burkitt Lymphoma
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc3308
This article has been retracted
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a serious neurological condition in which neurological dysfunction affects the lumbar and sacral nerve roots within the vertebral canal. The most common cause is central disc protrusion at L5 - S1 level. Diagnosis usually requires imaging studies including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) myelogram. We present a very rare case of CES due to extensive Burkitt lymphoma involving spinal cord.
Keywords: Burkitt lymphoma; Cauda equina syndrome; Magnetic resonance imaging
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a serious neurological condition in which neurological dysfunction affects the lumbar and sacral nerve roots within the vertebral canal. The most common cause is central disc protrusion at L5 - S1 level [1]. When diagnosis is suspected, neuroimaging with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of lumbar spine is the initial choice for confirmation and identification of the cause. Treatment involved urgent decompression of nerve roots. CES due to any cause is very rare, with incidence of seven per 100,000 in USA. We present a case of CES due to Burkitt lymphoma which is a very rare presentation.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 54-year-old male active smoker with recent diagnosis of recurrent Burkitt lymphoma presented with complain of back pain and hip pain. Patient was initially diagnosed with Burkitt lymphoma (Ki-67 100%, strong MYC protein staining, negative for MYC translocation, BCL2 or BCL6 rearrangements) few months back when had presented with syncope and was noted to have multiple lesions in lung, liver and kidney.
He presented again in start of this year with back pain, had biopsy of left iliac crest done. Two weeks later the patient presented to emergency department with acute worsening of back pain associated with left leg weakness and numbness. He was noted to have acute urine retention with overflow incontinence and complained of constipation. He denied having any trauma, fall or fevers.
On examination he was noted to have saddle anesthesia (loss of sensation in the perianal area left side much more so than the right) and decreased motor power (3/5) and sensations on left leg. Bladder scan showed 2,500 mL urine in bladder. MRI of LS spine and pelvis was done which showed extensive lesions at L4, L5, S3 causing nerve root compression and symptoms suggestive of CES (Fig. 1).
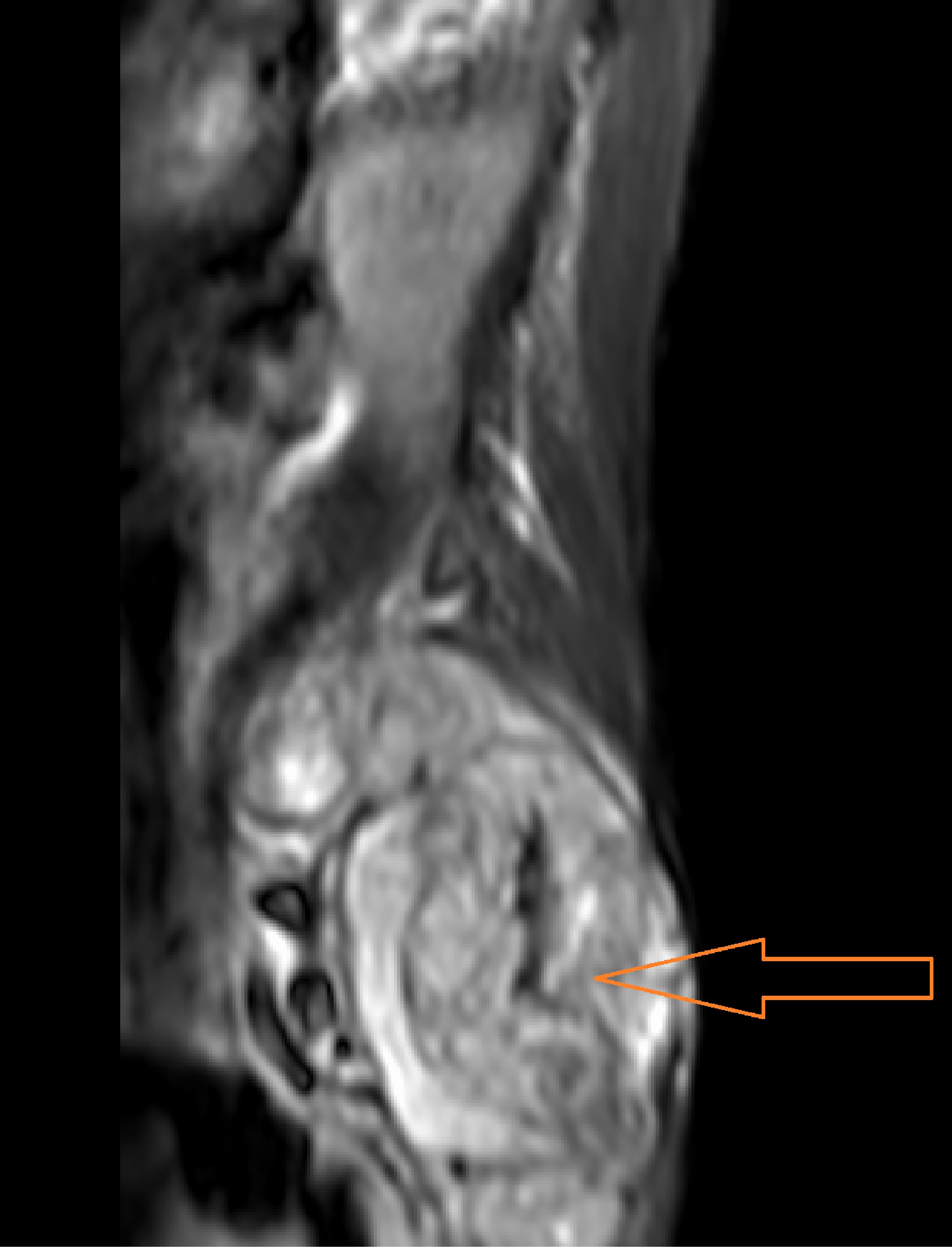 Click for large image | Figure 1. MRI with/without contrast of lumbar spine showing soft tissue mass compressing L5 nerve roots. |
Patient was immediately given intravenous (IV) steroids. Radiation oncology was consulted; patient was given five cycles of 3,000 cGy in 10 fractions with improvement of sensation in perianal area. Later he was started on three cycles of rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide (R-ICE). Patient’s symptoms improved significantly after chemoradiotherapy. His motor power improved and he was able to walk by himself, and there was also some improvement in saddle sensory loss and anal sphincter and bladder function. Follow-up imaging was done in 2 months showed improvement in mass on left side of L5 (Fig. 2). Surgery was not done due to presence of metastatic disease and improvement in patient’s symptoms after chemoradiation therapy.
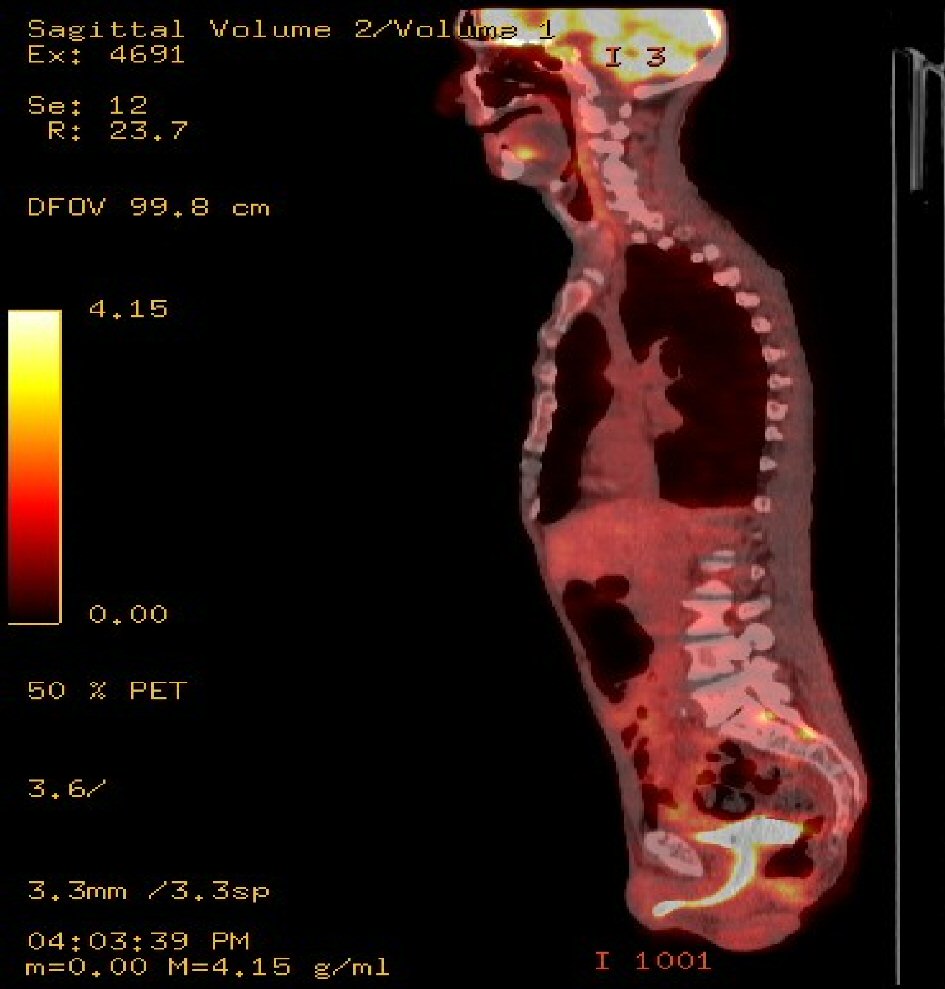 Click for large image | Figure 2. It shows the activity along the left side of the L5 vertebral body where previously there was activity along the right side of the L5 body which has since resolved. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
CES is a condition resulting from damage to bundle of spinal nerves below the end of spinal cord known as cauda equina [1]. Typical signs and symptoms associated with this disorder include low back pain, loss of bladder and bowel function, saddle anesthesia and unilateral or bilateral sciatica [2, 3]. The most common cause of CES is an intervertebral disc prolapse [4]. Other rare causes of CES include fracture, compression by tumor, penetrating trauma, chiropractic manipulation, chemonucleolysis, postoperative hematoma, free epidural fat graft, and ankylosing spondylitis [4].
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) rarely affects central nervous system (CNS). It most commonly involves brain (2% of primary CNS and 7-9% of metastatic brain tumors). The involvement of spinal cord or cauda equina is very rare. The incidence of lymphoma is less than 2% in tumors involving cauda equina [5].
Three different forms of CES have been reported: 1) Acute CES in a patient without previous back problems; 2) Acute neurologic deficits in a patient with chronic back issues; 3) Gradual progression to CES in a patient who have chronic back pain and sciatica [6]. However in 85% of cases, the signs and symptoms of CES develop with 24 h.
Several studies suggest that CES should be operated within 6 h of onset of symptoms. But literature review showed that there is no statistical difference in the outcome of patients who underwent surgery within 6 h or 48 h [7, 8]. However patients presenting with CES due to tumor compression should be immediately given IV steroids.
Our patient presented to hospital after 1 month of symptoms onset, if he had presented immediately after the symptoms onset the final outcome would have been more favorable. Delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to devastating outcomes in CES leading to persistent neurologic deficit [5]. In one of the retrospective review of 44 patients with CES it was noted that the delayed surgery group (> 48 h) demonstrated a significantly greater chance of permanent motor weakness, urological dysfunction, chronic severe pain and sexual dysfunction [9]. This finding was again supported by data from a meta-analysis of 322 cases of CES which showed a significant difference in outcome in those cases decompressed in within 48 h and those decompressed after 48 h [8].
Conclusions
We report a rare presentation of Burkitt lymphoma causing extradural compression and leading to CES. Clinicians must be aware of clinical manifestations of CES and it should be considered in differential diagnoses in patients presenting with neurological deficits with underlying lymphoma. MRI with contrast enhancement allows for timely diagnosis of the syndrome, and immediate surgical intervention should be done to avoid permanent disability.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
We do not have any financial disclosure or funding received from anyone.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict interest (all authors).
Informed Consent
Patient gave informed consent of the publication of this report.
Author Contributions
Each author contributed to writing of this report. Muhammad Idrees was responsible for writing abstract and case, and revision of the manuscript. Haisam abid and Timothy Korytko contributed to writing of discussion of this report.
| References | ▴Top |
- "Cauda equina syndrome". Genetic and rare diseases. Information Center GARD. 2015;9:2017.
- Gardner A, Gardner E, Morley T. Cauda equina syndrome: a review of the current clinical and medico-legal position. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(5):690-697.
doi pubmed - Ma B, Wu H, Jia LS, Yuan W, Shi GD, Shi JG. Cauda equina syndrome: a review of clinical progress. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(10):1214-1222.
- Contamin F, Doubrere JF, Struz PH, Baillet P. [Association of ankylosing spondylarthritis, cauda equina syndrome and dilatation of the lumbar cul-de-sac with voluminous arachnoid diverticulum. Clinical, radiological and tomodensitometric study of a case]. Sem Hop. 1983;59(18):1401-1404.
- Mathesul AA, Sonawane DV, Nemade PS, Biraris SR. A rare cause of Cauda equina syndrome: Epidural high grade primary non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clinical Cancer Investigation Journal. 2013;2(1):70.
doi - Tandon PN, Sankaran B. Cauda equina syndrome due to lumbar disc prolapse. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics. 1967;1(02):112.
- Kohles SS, Kohles DA, Karp AP, Erlich VM, Polissar NL. Time-dependent surgical outcomes following cauda equina syndrome diagnosis: comments on a meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(11):1281-1287.
doi - Ahn UM, Ahn NU, Buchowski JM, Garrett ES, Sieber AN, Kostuik JP. Cauda equina syndrome secondary to lumbar disc herniation: a meta-analysis of surgical outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(12):1515-1522.
doi - Shapiro S. Medical realities of cauda equina syndrome secondary to lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(3):348-351; discussion 352.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


