| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 9, Number 1, January 2018, pages 34-36
An Unusual Presentation of Acute Subdural Hematoma Secondary to Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Following Conservative Management of Placenta Increta
Muhammad Fairuz Abdul Rahmana, c, Ghee Kheng Chewb, Eng Loy Tana, Wei Ching Tana
aDepartment of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
bDepartment of General/Gynecological Oncology Surgery, Penang Adventist Hospital, Malaysia
cCorresponding Author: Muhammad Fairuz Abdul Rahman, Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Road, 169608, Singapore
Manuscript submitted December 12, 2017, accepted December 14, 2017
Short title: SDH Secondary to DIVC After Placenta Increta
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc2989w
This article has been retracted
| Abstract | ▴Top |
With increasing cesarean section rates around the world, there will be a corresponding rise in morbidly-adherent placenta cases, such as placenta increta. There have been no randomized controlled trials comparing different surgical treatment of placenta increta. Conservative management of placenta increta, though largely successful, can potentially lead to significant maternal morbidity, such as sepsis, hemorrhage, and mortality. We report a rare event of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIVC) with spontaneous maternal subdural hematoma (SDH) arising from the conservative management of placenta increta. To our knowledge, there has been no such case reported in the literature. The patient was managed by a multidisciplinary team of gynecologists, anesthesiologists, neurosurgeons and hematologists when she presented with right-sided progressive headache and extensive bruising 9 weeks postpartum. Blood products were given to correct her hemodynamic status and she subsequently underwent an emergency hysterectomy, with resolution of the DIVC and her symptoms.
Keywords: Acute subdural hematoma; Disseminated intravascular coagulation; Placenta increta
| Introduction | ▴Top |
With rising cesarean section rates around the world, combined with increasing maternal age, we are witnessing an increase in the incidence of morbidly-adherent placenta and its complications [1]. Several recognized risk factors for morbidly-adherent placenta include termination of pregnancy, intrauterine surgery, smoking, multi-fetal gestation, and increasing parity, apart from previous cesarean section and advance maternal age. A morbidly-adherent placenta is a condition when part of the placenta, or the entire placenta, invades through the decidua basalis into and through the myometrium [2]. This includes placenta accreta, increta and percreta. Researchers quote an incidence rate of 1 in 533 pregnancies for placenta accreta for the period of 1982 - 2002, compared to a rate of 1 in 4,027 pregnancies in the 1970s, and 1 in 2,510 pregnancies in the 1980s [3-5].
Placenta increta is an intermediate in the spectrum of abnormal placental villous implantation, where the placental villi extend beyond the confines of the endometrium and invade the myometrium. There are no randomized controlled trials to determine the most effective surgical management of placenta increta. For patients desiring future fertility, the conservative approach where the placenta is kept in situ at the time of cesarean section is fraught with potential complications, such as infection and hemorrhage [6]. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIVC) occurs in about 7% of such cases, and more often than not, patients end up requiring a hysterectomy for definitive treatment [7].
To date, there has been no reported case in the literature of a conservative management of placenta increta who presents with the primary diagnosis of subdural hematoma (SDH). A PubMed search using the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) “placenta increta”, “subdural hematoma” and “disseminated intravascular coagulation” yielded no matches. We present the first case of acute SDH secondary to DIVC as a result of the conservative management of placenta increta.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
Madam M is a multigravida with one previous lower segment cesarean section for breech presentation. She had no other significant medical history. She received routine antenatal care and was diagnosed with placenta previa major from the 20-week detailed ultrasound screening scan. Subsequent ultrasound scans showed a normally growing baby and low suspicion of placenta accreta. She underwent an elective cesarean section at term.
Intra-operatively, the lower uterine segment appeared to be bulging with placenta invading the myometrium and engorged blood vessels, raising the suspicion of placenta increta. A classical fundal incision was made to deliver the baby, and the uterus was repaired in three layers. A decision to leave the placenta in situ was made in view of minimal bleeding and no sign of placental separation.
Madam M was discharged well on post-operative day 4. She received intramuscular methotrexate 2 weeks postpartum which led to a gradual decline in her β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels (Fig. 1).
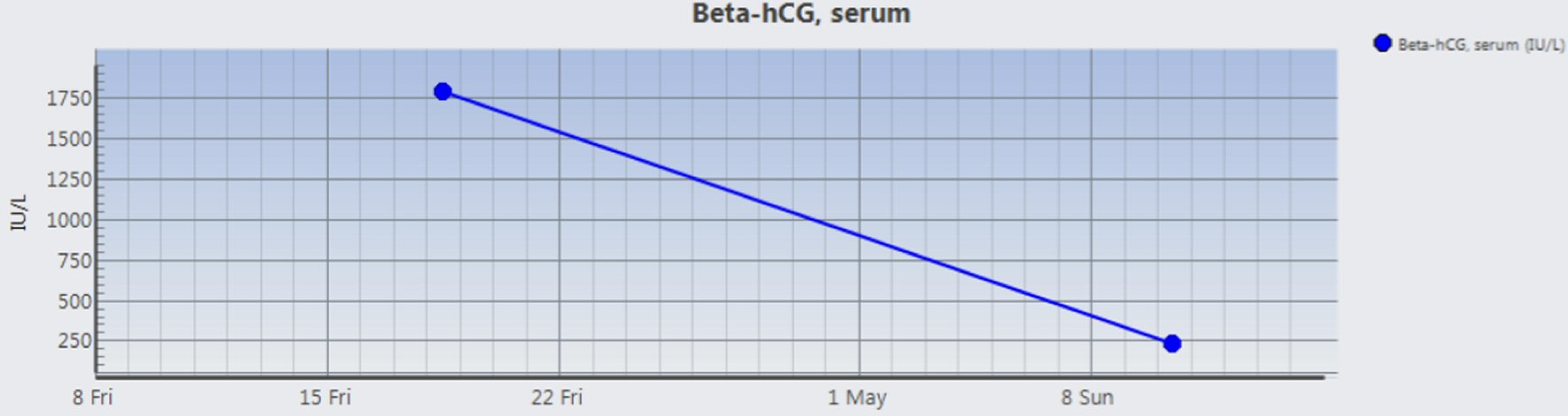 Click for large image | Figure 1. Postpartum trend of β-hCG levels. |
However, Madam M presented to the emergency department at 9 weeks postpartum with severe progressive right-sided headache and extensive right lower limb bruises. Examination revealed extensive ecchymoses on her limbs, and a large firm abdominopelvic mass up to the level of the umbilicus.
A computed tomography (CT) brain scan (Fig. 2) showed an acute SDH with midline shift. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis (Fig. 3) showed a markedly hypervascular mass within the uterus with dilated and tortuous vessels, with no evidence of peritoneal hematoma.
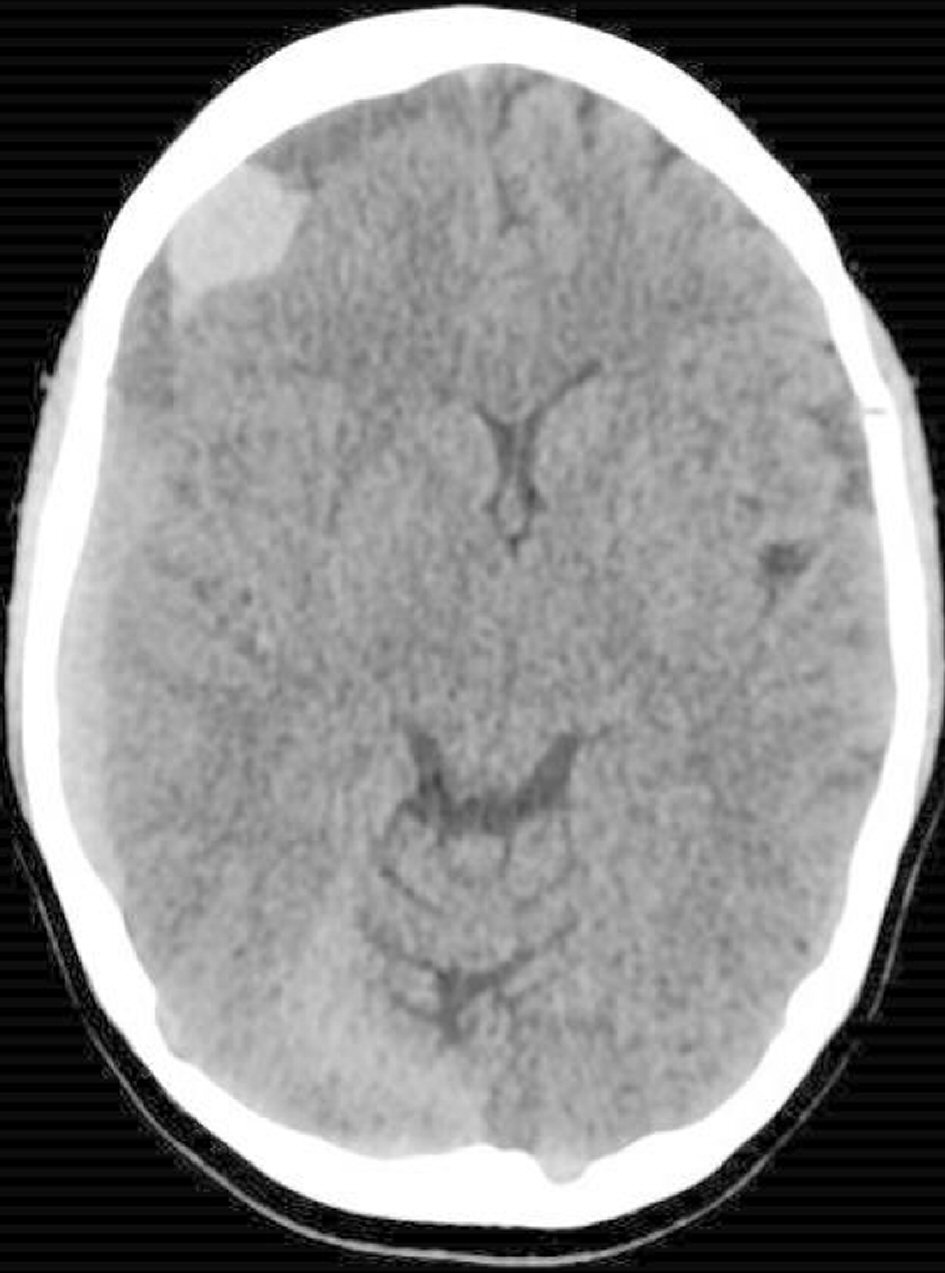 Click for large image | Figure 2. A CT scan of the brain at presentation. Acute subdural hematoma (SDH) overlying the right cerebral convexity, associated with mass effect and left-ward midline shift. |
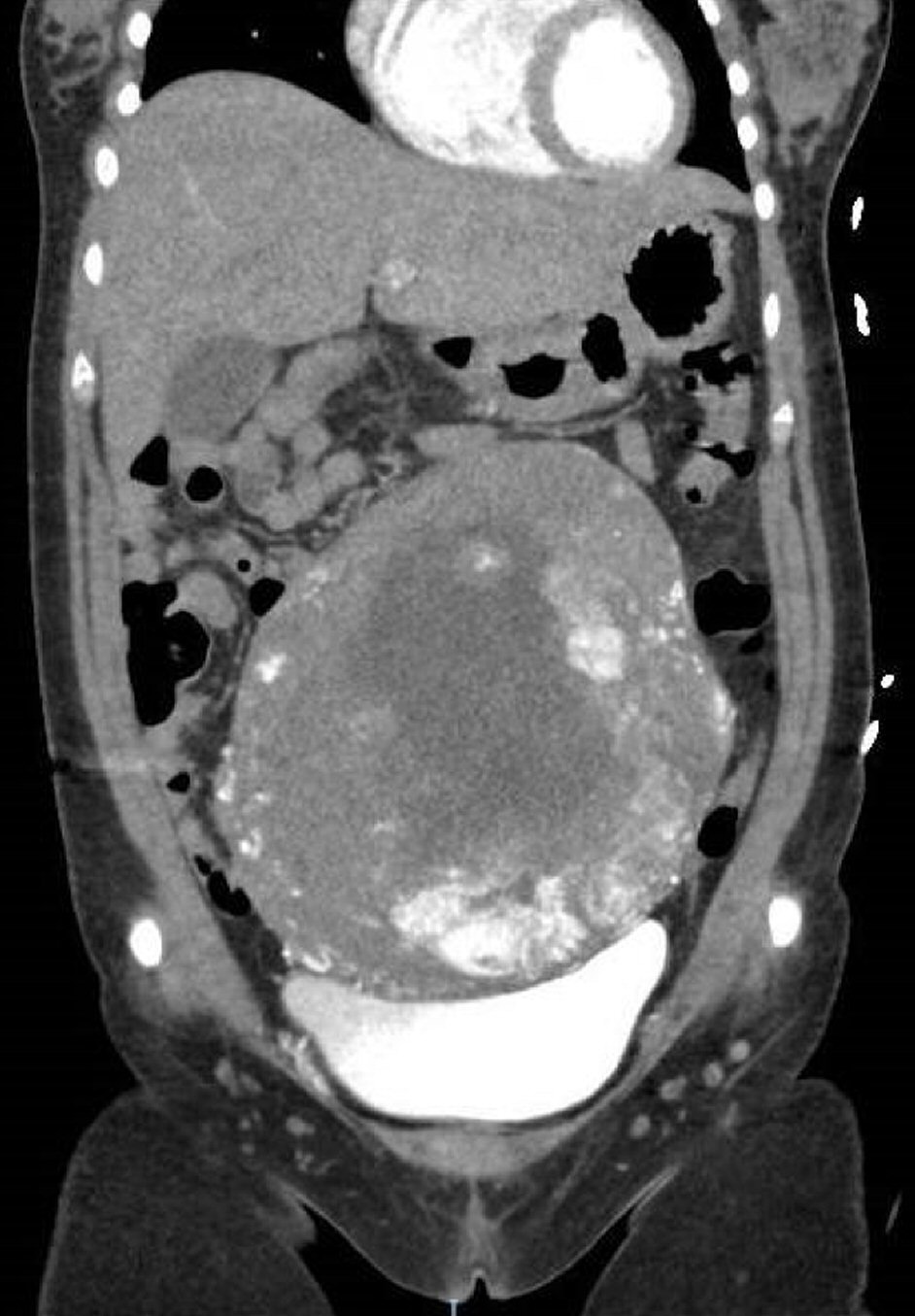 Click for large image | Figure 3. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. Enlarged uterus extending above the umbilicus. Markedly hypervascular mass within the uterus with dilated and tortuous vessels coursing the mass. |
She was confirmed to be in DIVC when laboratory investigations showed thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time (PT), and prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT), as well as elevated D-dimer and low fibrinogen level (Table 1).
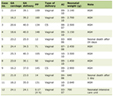 Click to view | Table 1. Pre-Operative Laboratory Values |
A multidisciplinary team meeting of consultant obstetricians and gynecologists, neurosurgeon, hematologist and anesthetist convened to plan the management. Multiple blood products including cryoprecipitate were administered. When coagulation status was stable, Madam M underwent a burr hole drainage of the SDH and emergency hysterectomy. Her DIVC resolved within 24 h postoperatively (Table 2). Histology confirmed the diagnosis of placenta increta. A repeat CT brain scan showed improvement in mass effects (Fig. 4).
 Click to view | Table 2. Resolution of DIVC Following Surgery |
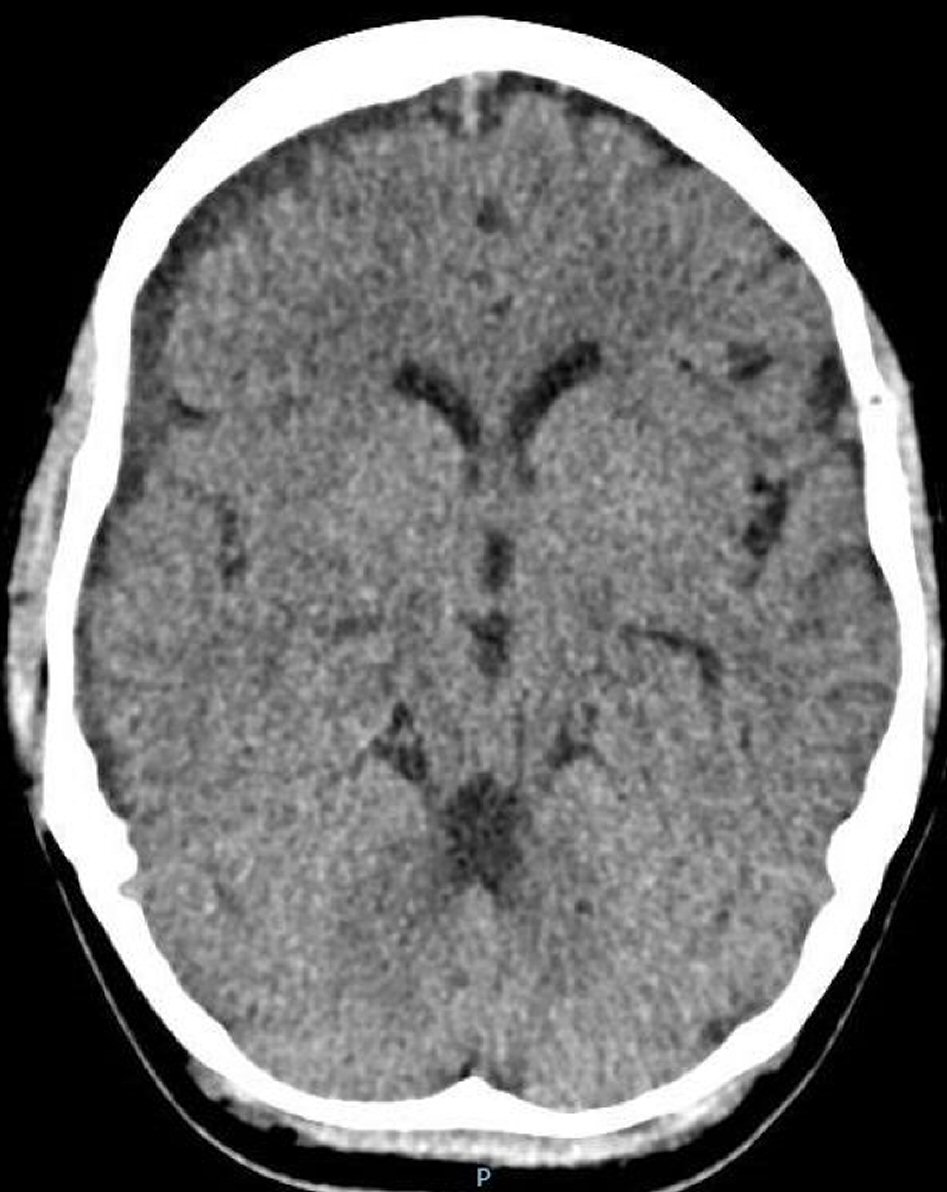 Click for large image | Figure 4. A CT scan of the brain 3 weeks post-hysterectomy. Interval expected evolution of previously noted intracranial hemorrhages with improvement in mass effects and left sided midline shift. |
Madam M was discharged well subsequently and continued her outpatient rehabilitation. She had no significant residual neurological deficits.
| Discussion | ▴Top |
In conclusion, the conservative management of placenta increta may be complicated by DIVC with potentially debilitating consequences for the patient. These patients should be closely followed up postpartum with serial investigations, ideally till there is evidence of complete resolution of placenta increta from imaging studies and until serum β-hCG becomes undetectable. However, there is a lack of clear guidance on the optimal follow-up protocol for such cases. In the absence of available guidance of the conservative treatment of placenta increta, management plan needs to be individualized with ready access to tertiary hospital care. This case of acute maternal SDH secondary to DIVC due to the conservative management of placenta increta is probably the first reported case in literature. DIVC predisposes one to bleeding, which may be obvious (such as per vaginal bleeding) or occult, such as in this case, where bleeding occurred in the subdural compartment and the skin. As complications secondary to conservative management of morbidly-adherent placenta will likely mirror rising cesarean section rates, early recourse to cesarean hysterectomy should be considered as the definitive surgical treatment, especially for women who have no desire for future fertility.
| References | ▴Top |
- Oyelese Y, Smulian JC. Placenta previa, placenta accreta, and vasa previa. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107(4):927-941.
doi pubmed - RCOG Green-top Guideline No. 27: Placenta praevia placenta praevia accreta and vasa praevia: diagnosis and management (January 2011).
- Wu S, Kocherginsky M, Hibbard JU. Abnormal placentation: twenty-year analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(5):1458-1461.
doi pubmed - Read JA, Cotton DB, Miller FC. Placenta accreta: changing clinical aspects and outcome. Obstet Gynecol. 1980;56(1):31-34.
pubmed - Miller DA, Chollet JA, Goodwin TM. Clinical risk factors for placenta previa-placenta accreta. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177(1):210-214.
doi - Eller AG, Porter TF, Soisson P, Silver RM. Optimal management strategies for placenta accreta. BJOG. 2009;116(5):648-654.
doi pubmed - Timmermans S, van Hof AC, Duvekot JJ. Conservative management of abnormally invasive placentation. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2007;62(8):529-539.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


